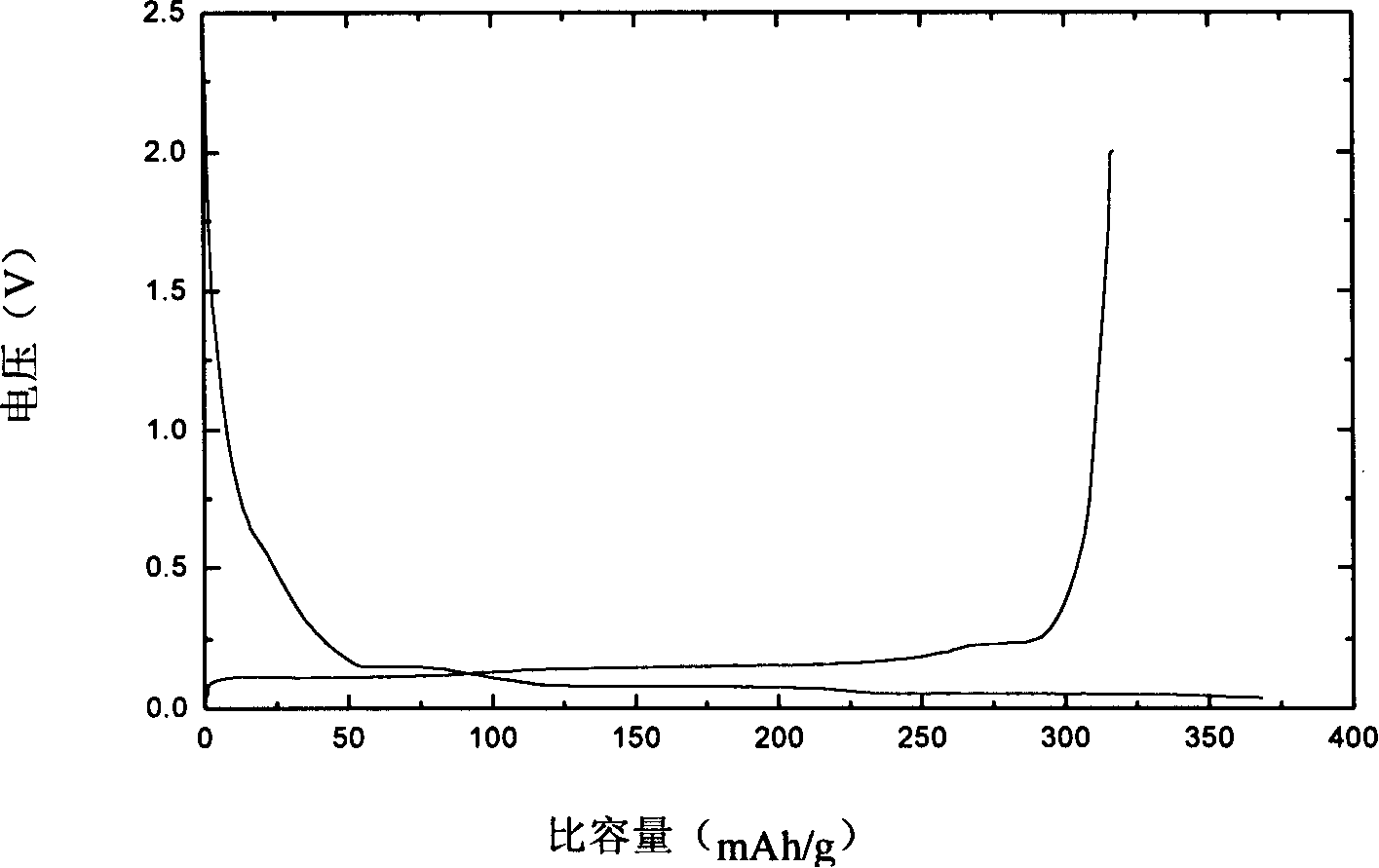
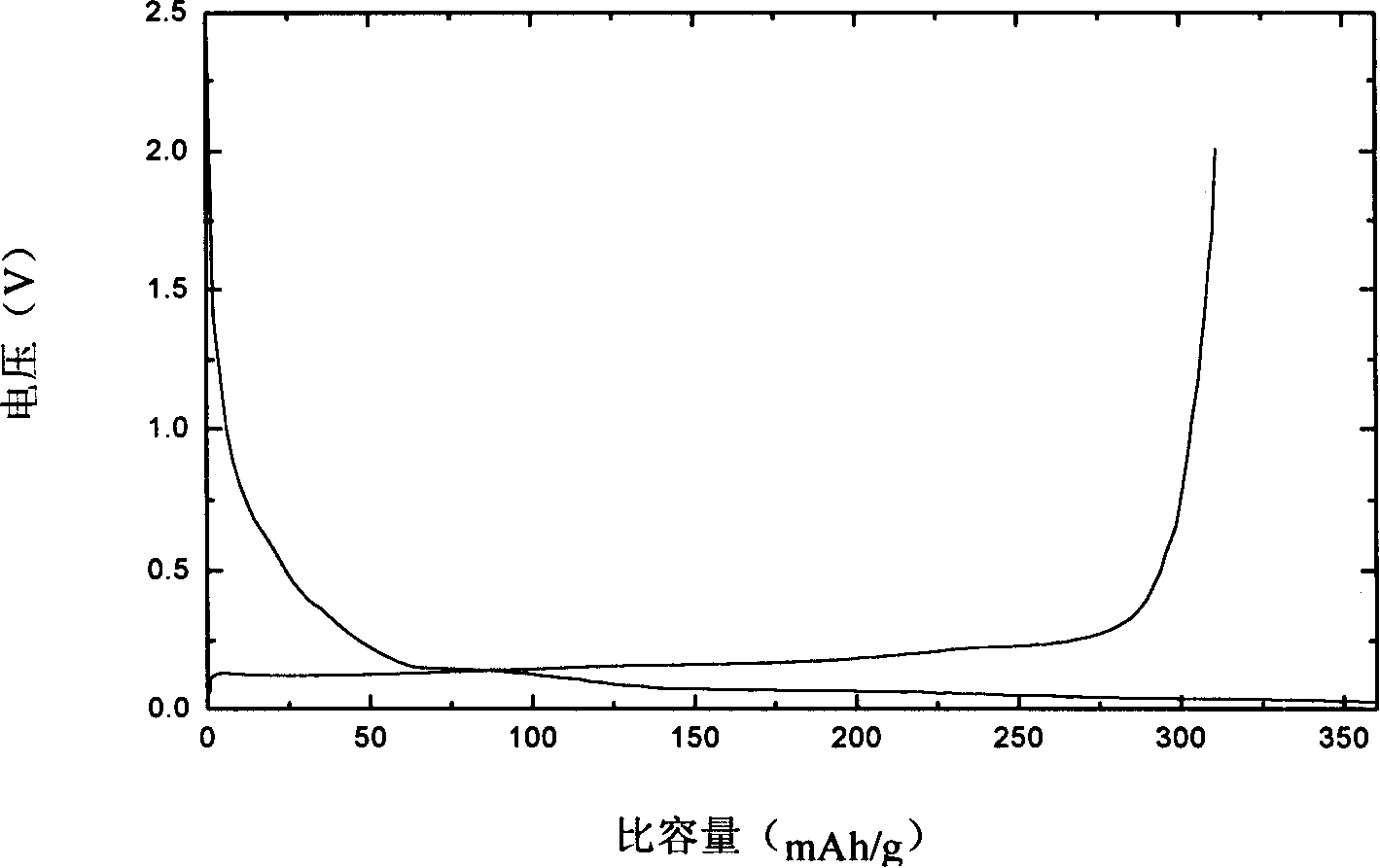
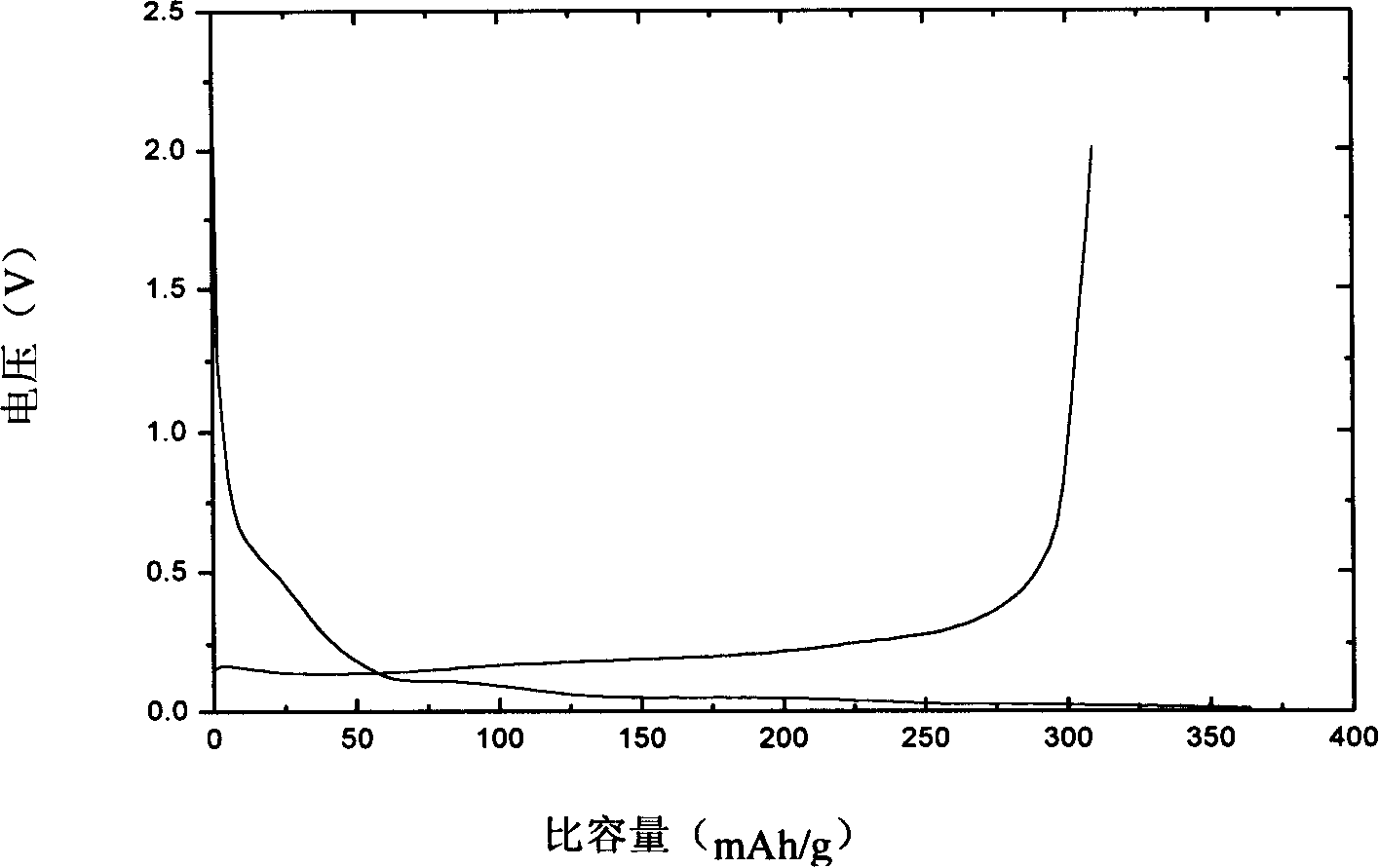
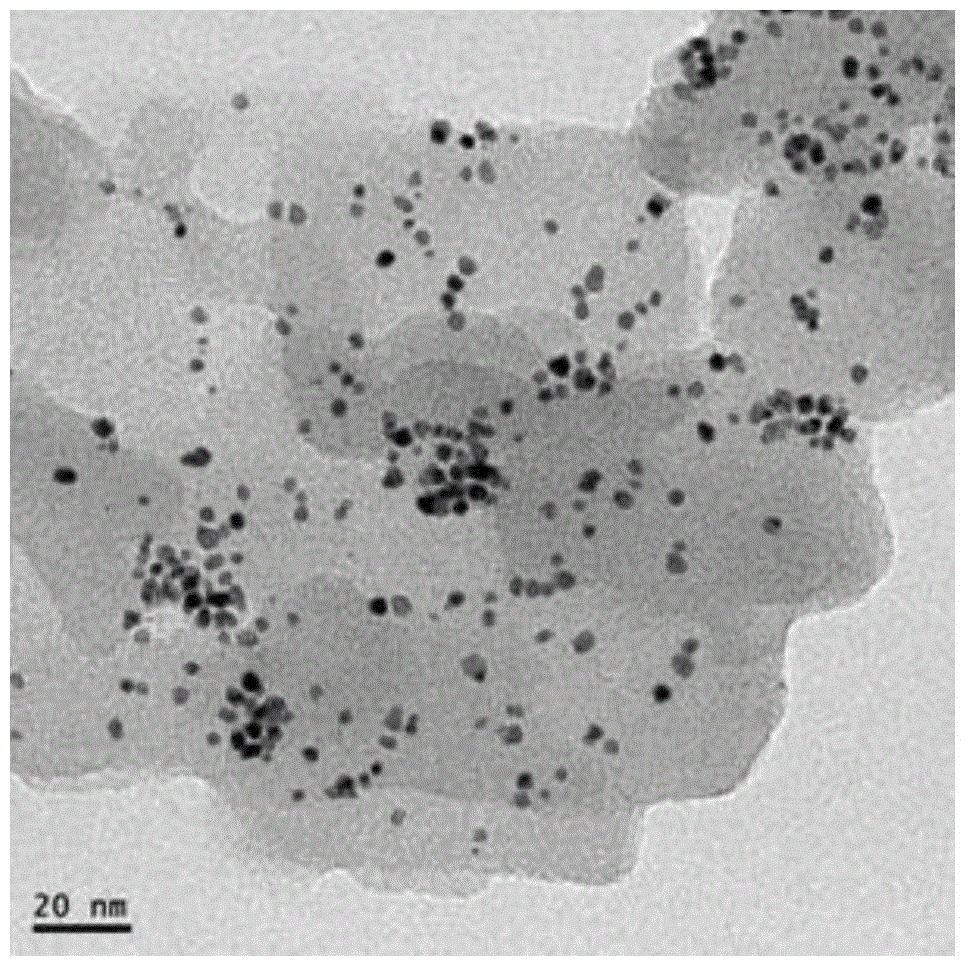
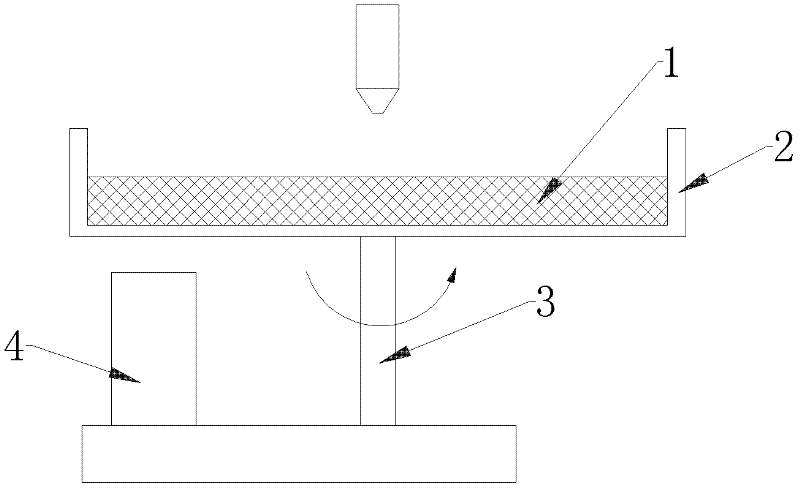
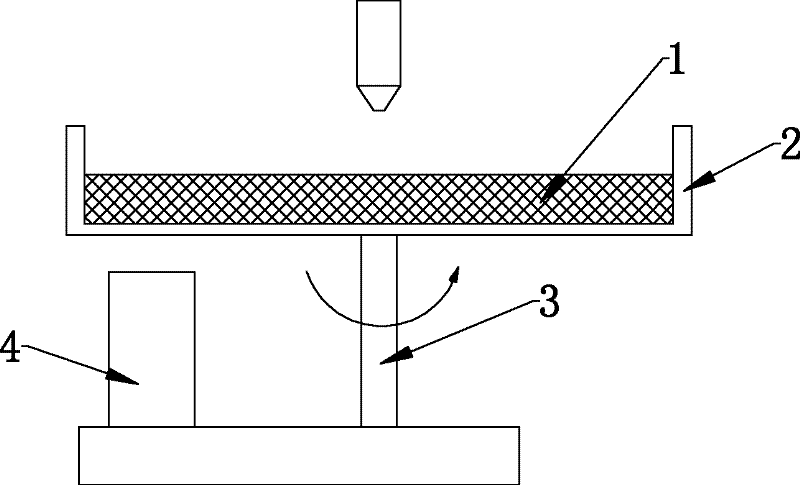
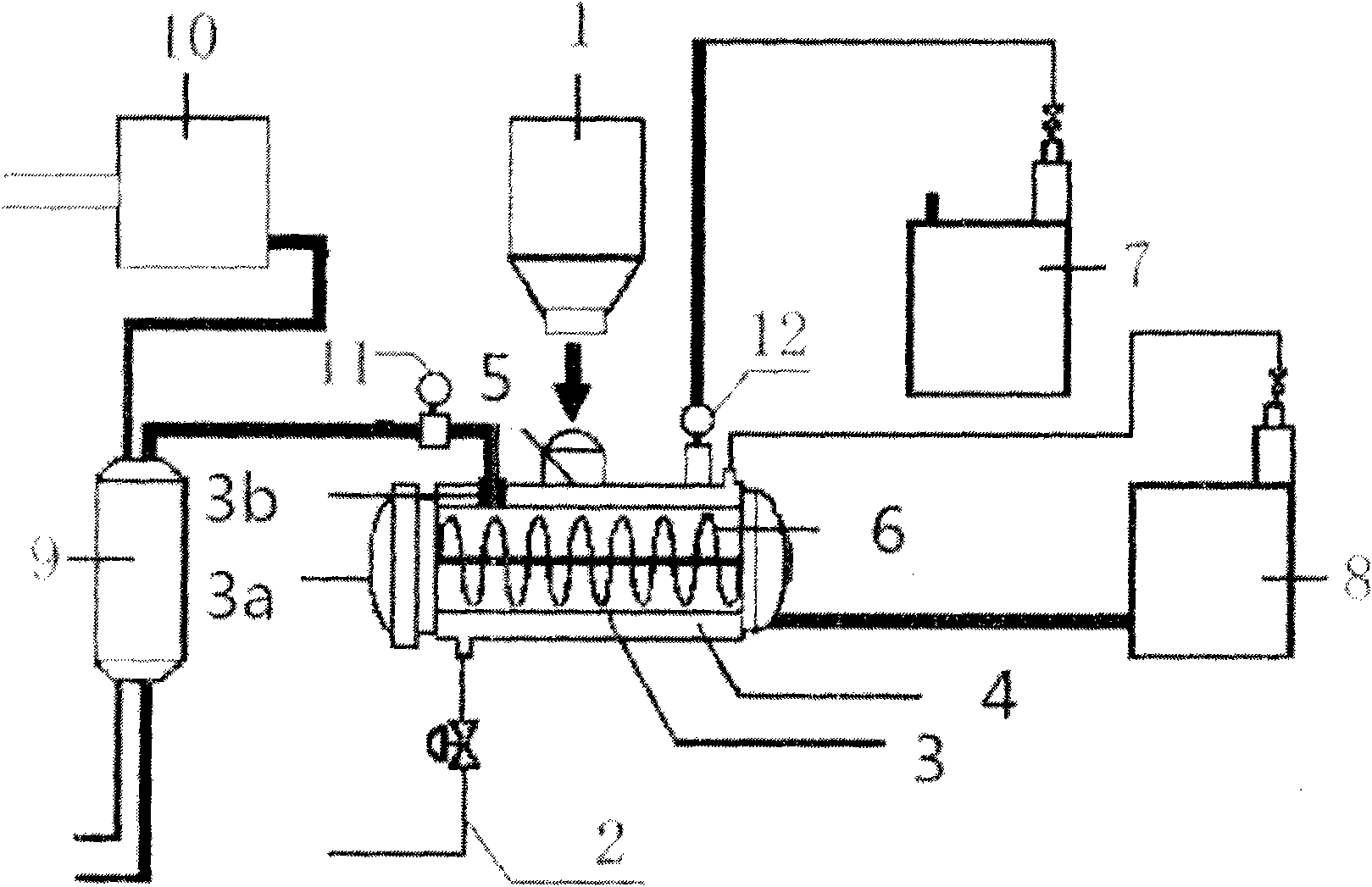
Patents
Literature
70 results about "Molecular solid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A molecular solid is a solid consisting of discrete molecules. The cohesive forces that bind the molecules together are van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole interactions, quadrupole interactions, π-π interactions, hydrogen bonding, halogen bonding, London dispersion forces, and in some molecular solids, coulombic interactions. Van der Waals, dipole interactions, quadrupole interactions, π-π interactions, hydrogen bonding, and halogen bonding (2-127 kJ mol⁻¹) are typically much weaker than the forces holding together other solids: metallic (metallic bonding, 400-500 kJ mol⁻¹), ionic (Coulomb’s forces, 700-900 kJ mol⁻¹), and network solids (covalent bonds, 150-900 kJ mol⁻¹). Intermolecular interactions, typically do not involve delocalized electrons, unlike metallic and certain covalent bonds. Exceptions are charge-transfer complexes such as the tetrathiafulvane-tetracyanoquinodimethane (TTF-TCNQ), a radical ion salt. These differences in the strength of force (i.e. covalent vs. van der Waals) and electronic characteristics (i.e. delocalized electrons) from other types of solids give rise to the unique mechanical, electronic, and thermal properties of molecular solids.
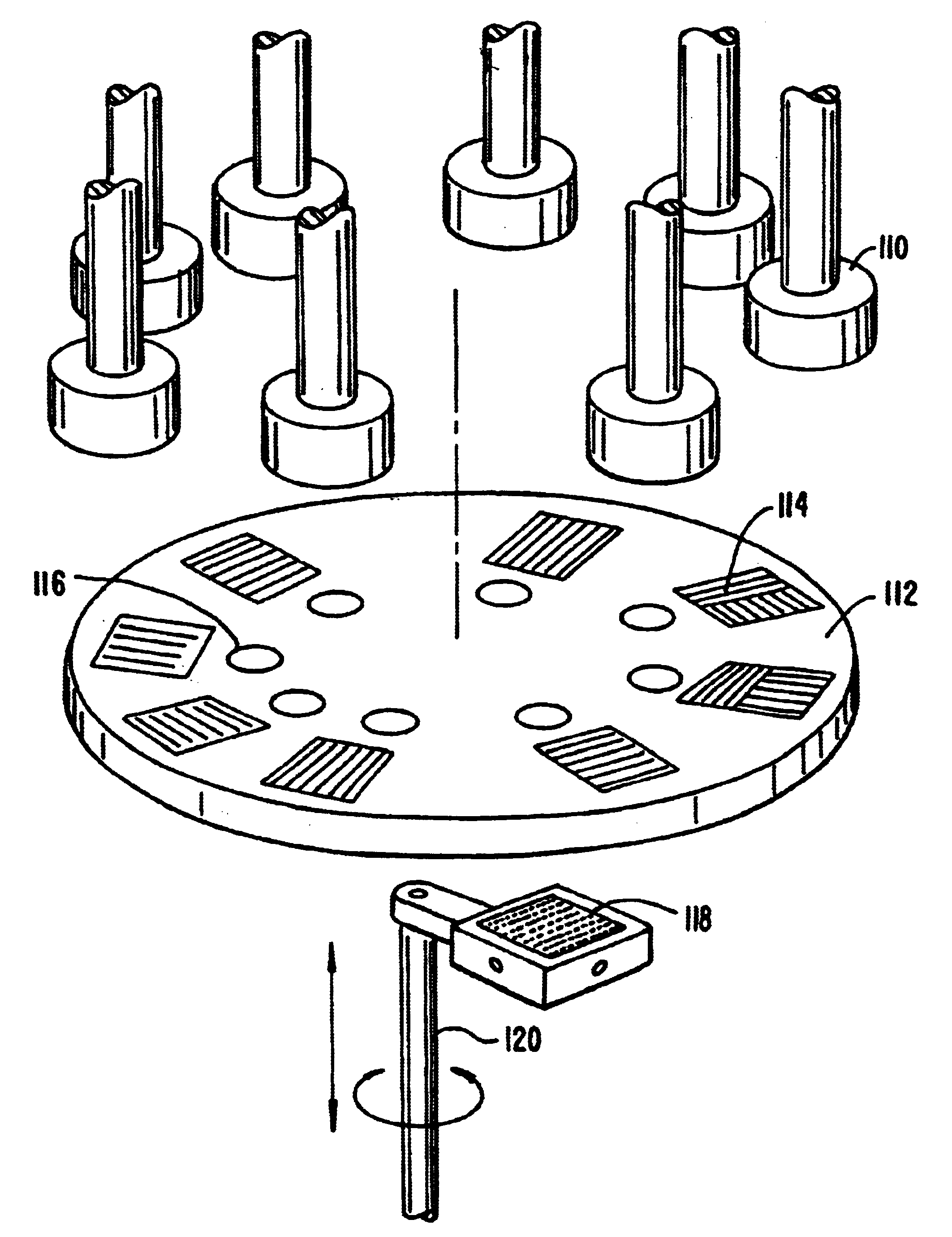
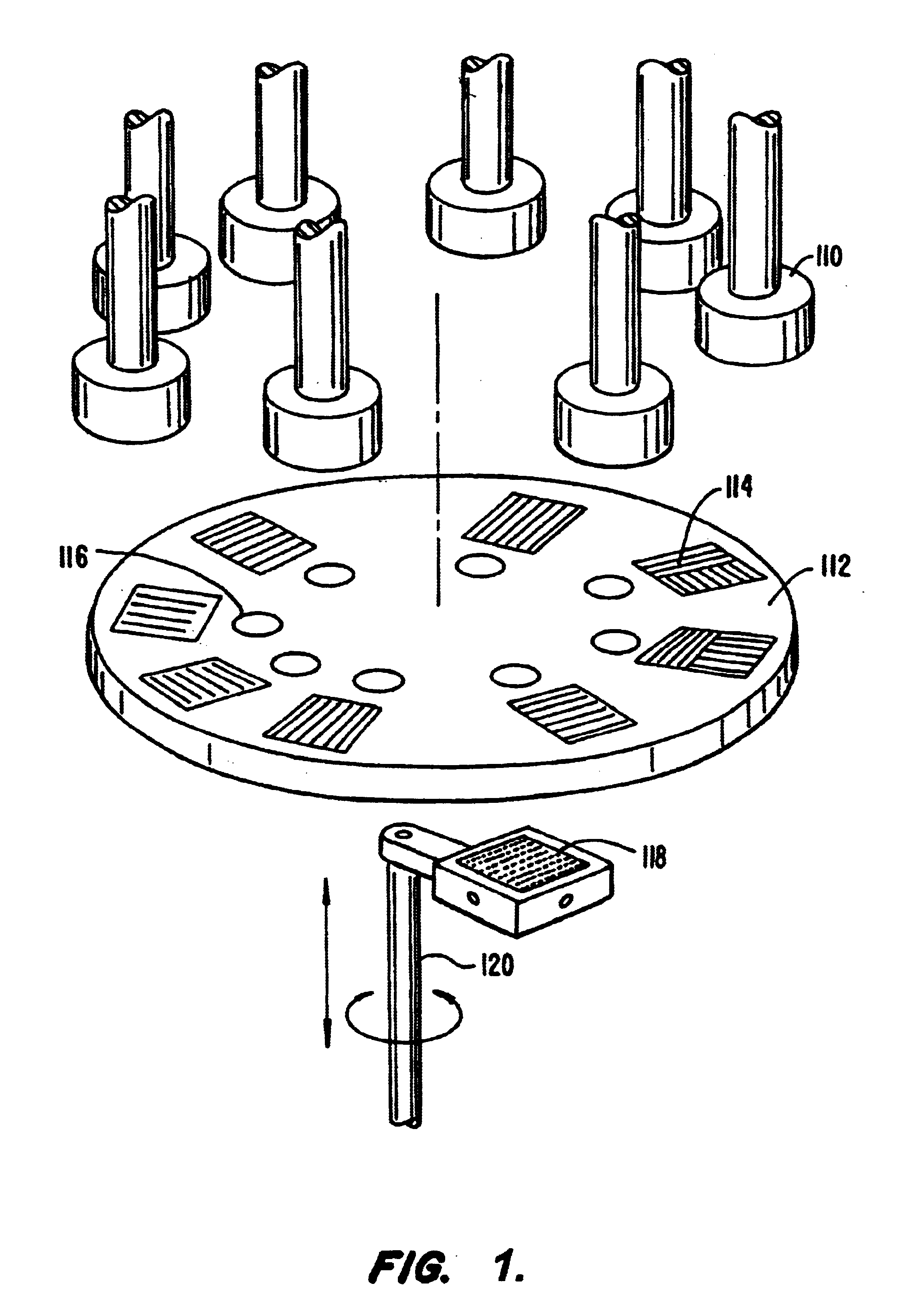
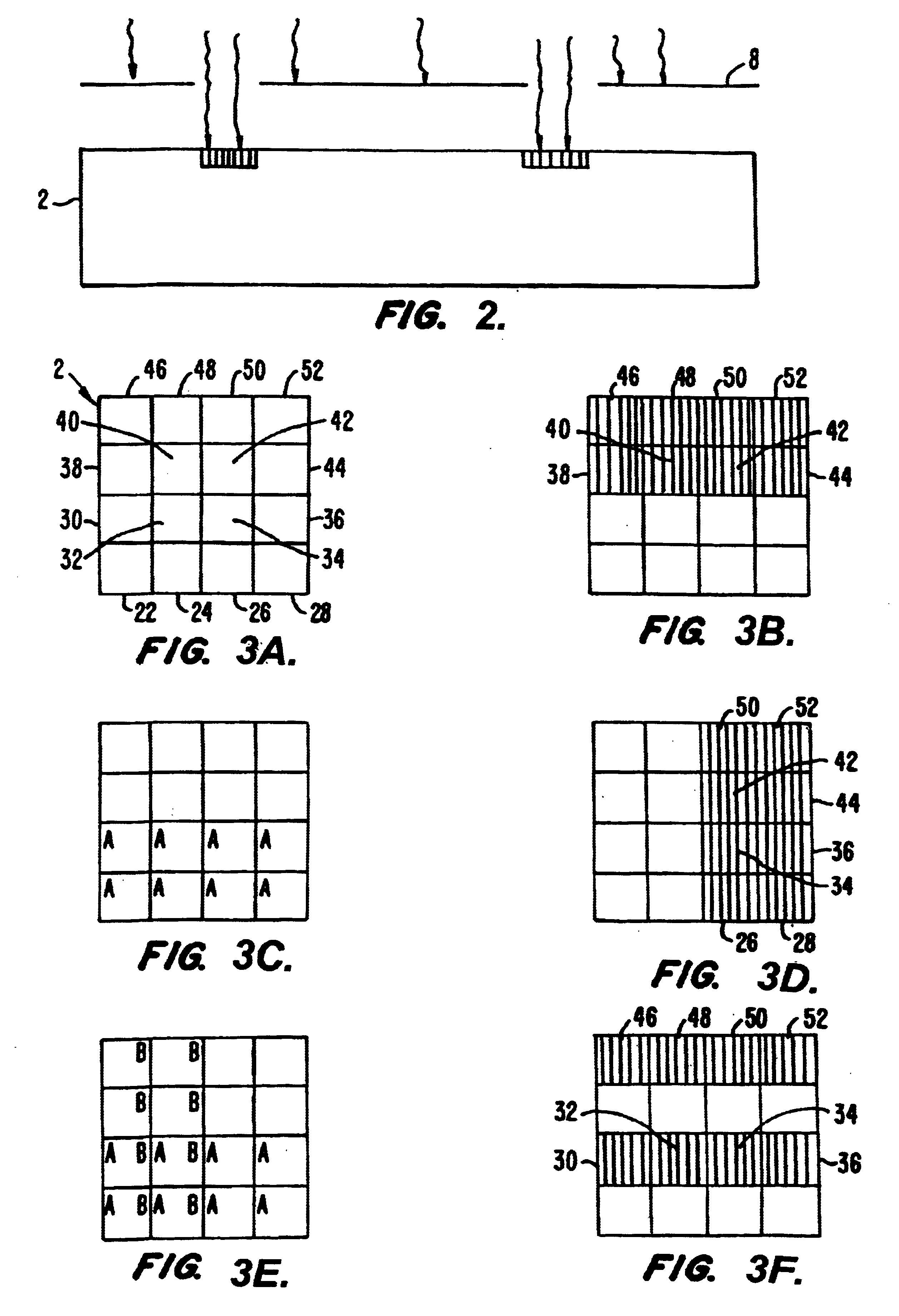
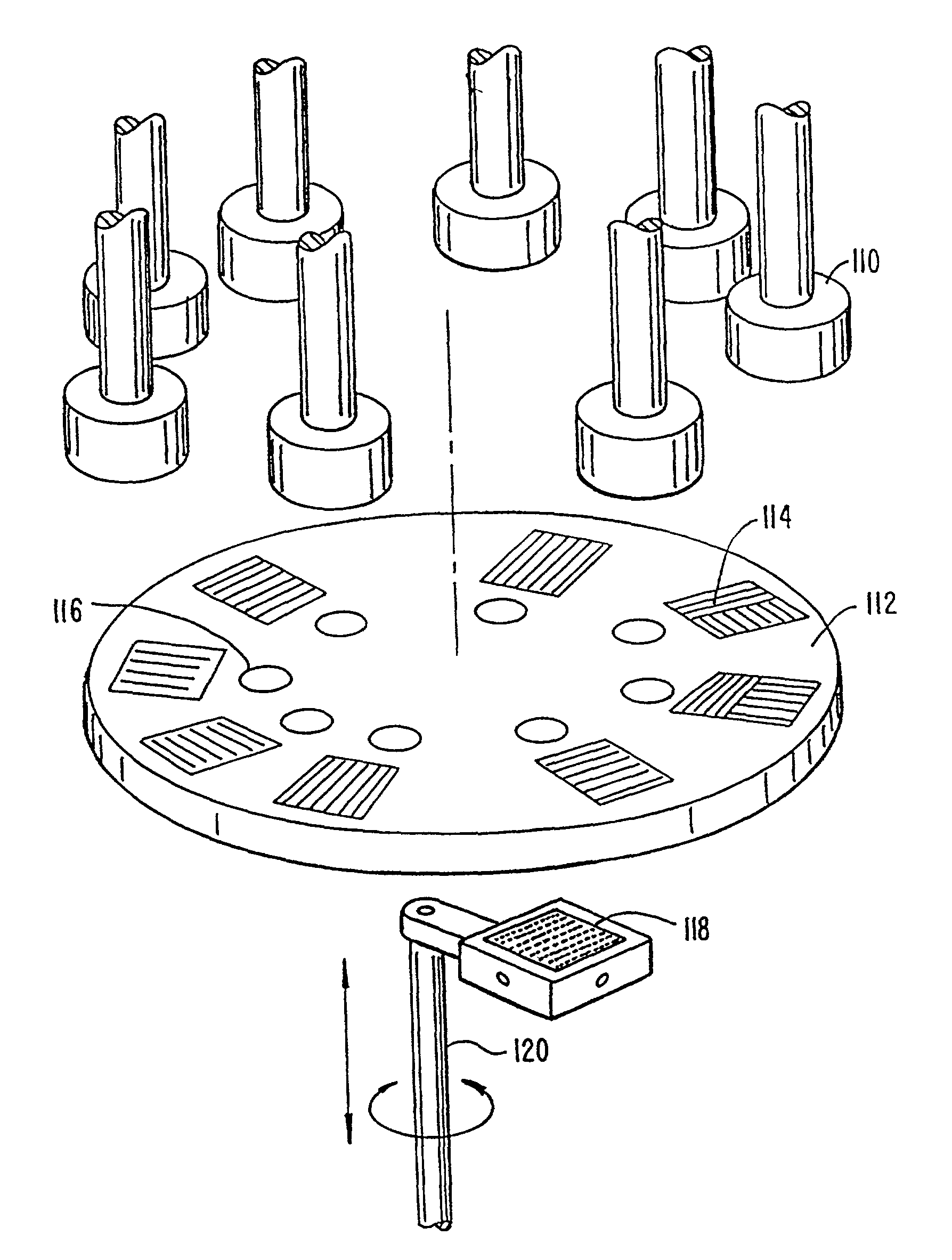
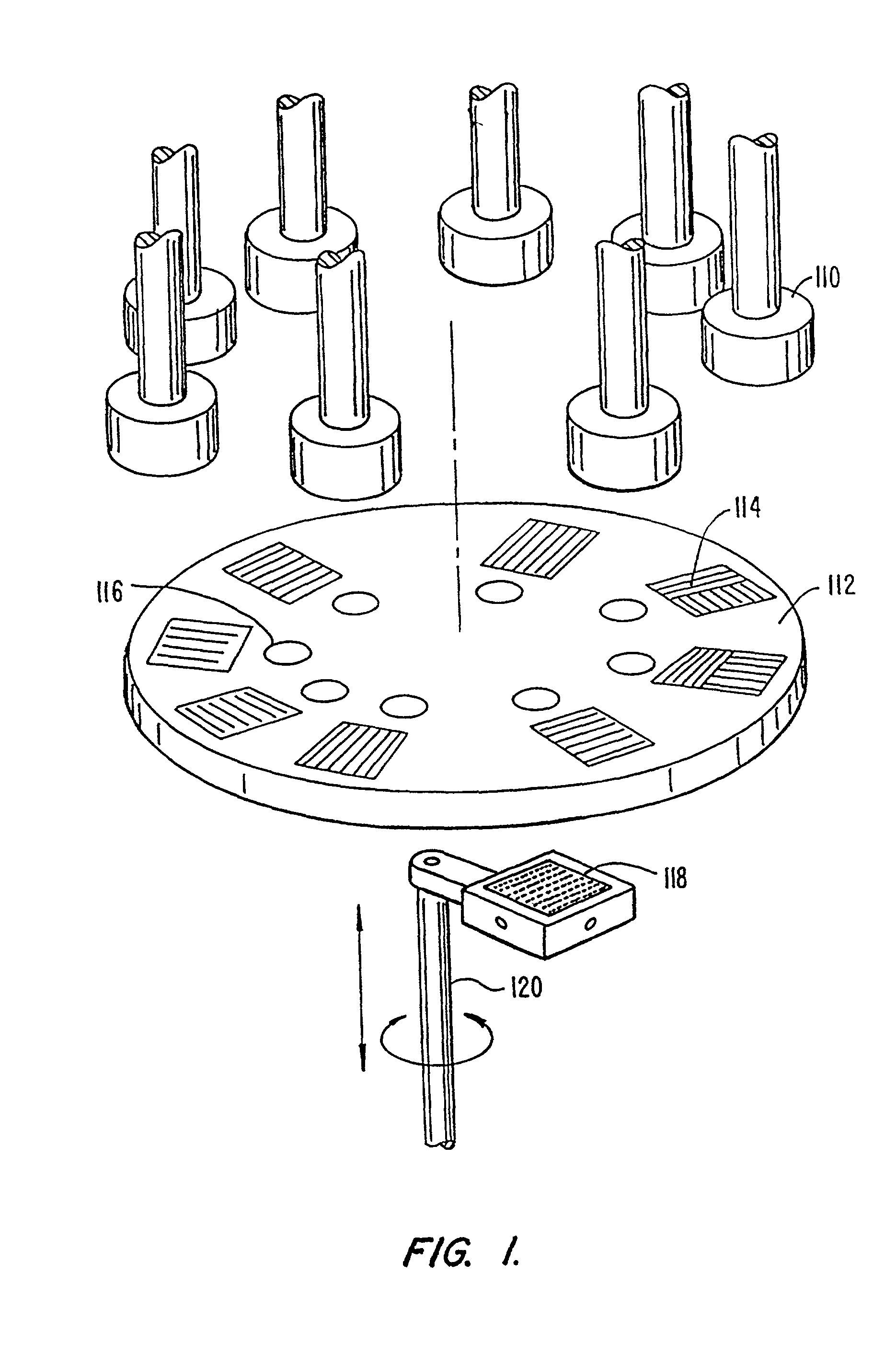
