Chemical analysis method for determining chloride ions in metal copper by restraining specific ion behaviors through generated molecular crystals
A molecular crystal and metal copper technology, applied in the field of chemical analysis, can solve the problems affecting the quality of electro-copper products, low salt conversion rate, destructive effect of production equipment, etc., so as to avoid the influence of the matrix effect of copper ions, improve the accuracy and Reliability, the effect of filling the gap of analysis and detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
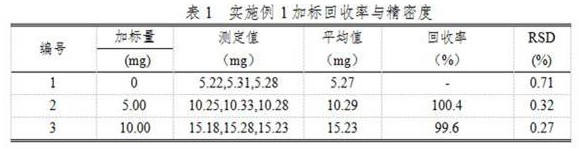
Embodiment 1
[0017] A chemical analysis method for determining chloride ions in metal copper by using molecular crystals to constrain specific ion behavior, comprising the following steps:
[0018] (1) Weigh about 1.000g of metallic copper sample into a 400mL beaker, add 50mL of 1:2 dilute nitric acid (containing 10g / L of mercury nitrate), heat to dissolve the sample completely, heat and boil to drive away nitrogen oxides, remove to cool;
[0019] (2) Add ammonia water to the cooled solution in step (1) while stirring, adjust the pH of the solution to about 9, and add 5-10 mL of excess ammonia water, and let it stand for 1-2 hours;
[0020] Filter the solution after standing in step (2) with slow filter paper, wash the beaker and the precipitate with 1:19 nitric acid 6-7 times each, keep the precipitate, discard the filtrate, and put the filter paper and the precipitate into the original beaker , after adding nitric acid mixed acid with a volume ratio of 2:1 for treatment, it is made into...
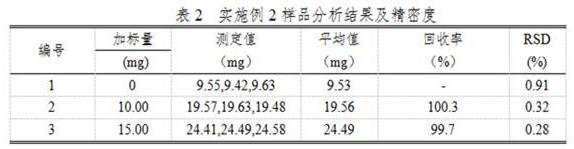
Embodiment 2
[0023] A chemical analysis method for determining chloride ions in metal copper by using molecular crystals to constrain specific ion behavior, comprising the following steps:
[0024] (1) Weigh about 2.000g of metallic copper sample into a 400mL beaker, add 50mL of 1:2 dilute nitric acid (containing 10g / L of mercury nitrate), heat to dissolve the sample completely, heat and boil to drive away nitrogen oxides, remove to cool;
[0025] (2) Add ammonia water to the cooled solution in step (1) while stirring, adjust the pH of the solution to about 9, and add 5-10 mL of excess ammonia water, and let it stand for 1-2 hours;
[0026] (3) Filter the solution after standing in step (2) with slow filter paper, wash the beaker and the precipitate with 1:19 nitric acid 6-7 times each, keep the precipitate, discard the filtrate, put the filter paper together with the precipitate into In the original beaker, after adding nitric acid mixed acid, it is made into a 1:9 hydrochloric acid solu...
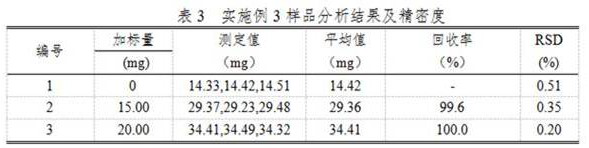
Embodiment 3
[0029] A chemical analysis method for determining chloride ions in metal copper by using molecular crystals to constrain specific ion behavior, comprising the following steps:
[0030] (1) Weigh about 3.000g of metallic copper sample into a 400mL beaker, add 50mL of 1:2 dilute nitric acid (containing 10g / L of mercury nitrate), heat to dissolve the sample completely, heat and boil to drive away nitrogen oxides, remove to cool;
[0031] (2) Add ammonia water to the cooled solution in step (1) while stirring, adjust the pH of the solution to about 9, and add 5-10 mL of excess ammonia water, and let it stand for 1-2 hours;
[0032] (3) Filter the solution after standing in step (2) with slow filter paper, wash the beaker and the precipitate with 1:19 nitric acid 6-7 times each, keep the precipitate, discard the filtrate, put the filter paper together with the precipitate into In the original beaker, after adding nitric acid mixed acid, it is made into a 1:9 hydrochloric acid solu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com