High-specificity exosome separation, detection and enrichment method
A high-specificity exosome technology, applied in cell dissociation methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, etc., can solve problems such as unreported, lack of characterization, and unconvincing test results. Achieve the effects of improved sensitivity, high sensitivity and selectivity, and high in situ amplification efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Embodiment 1 Pre-experiment
[0050] 1 Experimental materials
[0051] Chemicals, Cell Lines and Reagents
[0052] All oligonucleotide sequences in Table 1 were purchased from Shanghai Sangong Bioengineering Technology and Service Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Tris-borate EDTA buffer, DNA staining gel red, 30% polyacrylamide, DPEC water, Dulbecco's PBS, BSA, TMMED and APS were purchased from Shanghai Sanyuan Bioengineering Technology and Service Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). T4 DNA ligase, T4 polynucleotide kinase, Phi29 DNA polymerase and RiboLock RNase inhibitor were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). In RPMI1640 medium (Hyclone) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Hyclone) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Hyclone), in 5% CO 2 The A549 cell line was cultured at 37°C under atmosphere. Supernatant cell cultures were obtained from A549 cells. Confocal images were captured by an LSM 780SYSTEM (Zeiss, Germany) and observed using a JEM-1400...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Embodiment 2 system design and operation mechanism
[0071] 1 Experimental method
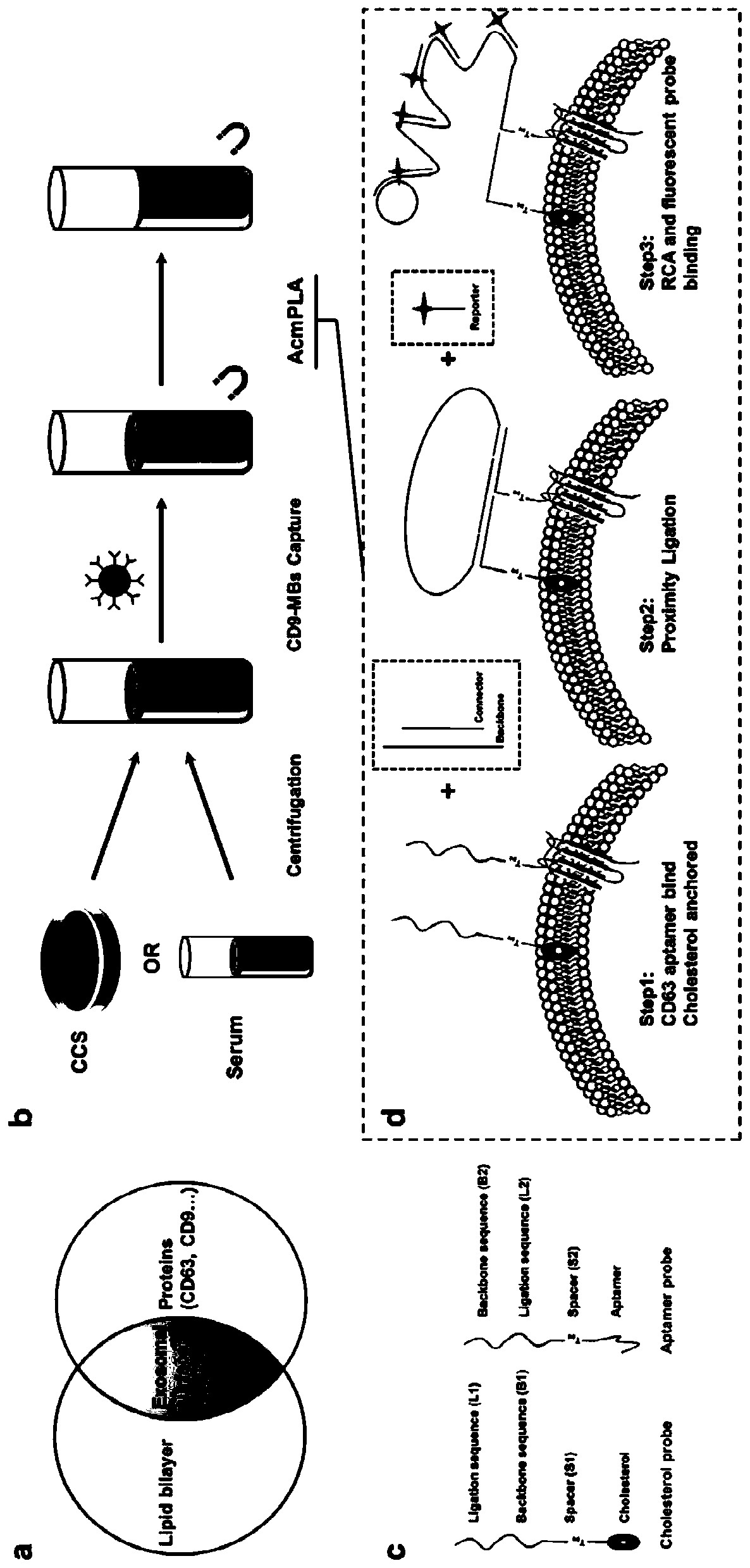
[0072] An aptamer-cholesterol-mediated proximity ligation assay (AcmPLA) was employed to specifically capture exosome surface proteins and minimize nonspecific background signals.