Preparation and screening of crystalline zeolite and hydrothermally-synthesized materials
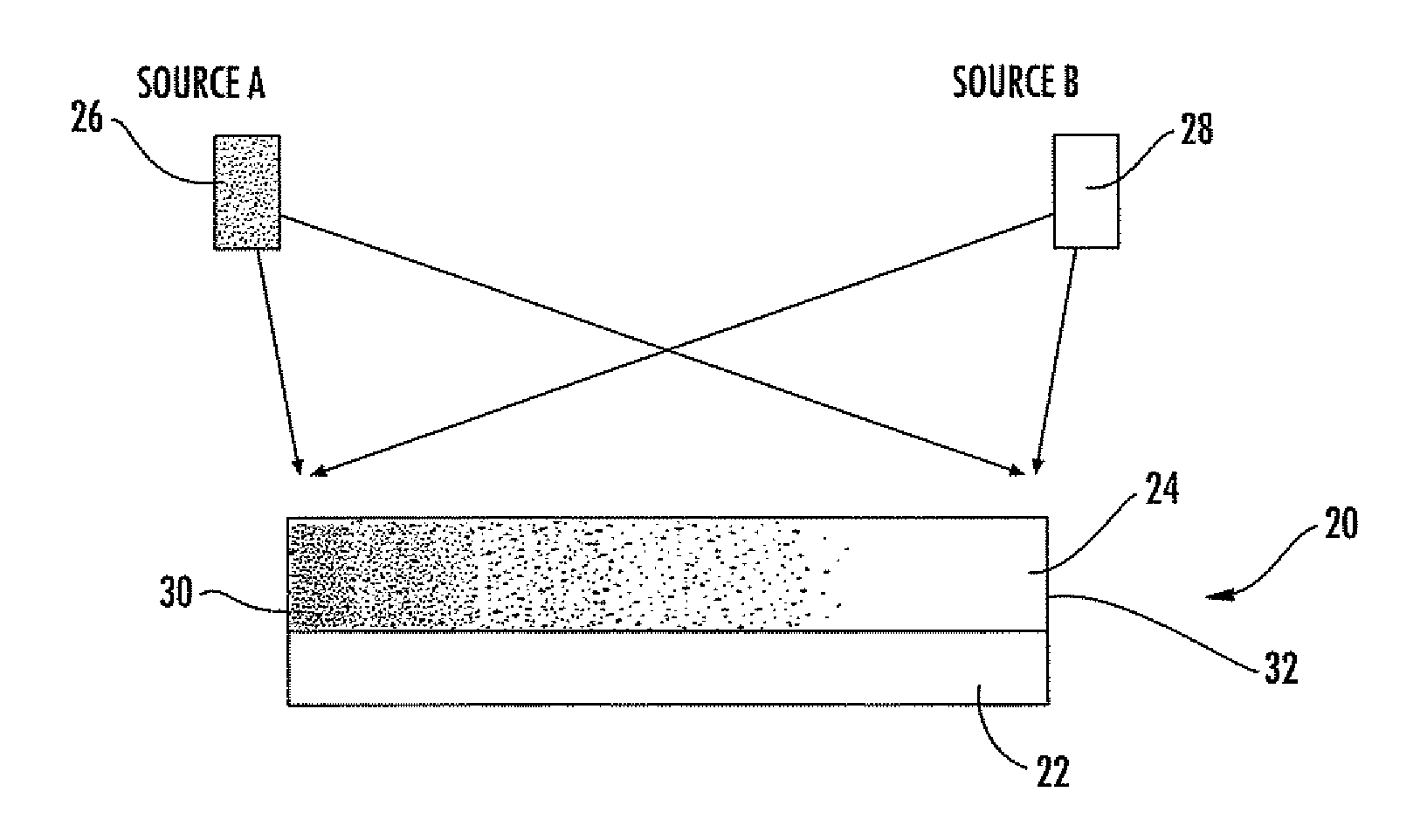
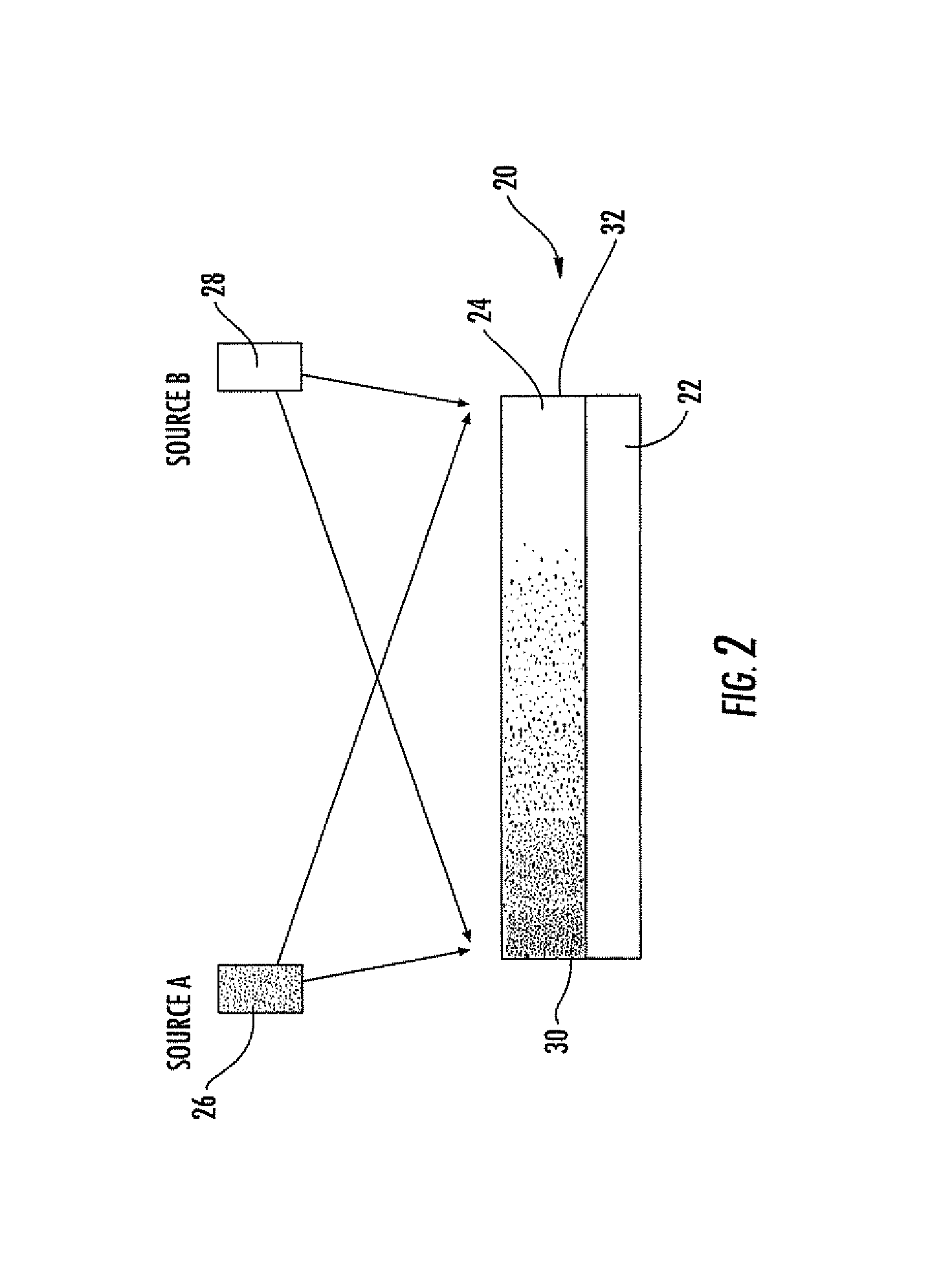
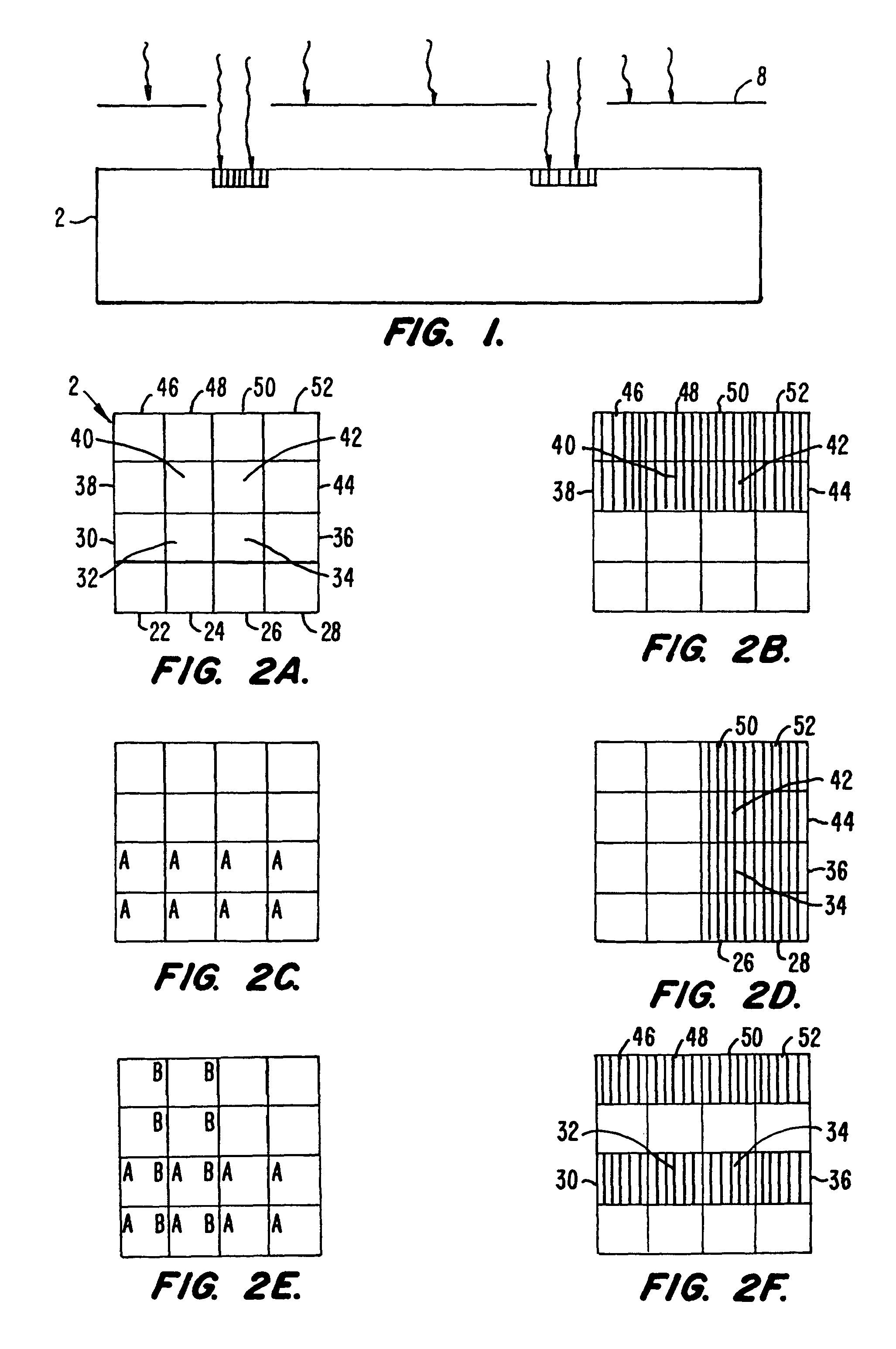
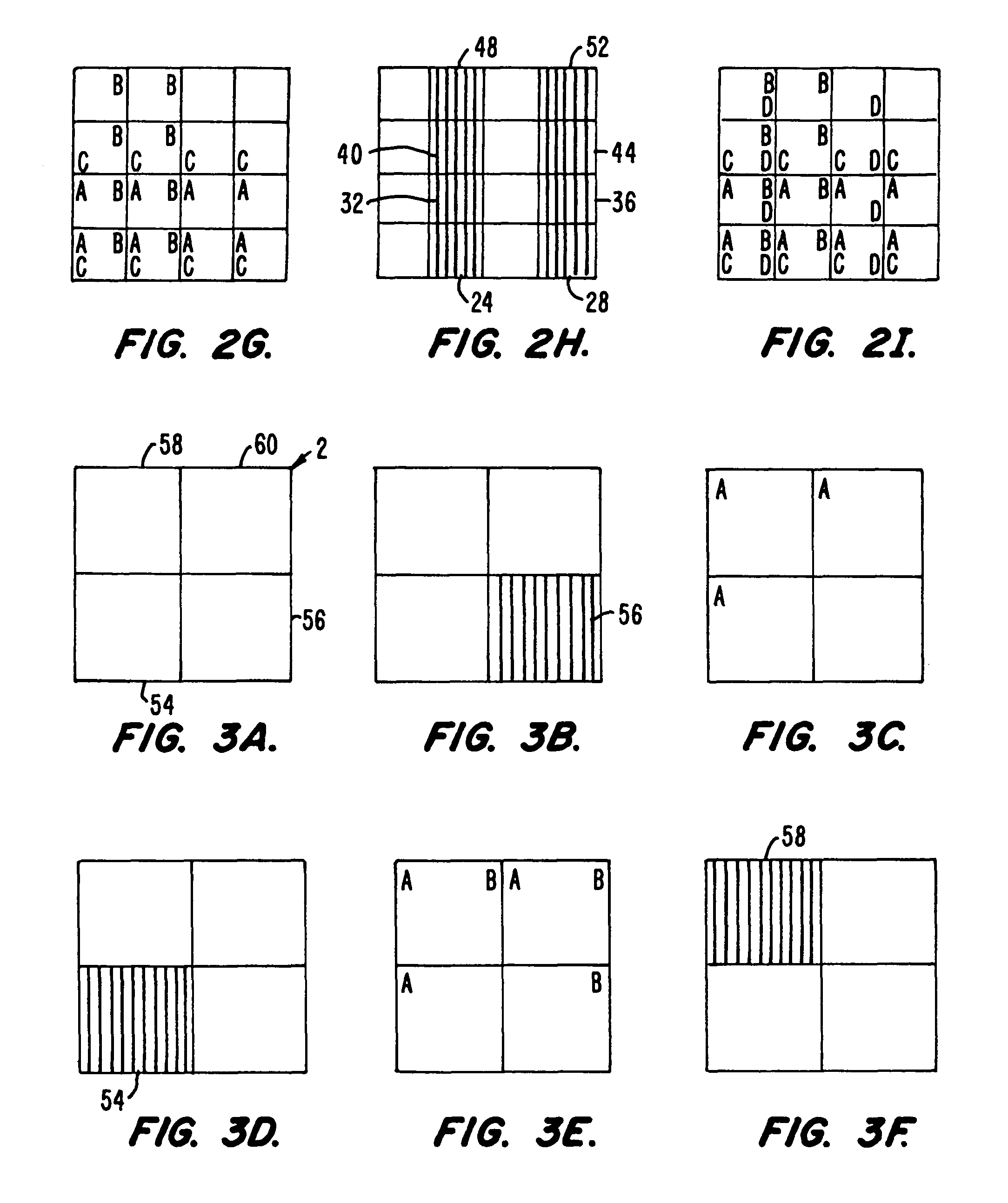
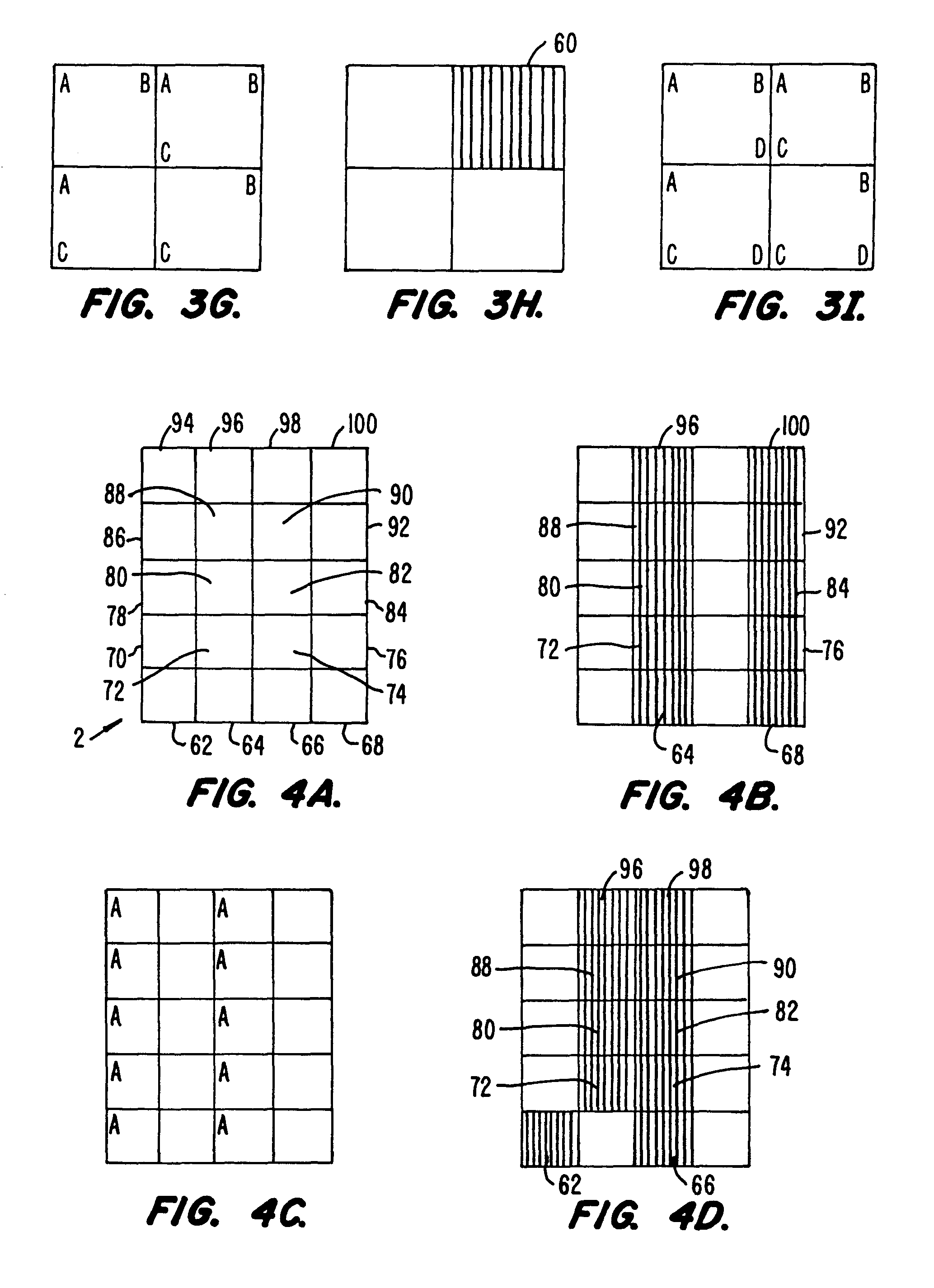
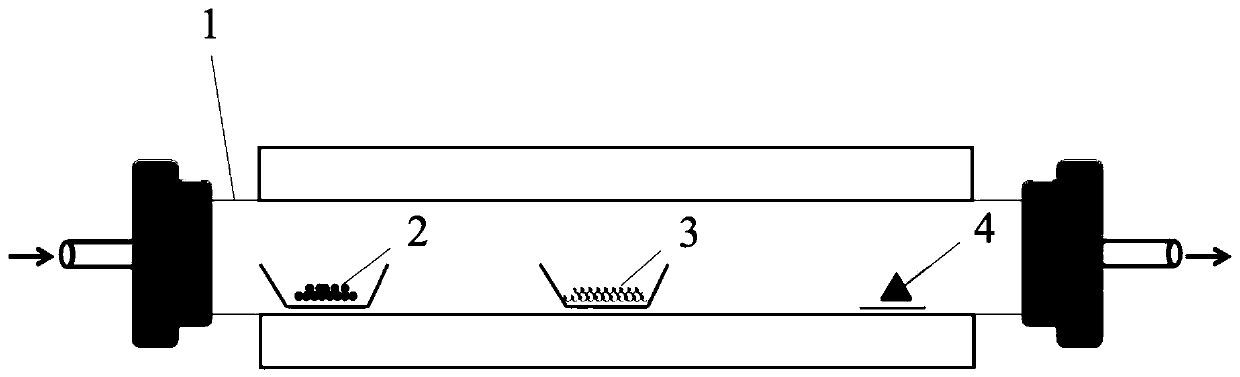
Methods and apparatus for the preparation and use of a substrate having an array of diverse materials in predefined regions thereon. A substrate having an array of diverse materials thereon is generally prepared by delivering components of materials to predefined regions on a substrate, and simultaneously reacting the components to form at least two materials. Materials which can be prepared using the methods and apparatus of the present invention include, for example, covalent network solids, ionic solids and molecular solids. More particularly, materials which can be prepared using the methods and apparatus of the present invention include, for example, inorganic materials, intermetallic materials, metal alloys, ceramic materials, organic materials, organometallic materials, non-biological organic polymers, composite materials (e.g., inorganic composites, organic composites, or combinations thereof), etc. Once prepared, these materials can be screened for useful properties including, for example, electrical, thermal, mechanical, morphological, optical, magnetic, chemical, or other properties. Thus, the present invention provides methods for the parallel synthesis and analysis of novel materials having useful properties.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Combinatorial synthesis and screening of non-biological polymers
