Method for determining binding rate of proteoglycan protein binding site in proteoglycan protein binding vaccine
A polysaccharide-protein-conjugated vaccine technology, applied in measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problem of no testing method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
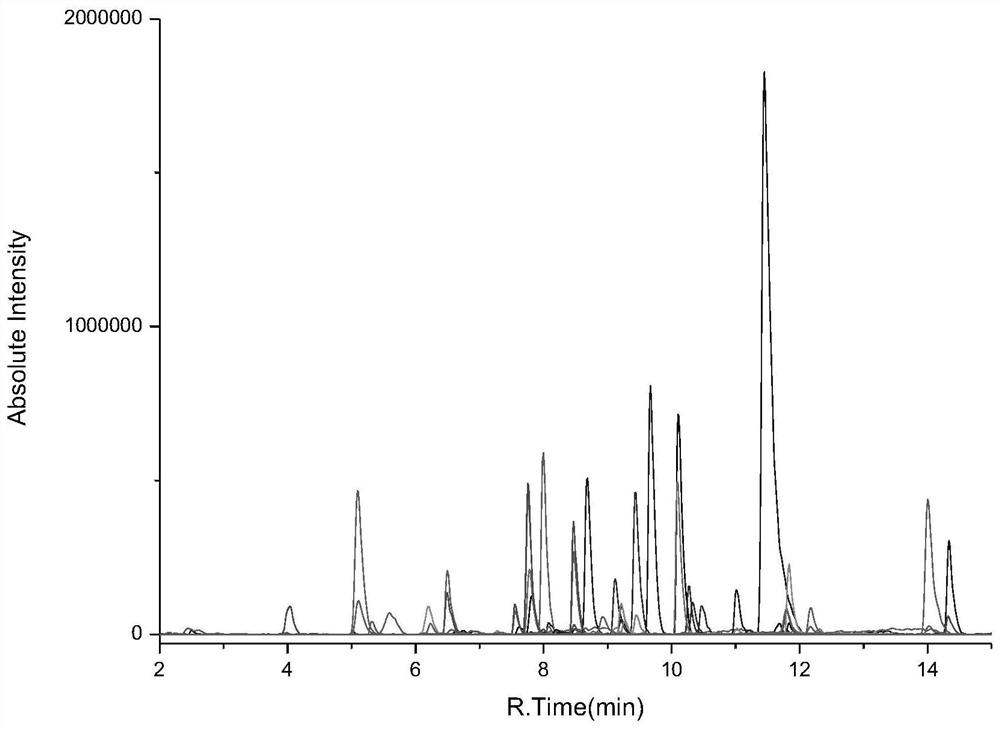
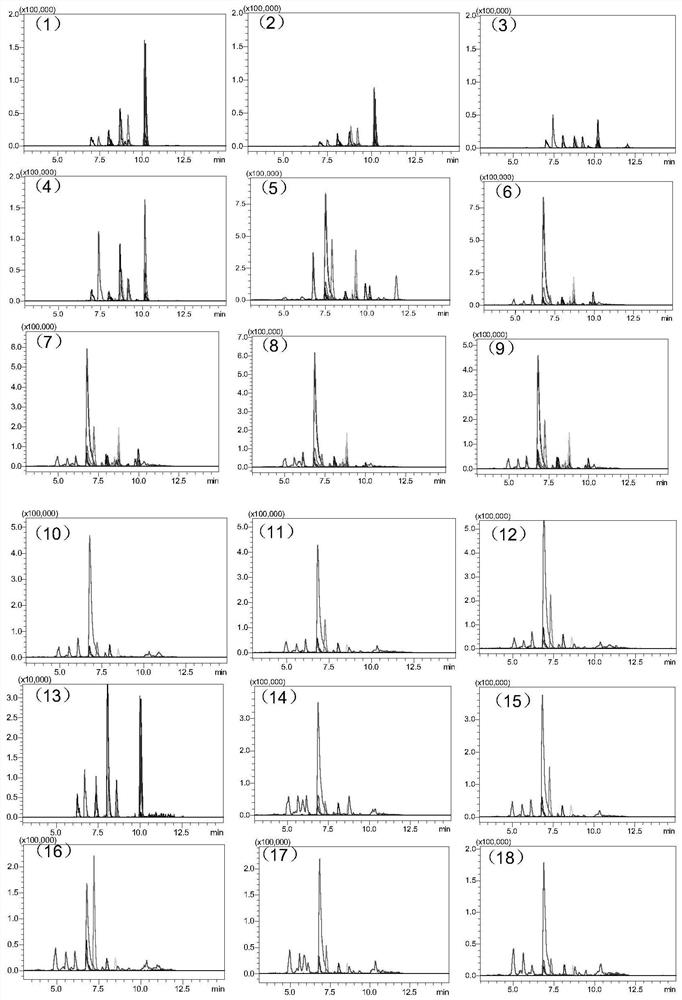
[0083] Example 1 Determination of Polysaccharide Protein Binding Site Binding Rate in Polysaccharide Protein Binding Vaccine Taking Tetanus Toxoid as Carrier
[0084] 1. Experimental instruments and equipment: high-pressure binary pump, degasser, autosampler, column thermostat and triple quadrupole mass spectrometer.
