Analysis method of metal impurity content, and analysis kit of metal impurity content
A technology of metal impurities and analysis methods, applied in the direction of analyzing materials, chemical instruments and methods, testing water, etc., can solve problems such as the type and shape of metal impurities, and achieve the effect of increasing the speed of liquid flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
reference example 1
[0234]
[0235] (I process: manufacture of bulk intermediates)
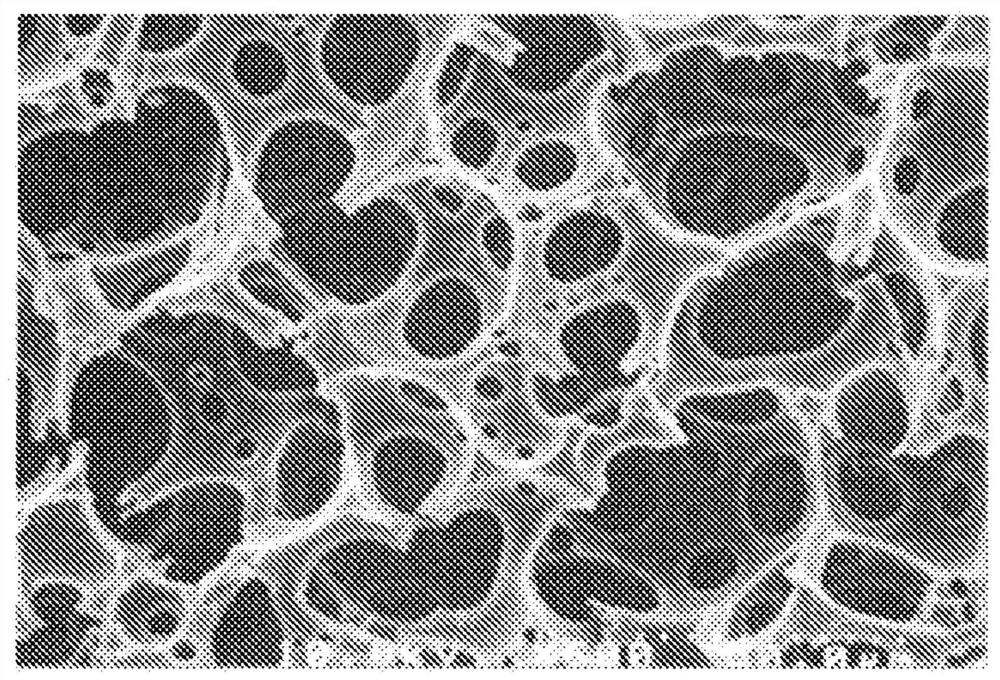
[0236] Mix 5.4 g of styrene, 0.17 g of divinylbenzene, 1.4 g of sorbitan monooleate (hereinafter abbreviated as SMO) and 0.26 g of 2,2'-azobis(isobutyronitrile) to make it uniform dissolve. Next, add this styrene / divinylbenzene / SMO / 2,2'-azobis(isobutyronitrile) mixture to 180 g of pure water, and use a planetary stirring device, namely, a vacuum stirring and defoaming mixer (EME company Production) Stirring under reduced pressure in the temperature range of 5 to 20° C. to obtain a water-in-oil emulsion. This emulsion was quickly transferred to a reaction vessel, sealed and then left to stand for polymerization at 60° C. for 24 hours. After the polymerization, the contents were taken out, extracted with methanol, and then dried under reduced pressure to produce a monolithic intermediate with a continuous macroporous structure. Observation of the internal structure of the thus obtained monolithic intermediate ...