Methods and apparatus for the preparation and use of a substrate having an array of diverse materials in predefined regions thereon. A substrate having an array of diverse materials thereon is generally prepared by delivering components of materials to predefined regions on a substrate, and simultaneously reacting the components to form at least two materials. Materials which can be prepared using the methods and apparatus of the present invention include, for example, covalent network solids, ionic solids and molecular solids. More particularly, materials which can be prepared using the methods and apparatus of the present invention include, for example, inorganic materials, intermetallic materials, metal alloys, ceramic materials, organic materials, organometallic materials, non-biological organic polymers, composite materials (e.g., inorganic composites, organic composites, or combinations thereof), etc. Once prepared, these materials can be screened for useful properties including, for example, electrical, thermal, mechanical, morphological, optical, magnetic, chemical, or other properties. Thus, the present invention provides methods for the parallel synthesis and analysis of novel materials having useful properties.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
High molecular solid/solid phase changing material with net type and comb type mixed structure and its preparing method
InactiveCN1616588APhase transition temperature is suitableSolid state goodHeat-exchange elementsPhase change enthalpyPolyethylene glycol
The present invention relates to a kind of high molecular solid / solid phase changing material with mixed net and comb structure, and features that polyglycol with two active end radical and polyglycol with one active end radical are fixed onto the high molecular skeleton material to form 3D mixed net and comb structure. The material of the present invention has relatively great phase change enthalpy up to 120 J / g, proper phase change temperature capable of being altered