[0085] 2. Experimental reagents: standard tetanus toxoid (1000 μg / L), 4-valent meningitis vaccine, TCEP, iodoacetamide (IAA), ammonium bicarbonate, RapiGest TM , trypsin, tetanus toxoid-based 4-valent meningitis vaccine, Hib vaccine and 13-valent pneumococcal vaccine. Meningitis vaccines A, W, C, Y, Hib vaccine, 13-valent pneumococcal vaccines 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, 19A, and 23F.
[0086] 3. Detection conditions:
[0087] Chromatographic conditions:
[0088] Chromatographic column: stationary phase 1 (biocompatible C18 chromatographic column);
[0089] Mobile phase: A: acetic acid aqueous solution (the volume ratio of acetic acid to water ...
Embodiment 2
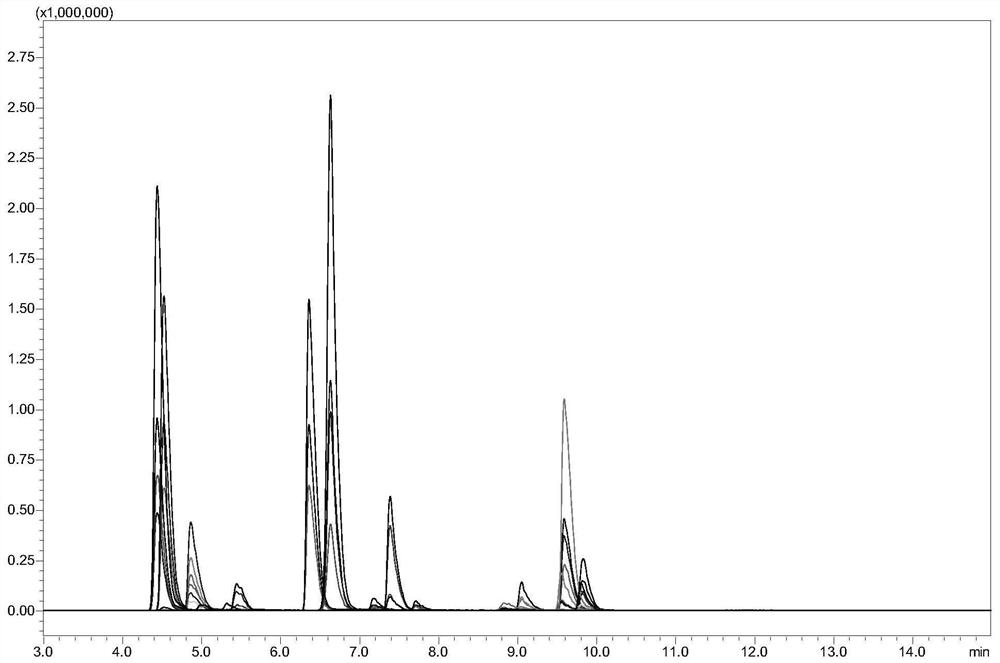
[0134] Example 2 Determination of the binding rate of the polysaccharide protein binding site in the polysaccharide protein conjugate vaccine with CRM197 protein as the carrier
[0135] 1. Experimental instruments and equipment: high-pressure binary pump, degasser, autosampler, column thermostat and triple quadrupole mass spectrometer.
[0136] 2. Experimental reagents: CRM197 protein standard (100 μg / L), TCEP, iodoacetamide (IAA), ammonium bicarbonate, urea, trypsin, meningitis vaccine A, W, C, Y with CRM197 protein as the carrier , Hib vaccine, 13-valent pneumonia vaccine 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F, 19A and 23F.
[0137] 3. Detection conditions:
[0138] Chromatographic conditions:
[0139] Chromatographic column: stationary phase 2 (biocompatible C8 column);
[0140] Mobile phase: A: acetic acid aqueous solution (the volume ratio of acetic acid to water is 1:1000); B: acetic acid-acetonitrile mixture (the volume ratio of acetic acid to acetonitrile is 1:100...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com