Embodiment 1
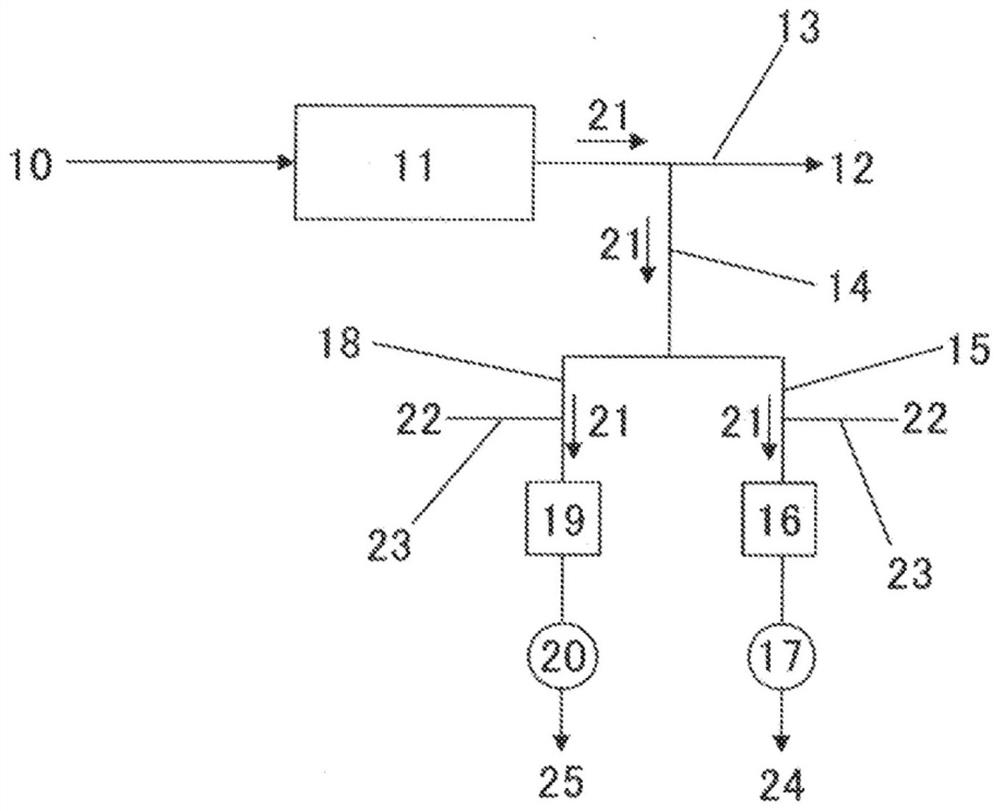
[0253] The monolithic anion exchanger A was cut into a shape having a diameter of 10 mm×a height of 20 mm, and filled in a filling container made of PFA (tetrafluoroethylene-perfluoroalkyl vinyl ether copolymer). Next, in the filled container, under the conditions shown in Table 1, at 33mL / min. (SV=1274h -1 ) was passed through the test water 1 described later, and the test water 1 was passed through the monolithic anion exchanger A. The total flow rate of the test water 1 at this time was 100 mL.
[0254] Next, the recovered solution was measured by ICP-MS to measure the concentration of each ionic impurity element.
[0255] Next, the total amount of each ionic impurity element in the test water which was calculated from the concentration of each ionic impurity element in the test water and the total amount of liquid passing, and the concentration of each ionic impurity element in the recovered liquid were obtained. The total recovery amount of each ionic impurity element i...
Embodiment 2
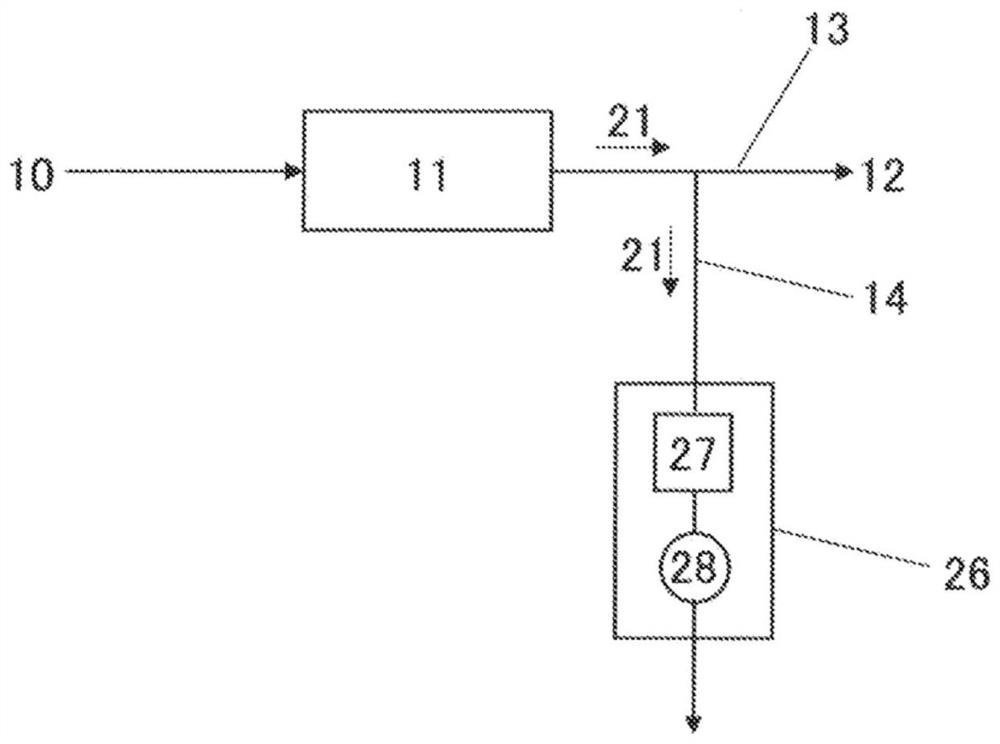
[0262] The monolithic cation exchanger B was cut out in the shape shown in Table 1, and it carried out similarly to Example 1 except having passed liquid on the conditions shown in Table 1. The results are shown in Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com