in 0-65 deg.c, stable solid state before and after phase change without supercooling, separating and other unstable phenomenon, high mechanical strength, high solvent resistance, good machining performance, no toxicity, no leakage, no corrosion, no pollution, long service life and other advantages. The present invention may be used widely in solar energy utilization, afterheat recovering, intelligent air conditioner and other fields.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and devices for high throughput crystallization
InactiveUS7229500B2Avoid large quantitiesHigh densityMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNucleationPhotoresist
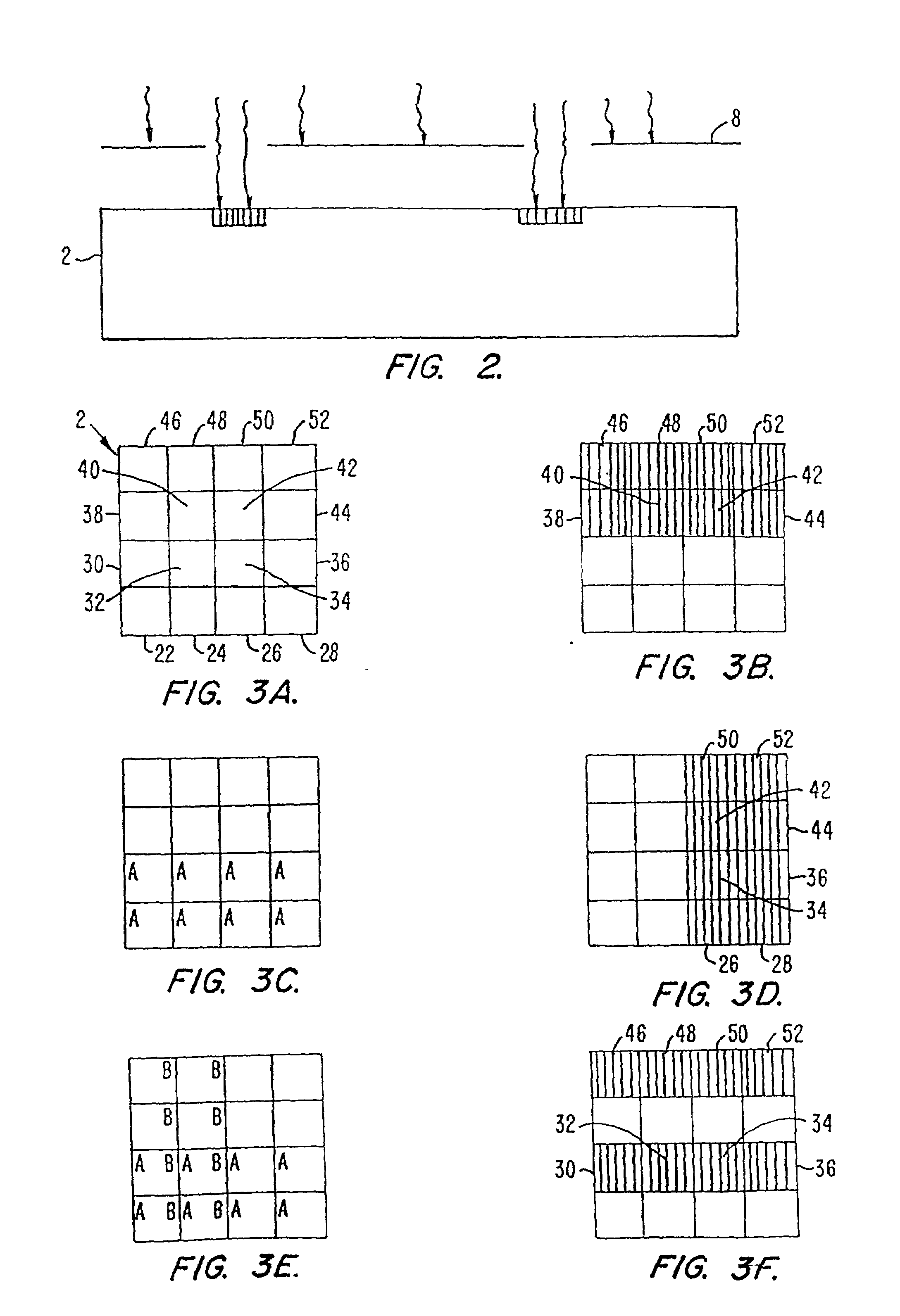
Crystallization Photoresist (PR) apparatus and methods which allow for fast screening and determination of protein crystallization conditions with small protein quantities and rapid crystallization. The apparatus comprise a first region comprising a first nucleation catalyst material and a second region comprising a second nucleation catalyst material, with the first and second regions positioned adjacent to each other and configured to support at least one crystal, and with the first region having a variation in a nucleation property of the first nucleation catalyst material in the first region. The crystal may be supported at an interface of the adjacent regions. The methods comprise providing a first region of a first nucleation catalyst material and a second region of a second nucleation catalyst material adjacent said first region, with the first region having a variation in a nucleation property of the first nucleation catalyst material, exposing the first and second regions to a solution of a selected molecule, and growing at least one crystal of the molecule in association with the first and second regions.
