A two-dimensional material transfer method based on a stepped substrate
A technology of two-dimensional materials and transfer methods, which is applied in the field of material transfer, can solve the problems of the contact area between two-dimensional materials and the substrate becomes smaller and cannot be transferred, and achieve the effects of increasing the bonding force, improving the success rate, and reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
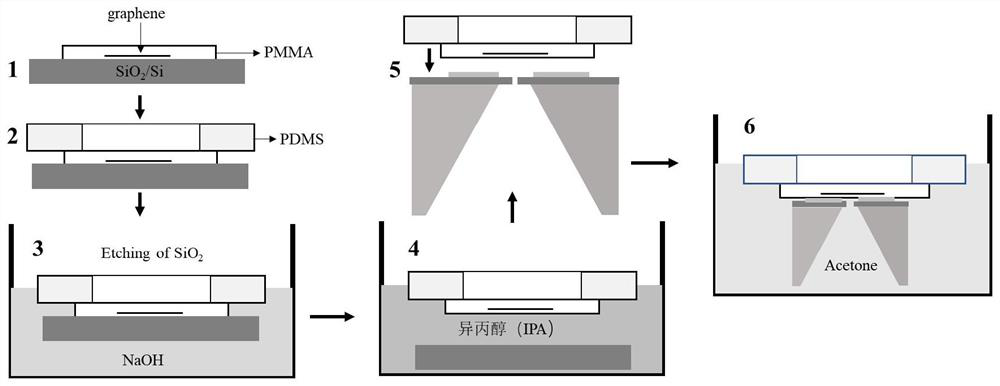
[0020] like figure 1 The two-dimensional material transfer method based on the stepped substrate shown includes the preparation and transfer process of the two-dimensional material. The preparation of the two-dimensional material adopts the mechanical lift-off method, and the transfer adopts the improved wet transfer method. In this example, the two-dimensional material is to be transferred. The material is graphene.
[0021] Specifically include the following steps:
[0022] (1) Graphene is peeled off on a silicon oxide / silicon substrate to form a graphene layer, preferably a silicon oxide / silicon substrate with a thickness of 285 nanometers of silicon oxide, and spin-coating 4% PMMA benzene on the graphene layer Diethyl ether solution, spin-coated 2 times to ensure the thickness of the PMMA film is 0.5 μm.
[0023] Graphene can also be exfoliated on PMMA first and then pressed onto a silicon oxide / silicon substrate.
[0024] (2) Under the optical microscope, the graphene / ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The present invention is based on a two-dimensional material transfer method with a stepped substrate, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0035] (1) peel off the graphene on the silicon oxide / silicon substrate to form a graphene layer, spin-coat PMMA on the graphene layer, and spin-coat twice to ensure that the thickness of the PMMA film is 0.65 microns;
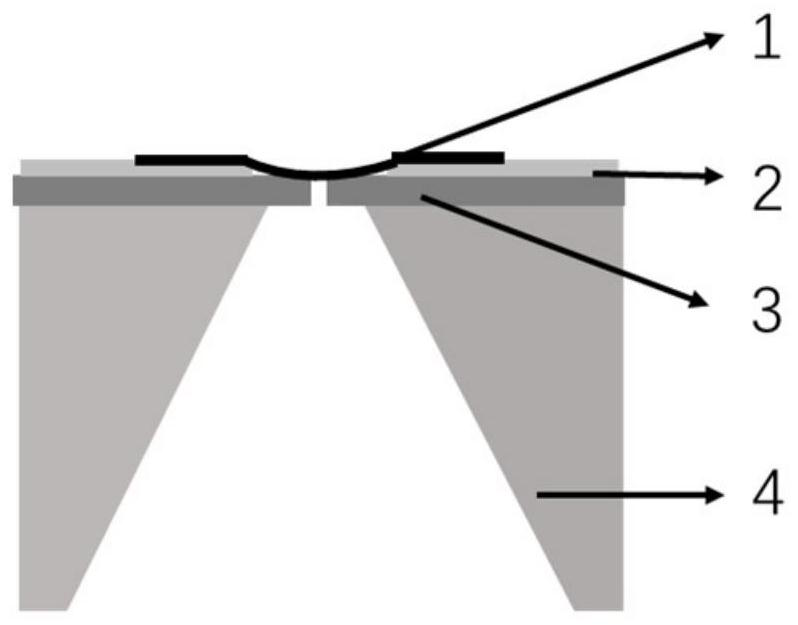
[0036] (2) Under the optical microscope, the graphene / PMMA layer was pressed tightly onto the punched PDMS square, and the graphene was located in the center of the hole; a cylindrical puncher was used, and the hole diameter was 2.5 mm.
[0037] (3) Put the whole sample obtained into sodium hydroxide solution to etch silicon oxide to release graphene / PMMA / PDMS; the mass fraction of sodium hydroxide solution is 33%.
[0038] (4) fish out the graphene / PMMA / PDMS and put it into isopropanol solution for cleaning, then fish out the graphene / PMMA / PDMS, align the graphene with the target position and press it...
Embodiment 3
[0041] The present invention is based on a two-dimensional material transfer method with a stepped substrate, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0042] (1) peel off the graphene on the silicon oxide / silicon substrate to form a graphene layer, spin-coat PMMA on the graphene layer, and spin-coat 3 times to ensure that the thickness of the PMMA film is 0.8 microns;
[0043] (2) Under an optical microscope, the graphene / PMMA layer was pressed onto the punched PDMS square, and the graphene was located in the center of the hole; a cylindrical puncher was used, and the hole diameter was 3 mm.
[0044] (3) Putting the obtained whole sample into sodium hydroxide solution to etch silicon oxide to release graphene / PMMA / PDMS; the mass fraction of sodium hydroxide solution is 35%.
[0045] (4) fish out the graphene / PMMA / PDMS and put it into isopropanol solution for cleaning, then fish out the graphene / PMMA / PDMS, align the graphene with the target position and press it with ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com