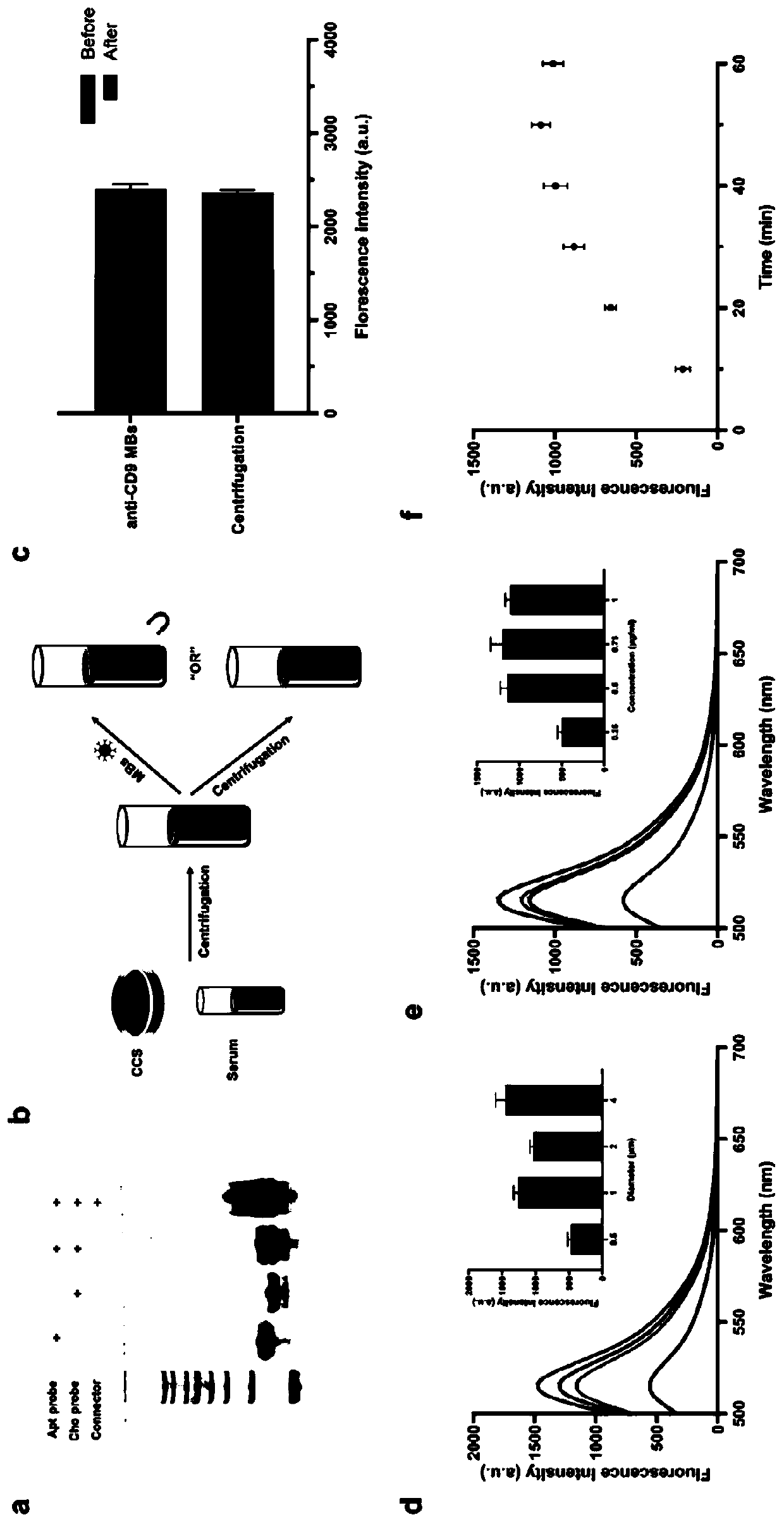
[0073] In the proposed strategy, cell culture supernatant (CCS) or serum samples are centrifuged to remove unwanted particles. The unrefined supernatant obtained consists of exosomes, free proteins and some other biological components. Then, CD9 antibody-labeled magnetic beads (anti-CD9 MBs) were used to capture and assemble CD9-positive biological components under a magnet. To achieve accurate exosome recognition, three active ingredients are used in AcmPLA. The first is two single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) with three functional domains each: a CD63 aptamer probe (Apt probe) and a cholesterol probe (Cho probe). In cholesterol probes, cholesterol that can be inserted into the lipid bilayer is labeled at the 5'...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3 Research on Exosome Extraction and Probe Identification
[0078] 1 Experimental method
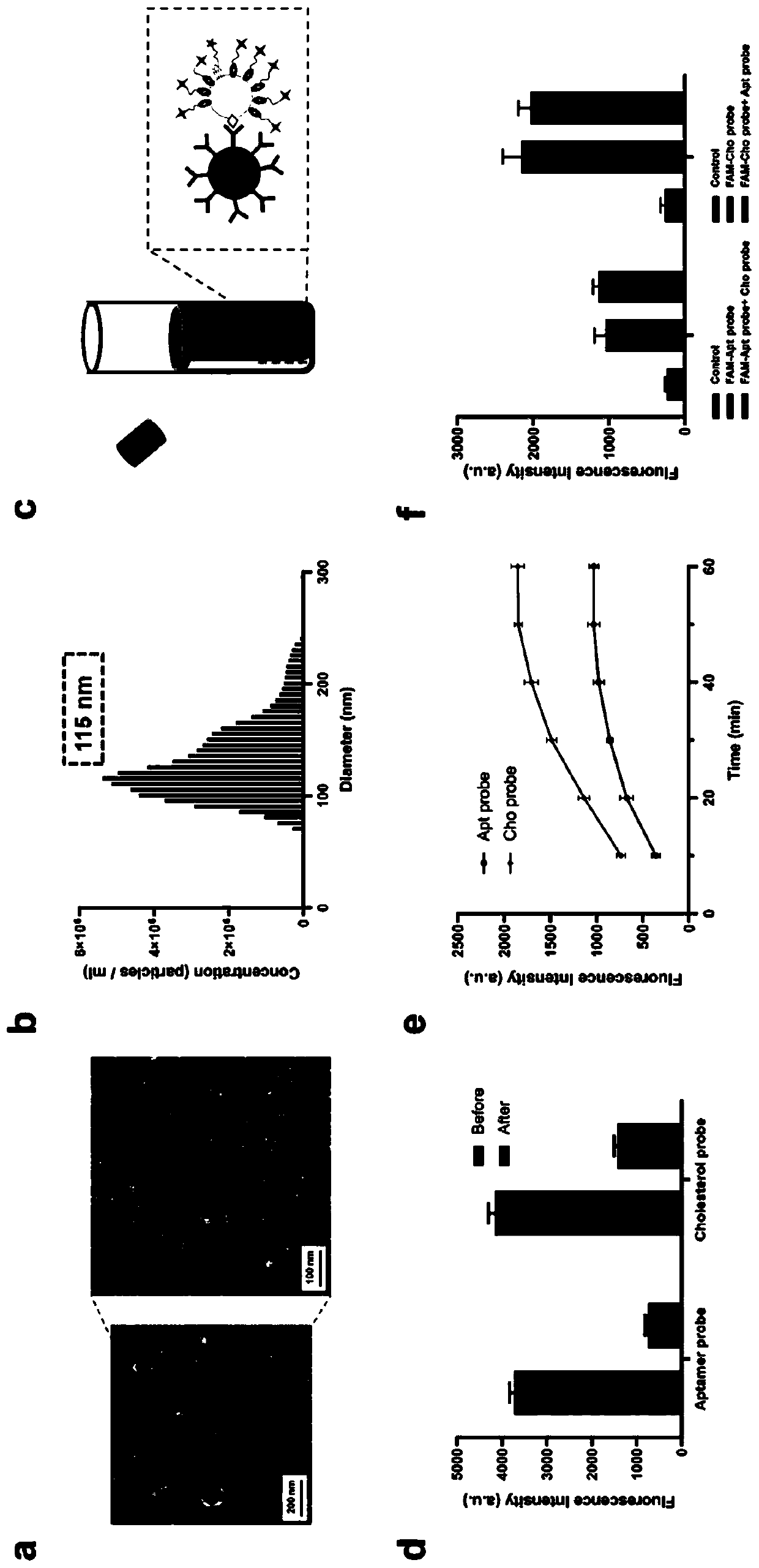
[0079] (1) To investigate whether AcmPLA can be used for accurate exosome identification, we used extracted exosomes obtained from A549 cell CCS by differential centrifugation as a simple model. The isolated exosomes were rigorously characterized using TEM and NTA for morphology observation and protein validation using western blotting. The peak at 115 nm in the diameter distribution determined by NTA is consistent with previous literature. We then detected the isolated exosomes and the proteins (CD9 / CD63 / CD81) expressed on the surface of A549 cells by western blotting.
[0080] (2) Considering that the binding affinity of aptamer probe and cholesterol probe is the key factor to determine the labeling efficiency of AcmPLA, we tested the FAM-labeled CD63 aptamer probe and FAM-labeled cholesterol probe with exosomes, respectively. ( figure 2 c). To avoid undesired fluo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com