Owner:PARALLEL SYNTHESIS TECH
Combinatorial synthesis of inorganic or composite materials
InactiveUS7767627B1Improve responseEvenly distributedSequential/parallel process reactionsLibrary screeningMolecular solidAlloy
Methods and apparatus for the preparation and use of a substrate having an array of diverse materials in predefined regions thereon. A substrate having an array of diverse materials thereon is generally prepared by delivering components of materials to predefined regions on a substrate, and simultaneously reacting the components to form at least two materials or, alternatively, allowing the components to interact to form at least two different materials. Materials which can be prepared using the methods and apparatus of the present invention include, for example, covalent network solids, ionic solids and molecular solids. More particularly, materials which can be prepared using the methods and apparatus of the present invention include, for example, inorganic materials, intermetallic materials, metal alloys, ceramic materials, organic materials, organometallic materials, nonbiological organic polymers, composite materials (e.g., inorganic composites, organic composites, or combinations thereof), etc. Once prepared, these materials can be screened for useful properties including, for example, electrical, thermal, mechanical, morphological, optical, magnetic, chemical, or other properties. Thus, the present invention provides methods for the parallel synthesis and analysis of novel materials having useful properties.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Synthesis method of graphite phase carbonitride homotype heterojunction photocatalysis material with multilayer structure and application
InactiveCN106732712APromote absorptionThe synthesis method is simplePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHeterojunctionSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a graphite phase carbonitride homotype heterojunction photocatalysis material with a multilayer structure. The method comprises the following steps of preparing a melamine / cyanuric acid suspension and urea water solution; performing preparation by using the melamine / cyanuric acid suspension to obtain melamine / cyanuric acid suspension macromolecular crystals completing the assembly reaction; adding the melamine / cyanuric acid suspension macromolecular crystals into the urea water solution; performing calcination on the urea-(melamine / cyanuric acid) composite precursor obtained through preparation to obtain the graphite phase carbon nitride (g-C3N4) homotype heterojunction photocatalysis material with multilayer structures with g-C3N4 nanometer particles deposited on the g-C3N4 micrometer tubes. The synthesis method provided by the invention has the advantages that the conditions are mild; the preparation process is simple and convenient; the controllability is high; the obtained photocatalysis material can be applied to methyl orange degradation in visible light; the effect is obvious.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Carbon negative electrode material of lithium ion cell, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN1412873AHigh purityHas low temperature processabilityElectrode manufacturing processesLithiumMolecular solid
The present invention discloses a carbon negative electrode material of lithium ion cell, and is characterized by that it uses natural graphite as raw material, a layer of monomer of polymer is adsorbed on the surface of natural graphite by means of dipping process, then radiation method is adopted to make polymerization or cross-linking reaction, so that the surface of the natural graphite is covered with a layer of high-molecular solid electrolyte. Said invention also discloses its preparation method and application as working electrode of lithium ion cell.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
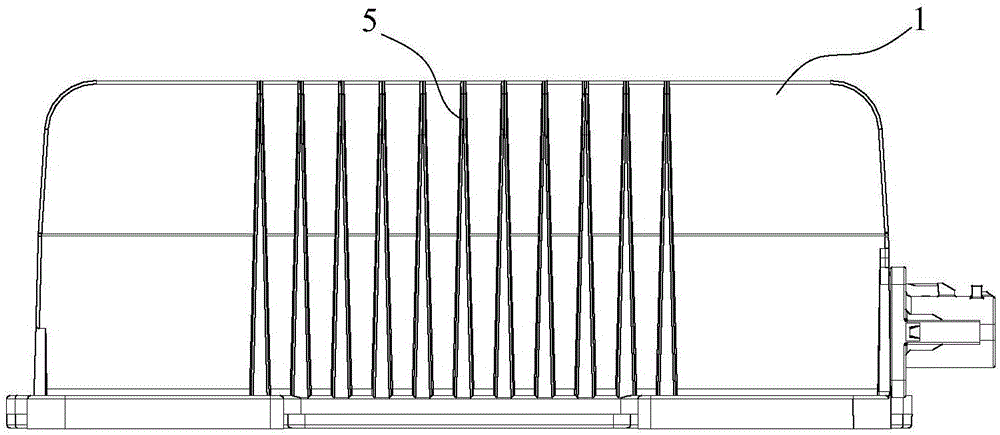
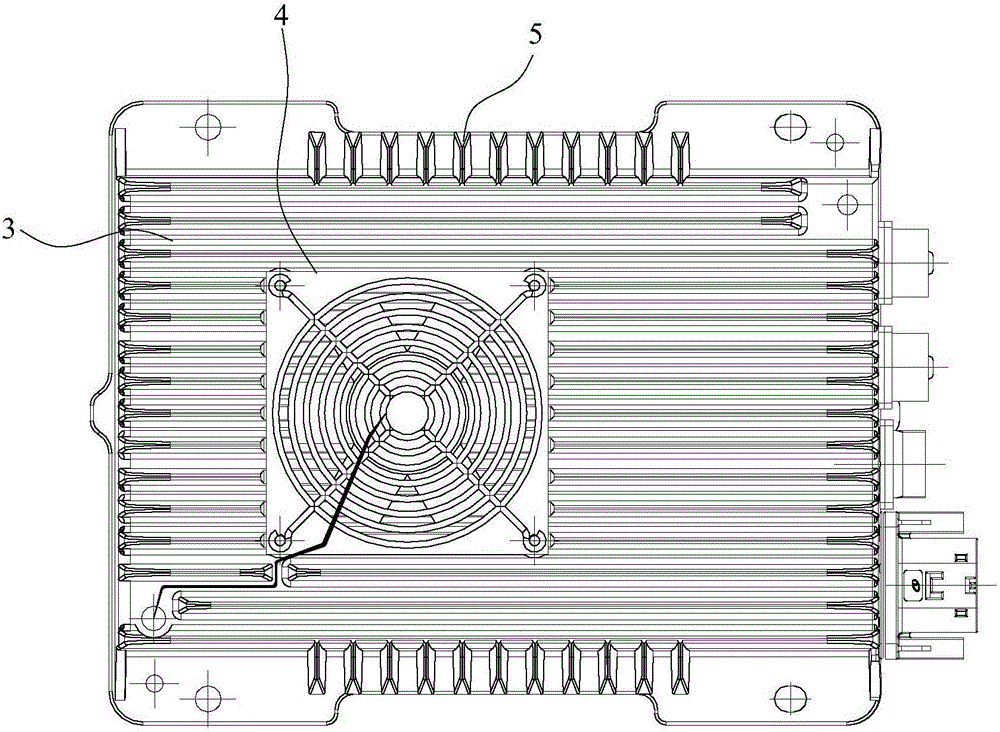
DC/DC converter
InactiveCN106059287AAvoid the hidden danger of inter-turn open circuitImprove high temperature resistanceDc-dc conversionCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsCapacitanceMolecular solid
The invention discloses a DC / DC converter, and the converter comprises a plane transformer, a high-molecular solid capacitor, and a housing. The interior of the inner cavity of the housing is provided with an accommodation part which is used for accommodating the plane transformer and the high-molecular solid capacitor. The top of the housing is provided with first cooling fins which are arranged in a left / right direction, and a cooling fan is disposed above the first cooling fins. The converter employs the plane mirror to avoid the hidden troubles of turn-to-turn short circuit, employs the high-molecular solid capacitor to improve the performance of high temperature resistance, and improves the heat dissipation performance and stability through the cooling fan and the first cooling fins.
Owner:深圳市康灿新能源科技有限公司
Preparation method for gradient change silicon-nitrogen-carbon ceramic fibers
InactiveCN106835359ASimple processThe operation process is simple and convenientFibre chemical featuresCross-linkYarn
The invention discloses a preparation method for gradient change silicon-nitrogen-carbon ceramic fibers, and relates to an inorganic non-metal material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing melt spinning on high-molecular solid-state polycarbosilane serving as a precursor, and then performing non-melting treatment to obtain cross-linking yarns; performing an ammonolysis reaction on the obtained cross-linking yarns under an NH3 atmosphere, and continually pyrolyzing under an N2 atmosphere after reaching a target temperature to obtain the gradient change silicon-nitrogen-carbon ceramic fibers. The high-molecular solid-state polycarbosilane is taken as the precursor which is subjected to the procedures of melt spinning, non-melting treatment, ammoniation, high-temperature pyrolysis and the like to obtain silicon nitride / silicon carbide fibers, and the gradient change of the nitrogen content is regulated and controlled by controlling the ammonolysis temperature. The process is simple, and the operation process is simple and convenient; the controllability of the fiber surface gradient thickness is realized by controlling the ammoniation temperature; the fiber structure is novel, and the fibers have potential application on the aspect of wave absorbing.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
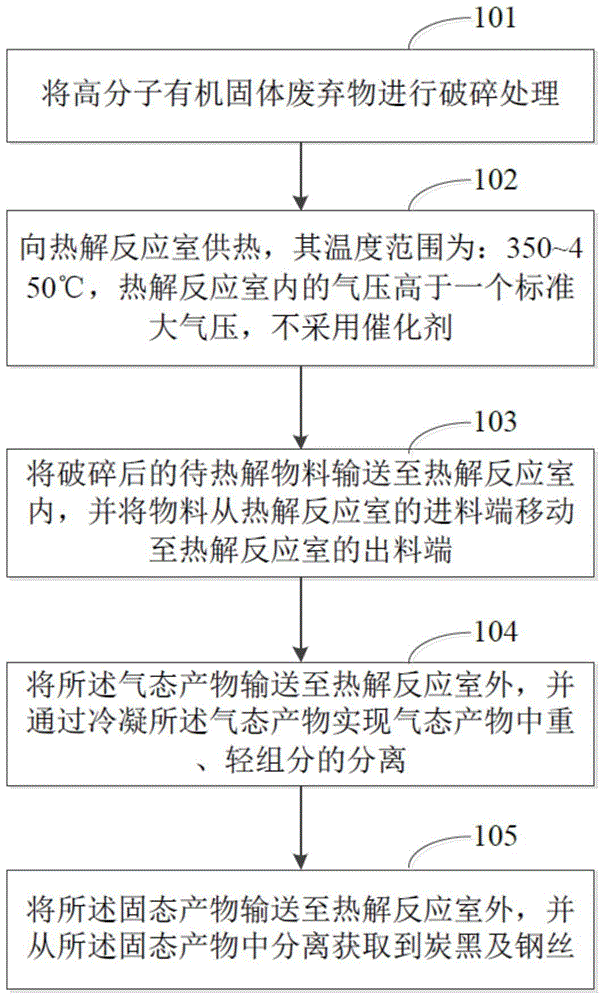
Thermal pyrolysis treatment method for organic wastes
InactiveCN105670675ARealize secondary useImprove protectionPigmenting treatmentSolid waste disposalMolecular solidGas phase
The invention relates to a thermal pyrolysis treatment method for organic wastes, which includes the following steps: (1) crushing high-molecular solid organic wastes; (2) melting the crushed high-molecular solid organic wastes at certain temperature to obtain a liquid to-be-pyrolyzed material; and (3) feeding the liquid to-be-pyrolyzed material to a pyrolytic reaction chamber and moving the material from a feeding end of the pyrolytic reaction chamber to a discharge end of the pyrolytic reaction chamber, so that the material is continuously subjected to a pyrolysis reaction during the moving process for converting the liquid to-be-pyrolyzed material into a gas-phase product and a solid-phase product through the pyrolysis reaction, wherein the pyrolysis reaction is 370-410 DEG C in temperature range and is carried out without a catalyst. The pyrolysis reaction effectively improves device safety performance and service life and reduces production cost on the basis of ensuring pyrolysis reaction efficiency and process yield.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG HUACHENG LOCOMOTIVE PRECISION PIPE MFG
High molecular solid-to-solid phase transition energy storage material and preparation method thereof
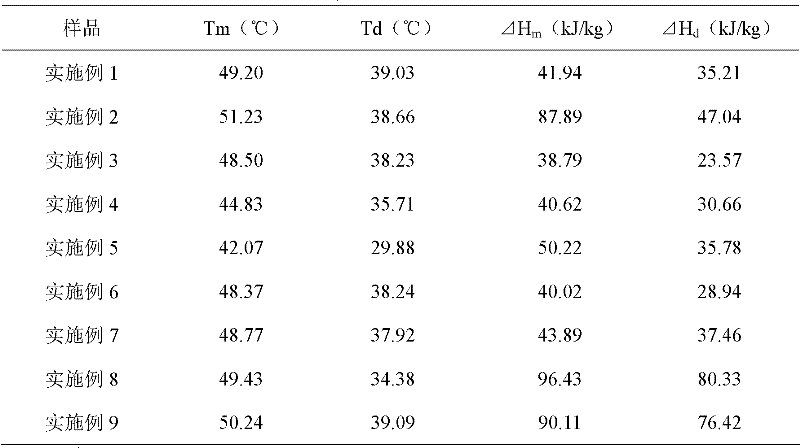
The invention discloses a high molecular solid-to-solid phase transition energy storage material and a preparation method thereof. Fatty acid or fatty alcohol with phase transition performance is introduced into high-reaction active (methyl) crylic acid; an obtained polymerizable ester serves as a phase transition part; and a (methyl) acrylic ester polymer, a polymer of (methyl) acrylic ester-(methyl) acrylic acid and a quaternary ammonium salt of a (methyl) acrylate-(methyl) acrylic acid copolymer are prepared with a free radical copolymerization method. The phase transition temperature of the obtained high molecular solid-to-solid phase transition energy storage material is 29-52 DEG C, and the phase transition enthalpy can be up to 96 kJ / kg in maximum; and the material can keep in a solid state before and after phase transition, is free from small molecule leakage, is not required to be accommodated in a container, and is nontoxic and harmless.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Fluorescent color changing eutectic material under ultrahigh pressure conditions and preparation method thereof
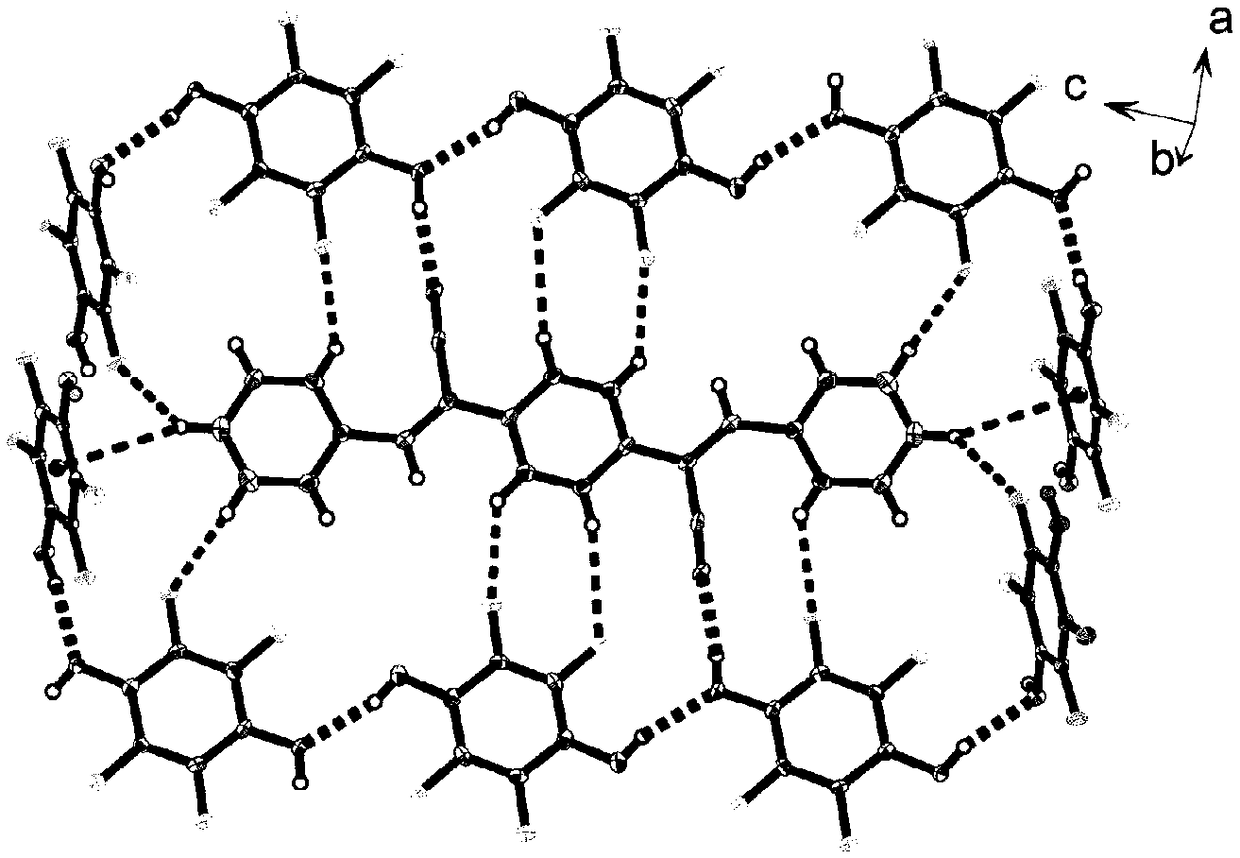
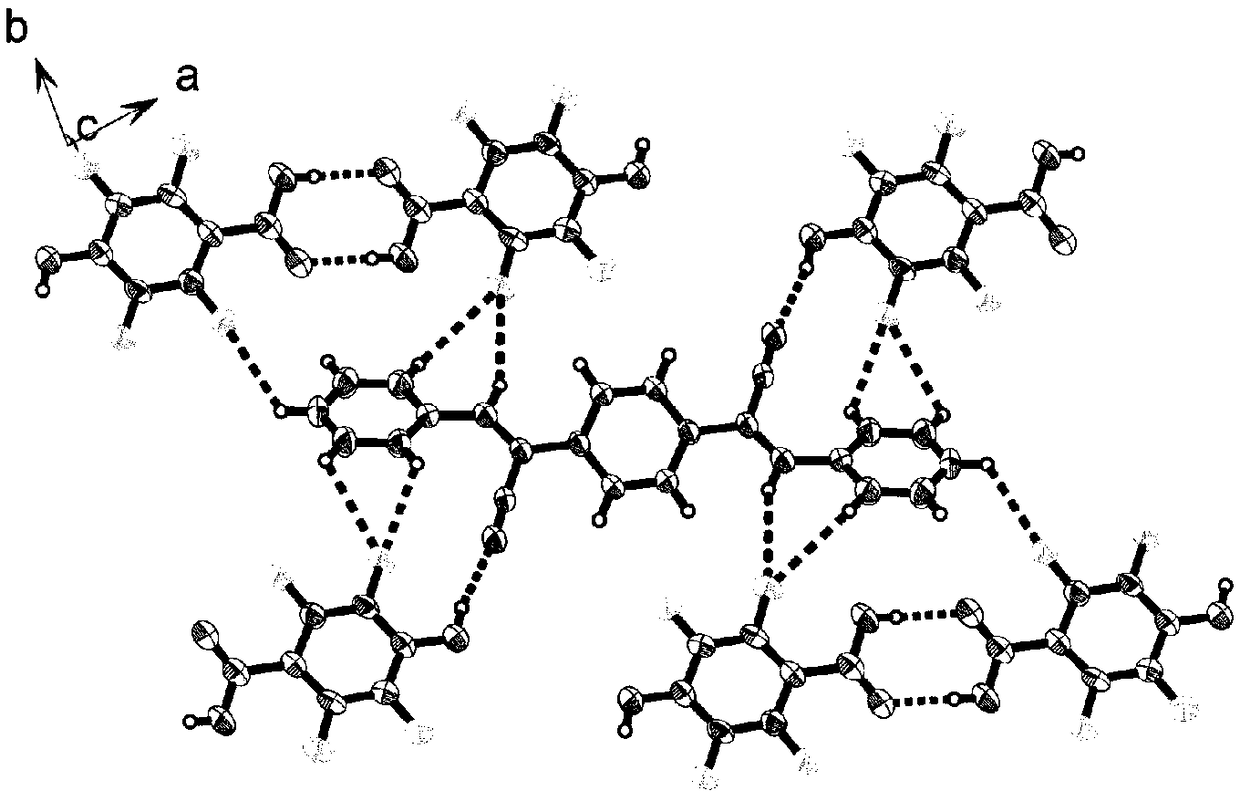
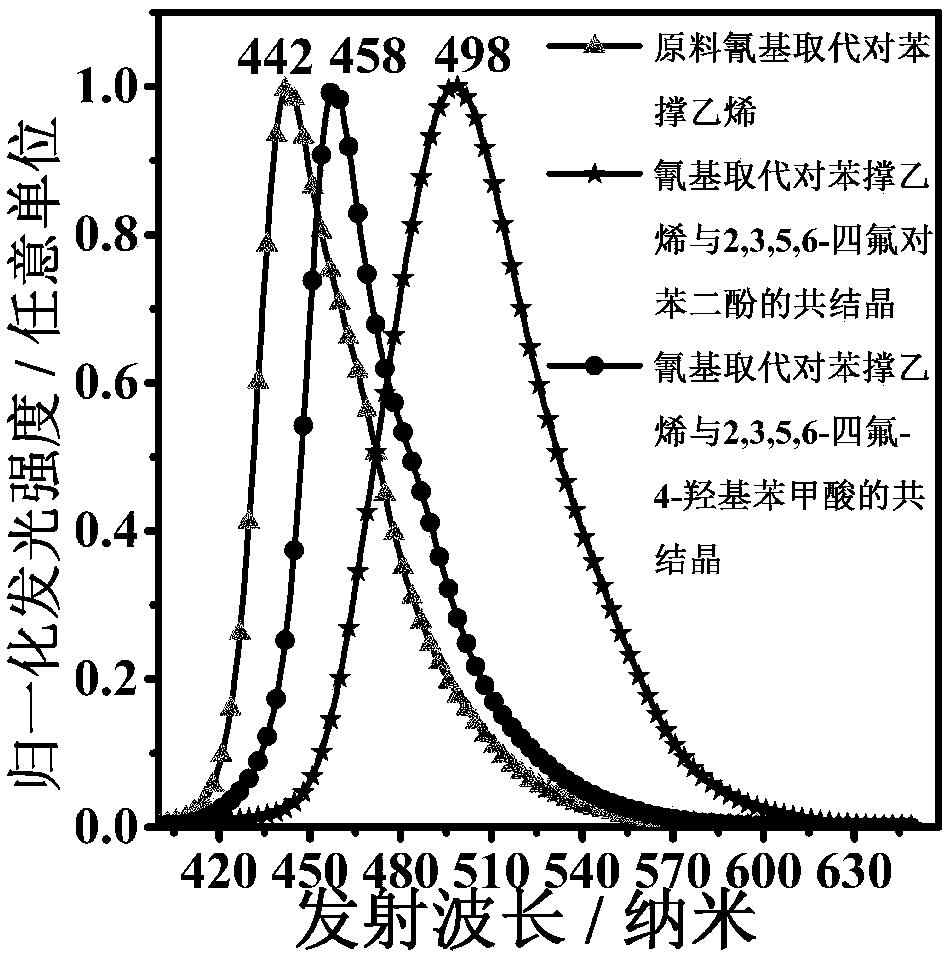
ActiveCN109020805AChange molecular configurationChange structureOrganic chemistry methodsTenebresent compositionsUltra high pressureSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a fluorescent color changing eutectic material under ultra-high pressure conditions and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of molecular solid-state light-emitting materials. A plurality of multi-fluoro-substituted organic small molecules are selected as co-assembly units, and a novel multi-component molecular co-crystal compound is prepared by using a solvent-assisted grinding method, a solvent evaporation method, an ultrasonic synthesis method and the like. Cyano substituted p-phenylene vinyl type molecules and the co-assembled small molecules mutually recognize each other through multiple hydrogen bonds, Pi- Pi force and other non-covalent forces to form a structure-ordered supramolecular structure, changing self-stacking molecular configuration and spatial arrangement of original cyano-substituted phenylene vinyl type molecules so as to achieve a certain modulation effect on photophysical properties. The novel fluorescent color changing eutectic material prepared by the method can produce different fluorescent discoloration behaviors under the ultra-high pressure conditions, is the first fluorescent discoloration eutectic system underthe ultra-high pressure conditions, and has application prospects in the fields of new optical sensors and pressure sensitive materials and the like.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
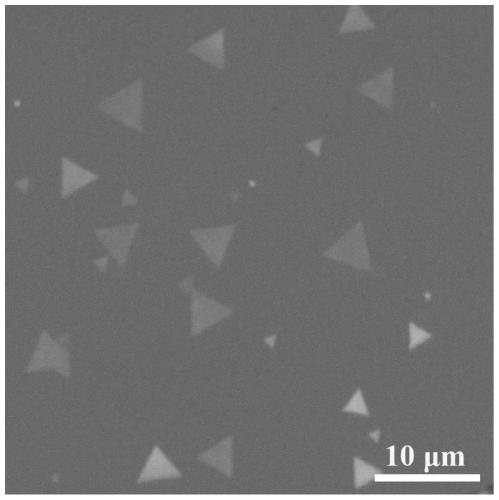
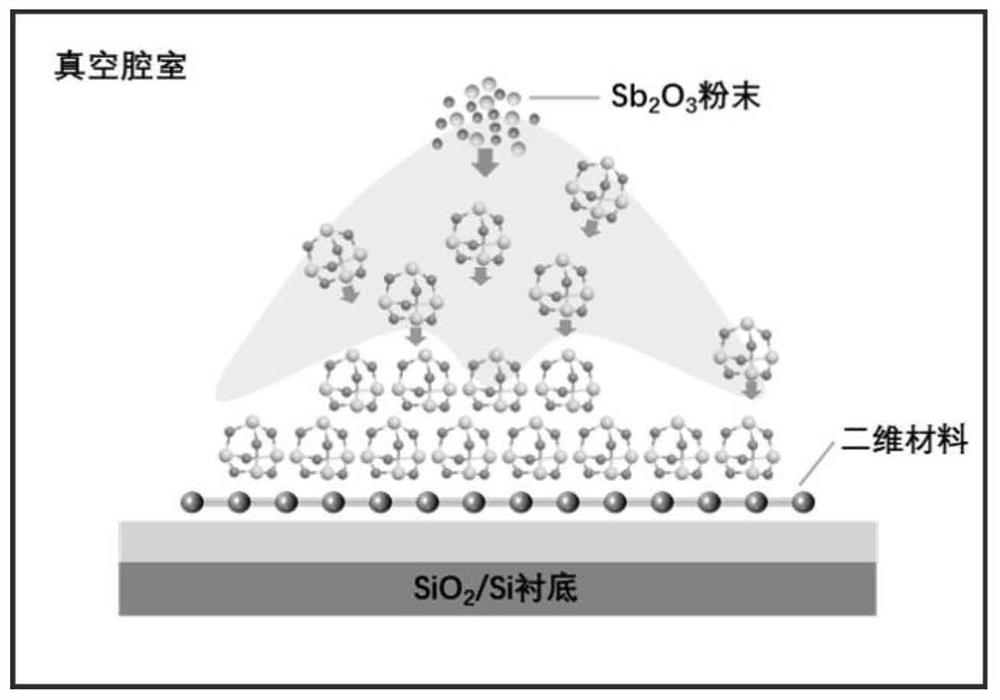
Two-dimensional inorganic molecular crystal materials and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110284191AYi ShenghuaEasy to condensePolycrystalline material growthFrom condensed vaporsCrystallographyMolecular composition
The invention relates to two-dimensional inorganic molecular crystal materials and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of preparation of two-dimensional materials. The two-dimensional inorganic molecular crystal materials are two-dimensional flaky materials formed by tiling inorganic molecules; the inorganic molecules in the two-dimensional flaky materials are connected by van der Waals force. The preparation method is characterized in that a vapour deposition method is adopted; molecular crystal powder is taken as a raw material; the molecular crystal powder is evaporated into a gas-state precursor; the gas-state precursor is transported with carrier gas and is deposited on a substrate under the effect of a passivating agent to obtain two-dimensional inorganic molecular crystal flakes. Two-dimensional inorganic molecular crystals obtained by the method are of two-dimensional flaky structures formed by the inorganic molecules, and the molecules are connected by the van der Waals force. The preparation method is simple, low in cost and strong in universality. By utilizing the method involved in the invention, the two-dimensional inorganic molecular crystal materials with uniform thickness and consistent shapes are prepared, and have wide prospects in the application of phase-change devices.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
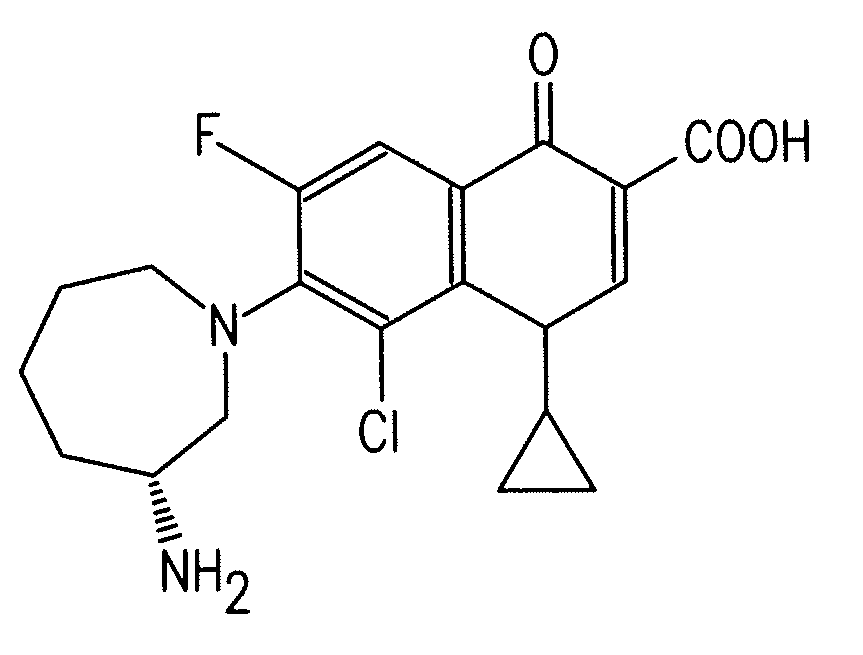
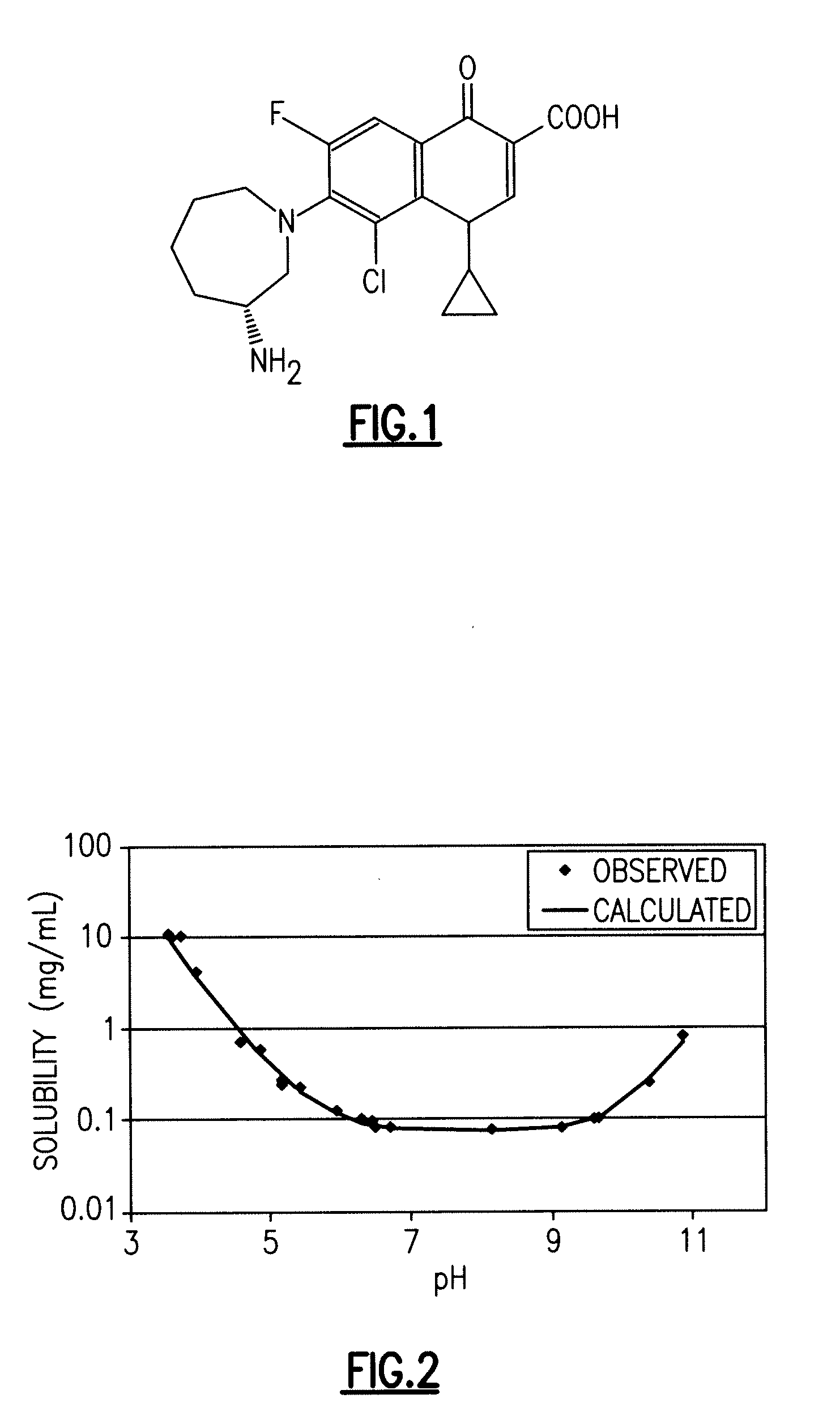
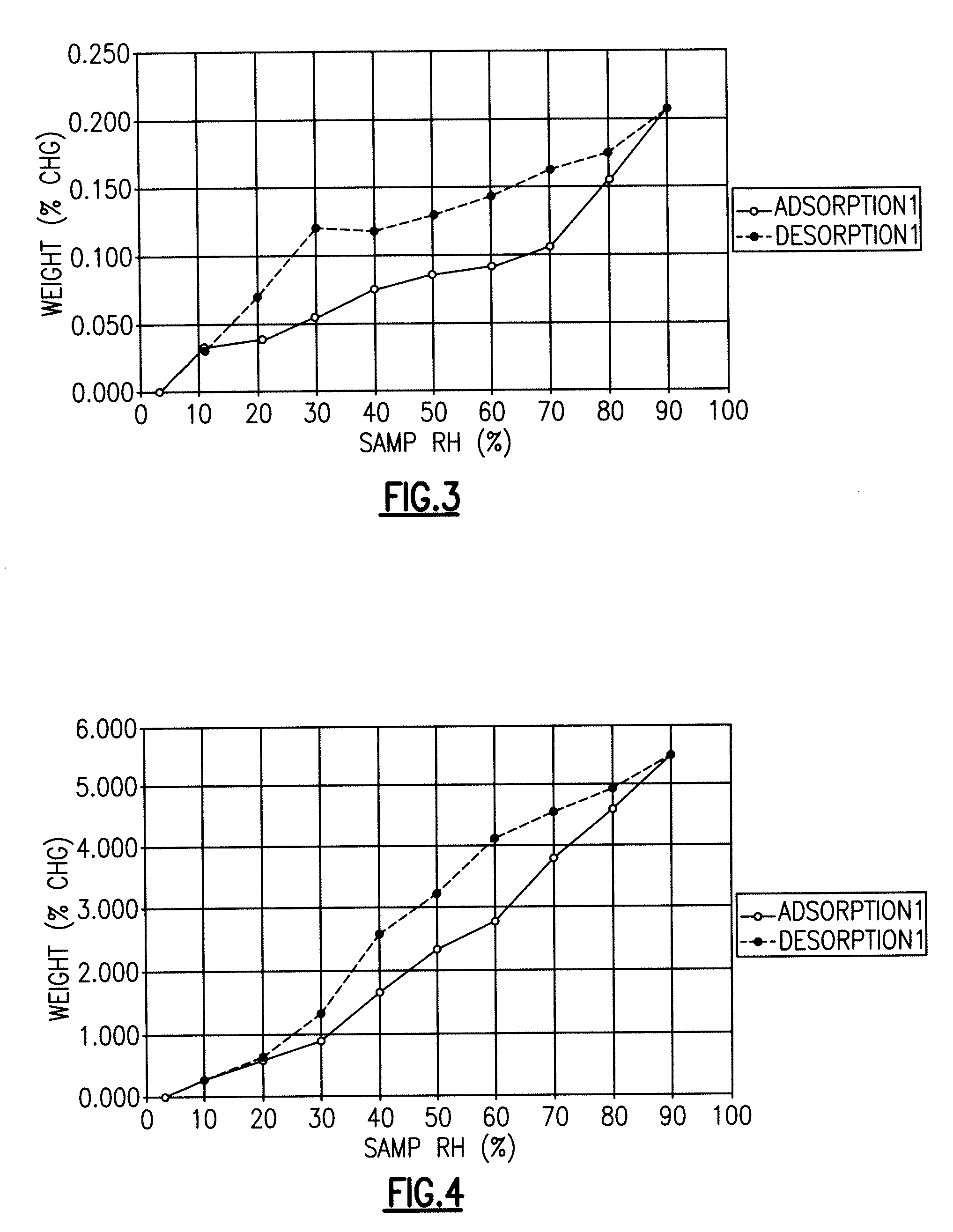
Fluoroquinolone Carboxylic Acid Molecular Crystals
A molecular crystal form of (R)-(+)-7-(3-amino-2,3,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-azepin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid is characterized by at least one of: (a) an X-ray powder diffraction (“XRPD”) spectrum that comprises peaks at 2θ angles of 10.6, 15, 19.7, 21.1, and 22°±0.2°; (b) a DSC melting peak at 288° C.; (c) a 13C NMR spectrum having peaks at 23.3, 27.7, 41.1, 54.5, 116.6, and 153.5 ppm; and (d) pKa values of 5.65 and 9.91.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Preparation method of functionalized two-dimensional nano-material and functionalized nano thin film
InactiveCN108455541AIncrease productionQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsMolecular solidColloid
The invention provides a preparation method of a functionalized two-dimensional nano-material and a functionalized nano thin film and relates to the technical field of preparation of nano-materials. According to the preparation method provided by the invention, a Van der Waals laminar solid material and an organic small molecular solid material with a functional group are mixed and the mass of theorganic small molecular solid material is greater than or equal to the mass of the Van der Waals laminar material; a mixture is subjected to ball milling operation under normal temperature and pressure conditions to prepare a functionalized two-dimensional nano-sheet; then the mixture subjected to the ball milling is washed through de-ionized water and an obtained colloid solution is subjected tovacuum filtering and drying to prepare the functionalized nano thin film. The preparation method provided by the invention is realized under the normal temperature and pressure conditions and has thecharacteristics of high yield, high quality, good repeatability, low cost, no catalysis, no template, environment friendliness and the like.
Owner:刘丹
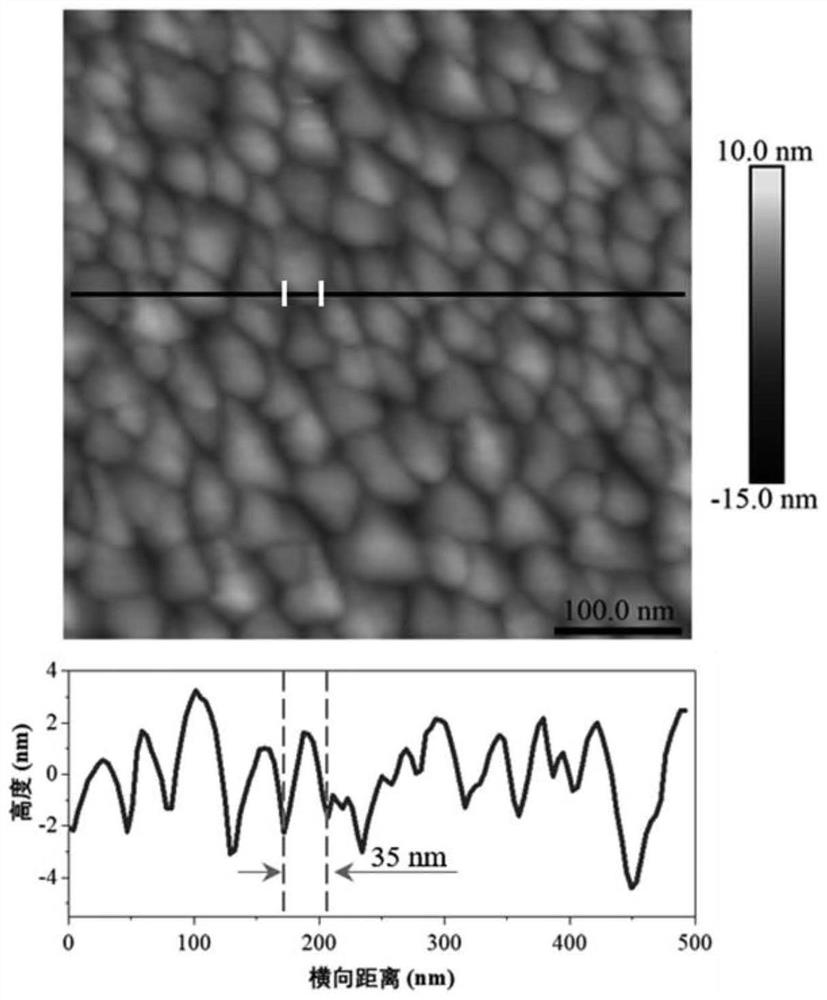
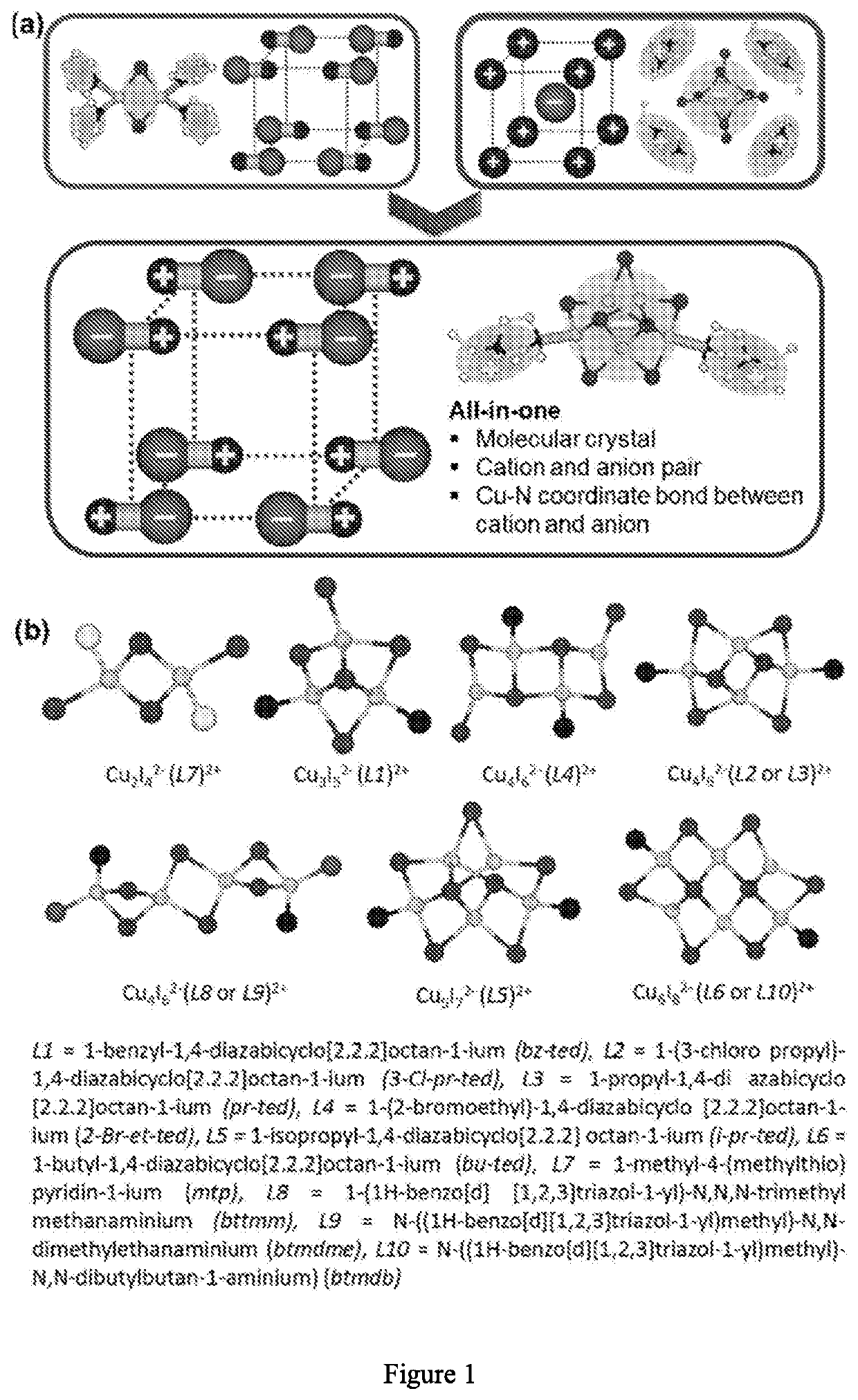
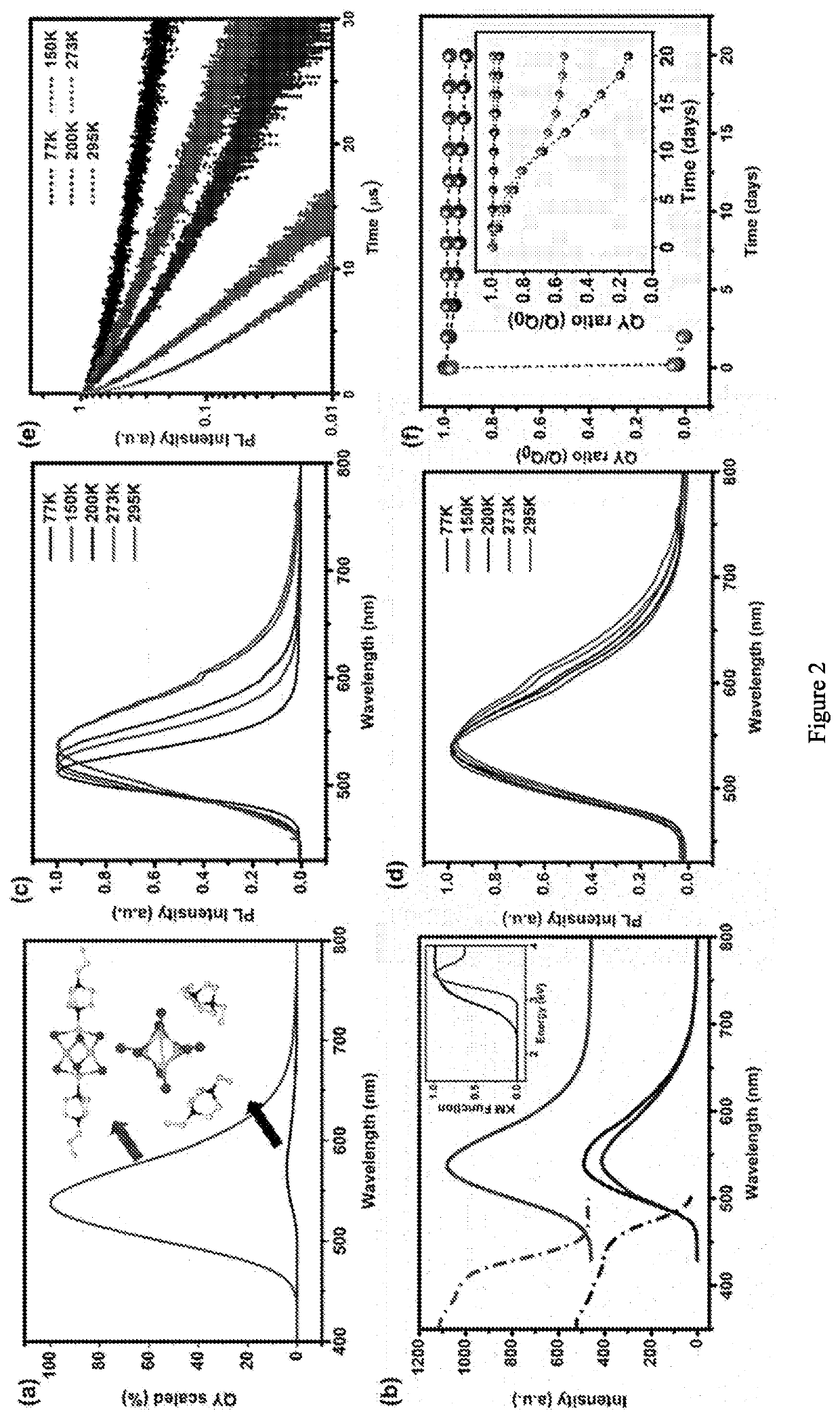
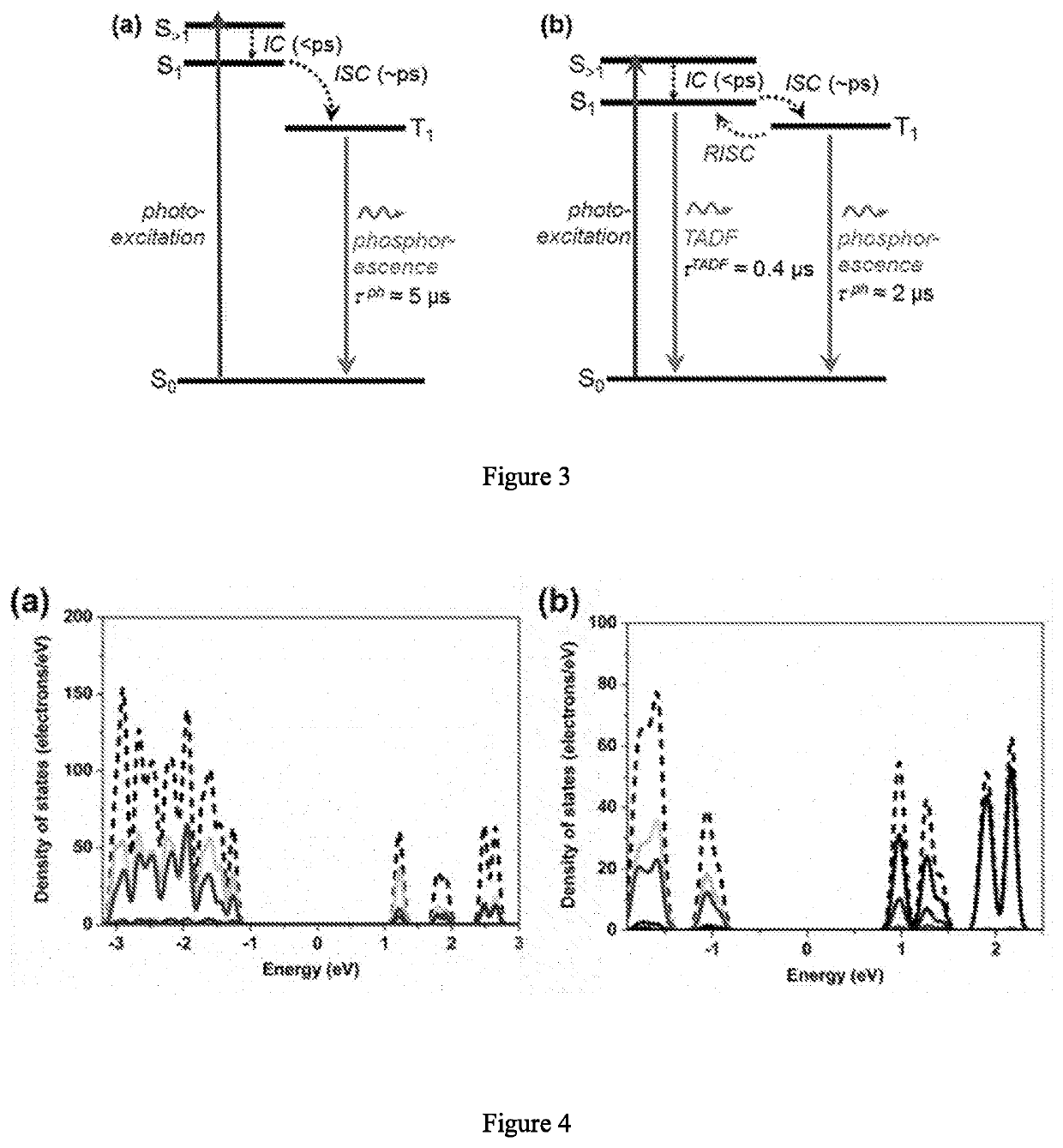
Luminescent and dispersible hybrid materials combining ionic and coordinate bonds in molecular crystals
ActiveCN110785424AGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMolecular solidMolecular cluster
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Organic molecular crystal construction method and system
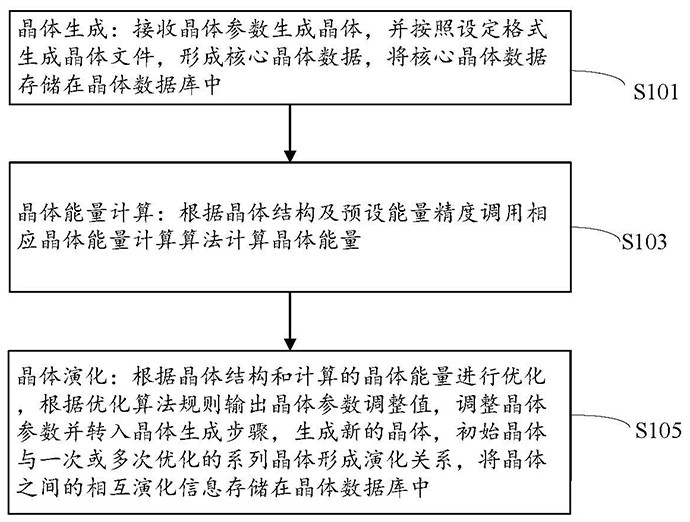
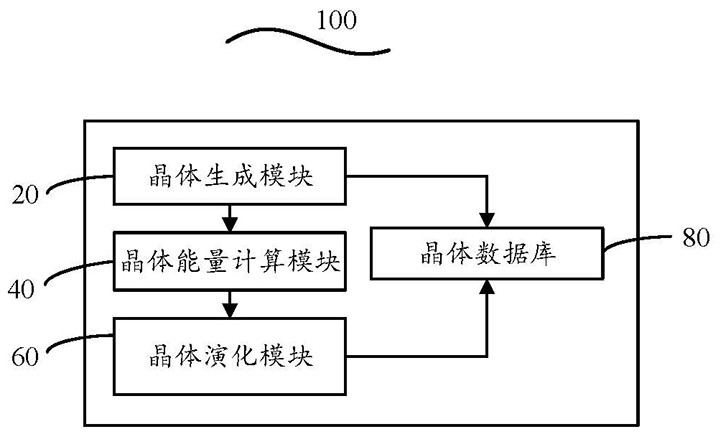
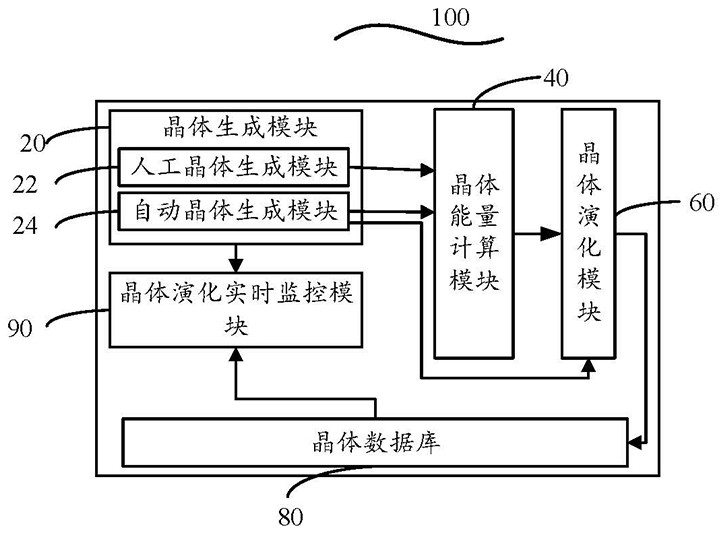
The invention discloses an organic molecular crystal construction method and system. The method comprises the steps of receiving crystal parameters to generate a crystal, generating a crystal file according to a set format, forming core crystal data, and storing the core crystal data in a crystal database; calling a corresponding crystal energy calculation algorithm to calculate crystal energy according to the crystal structure and preset energy precision; optimizing according to the crystal structure and the calculated crystal energy, outputting a crystal parameter adjustment value accordingto an optimization algorithm rule, adjusting the crystal parameter, turning to a crystal generation step, generating a new crystal, and forming an evolution relationship between the initial crystal and one or more optimized series crystals, and storing the mutual evolution information between the crystals in the crystal database; According to the organic molecular crystal construction method and system, optimization is conducted according to the crystal structure and crystal energy through crystal evolution, crystal parameters are adjusted according to an optimization algorithm, iteration is conducted in the crystal generation step, and the crystal structure with better properties is obtained through iterative optimization.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINGTAI TECH CO LTD
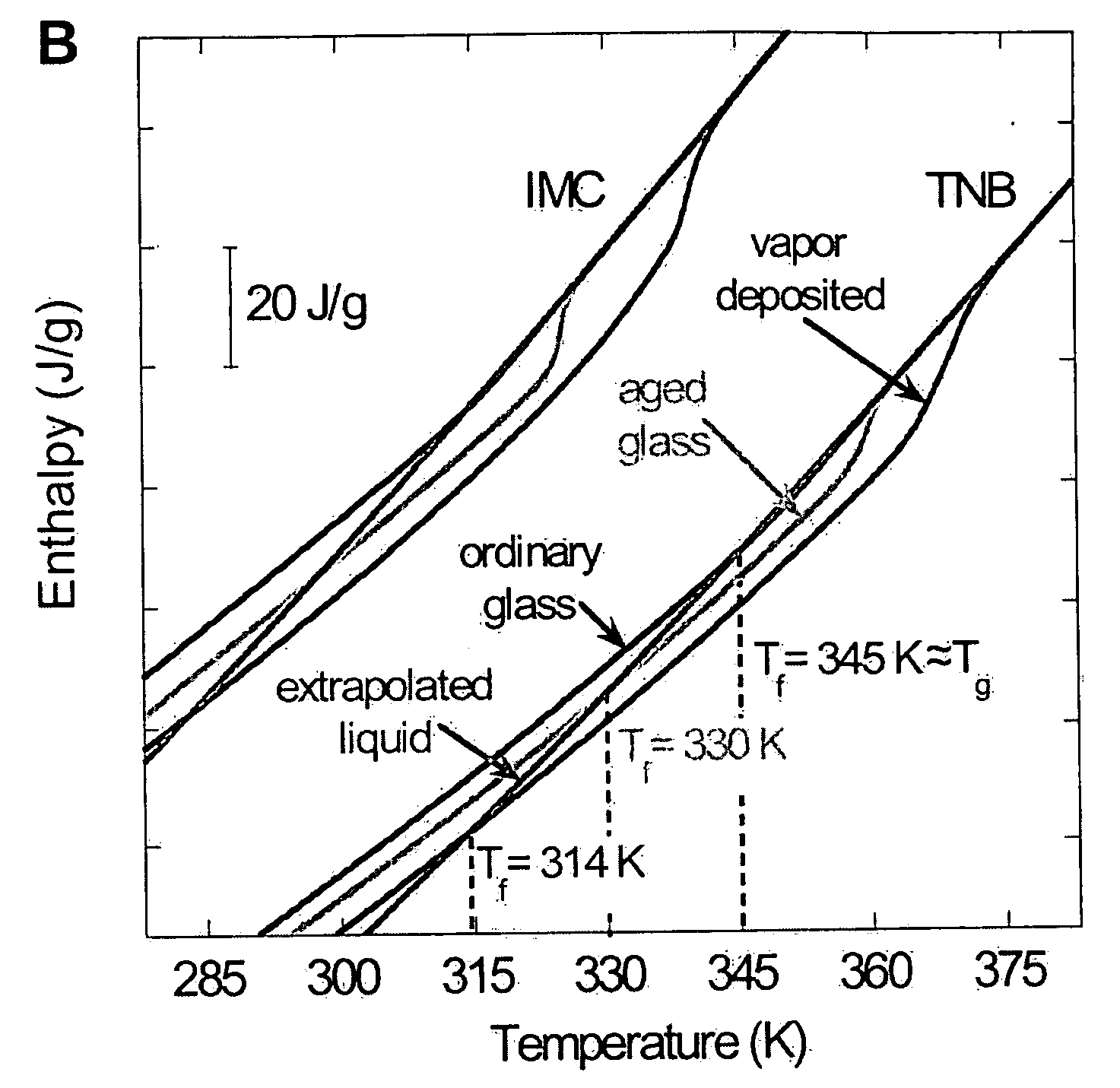
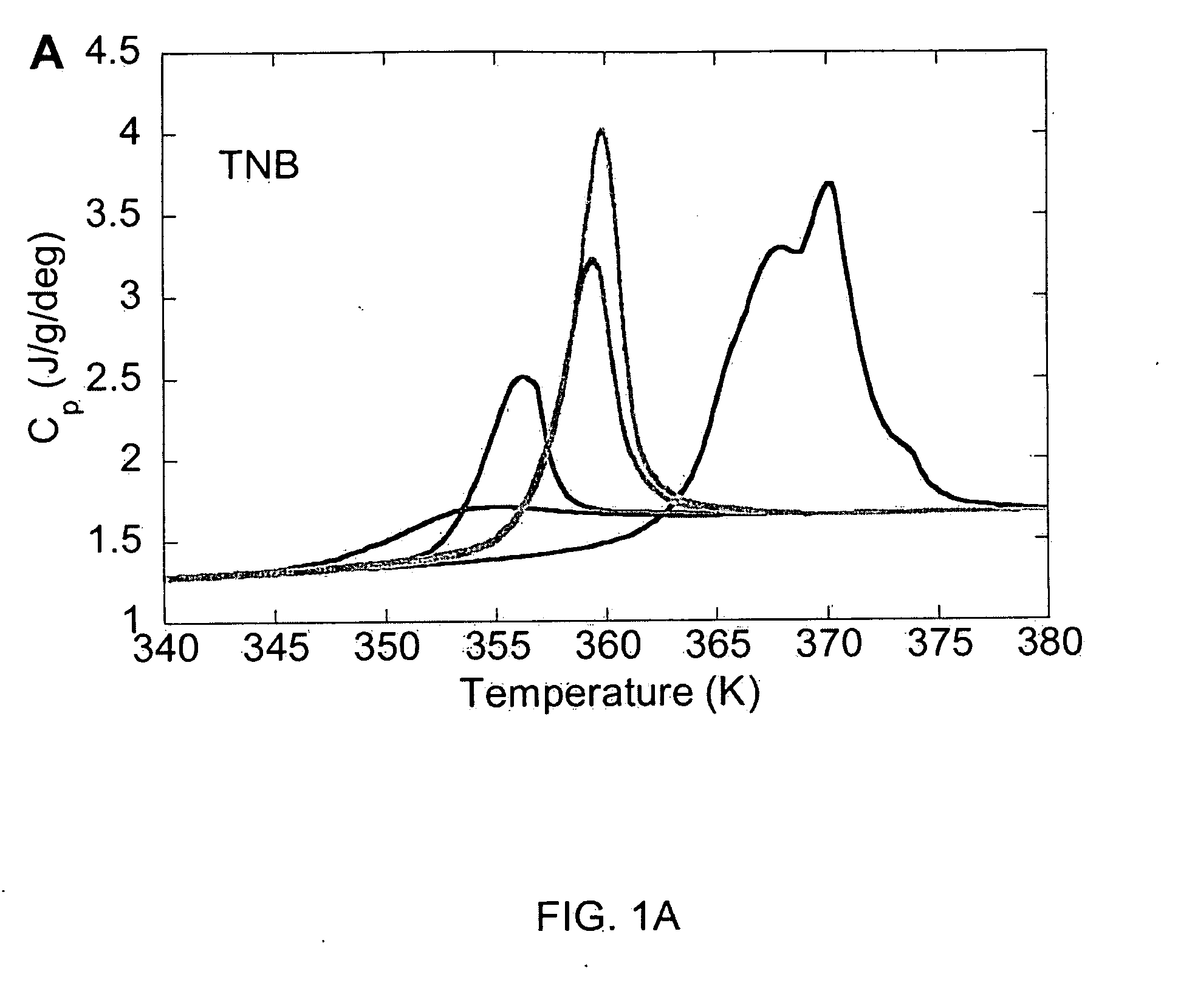
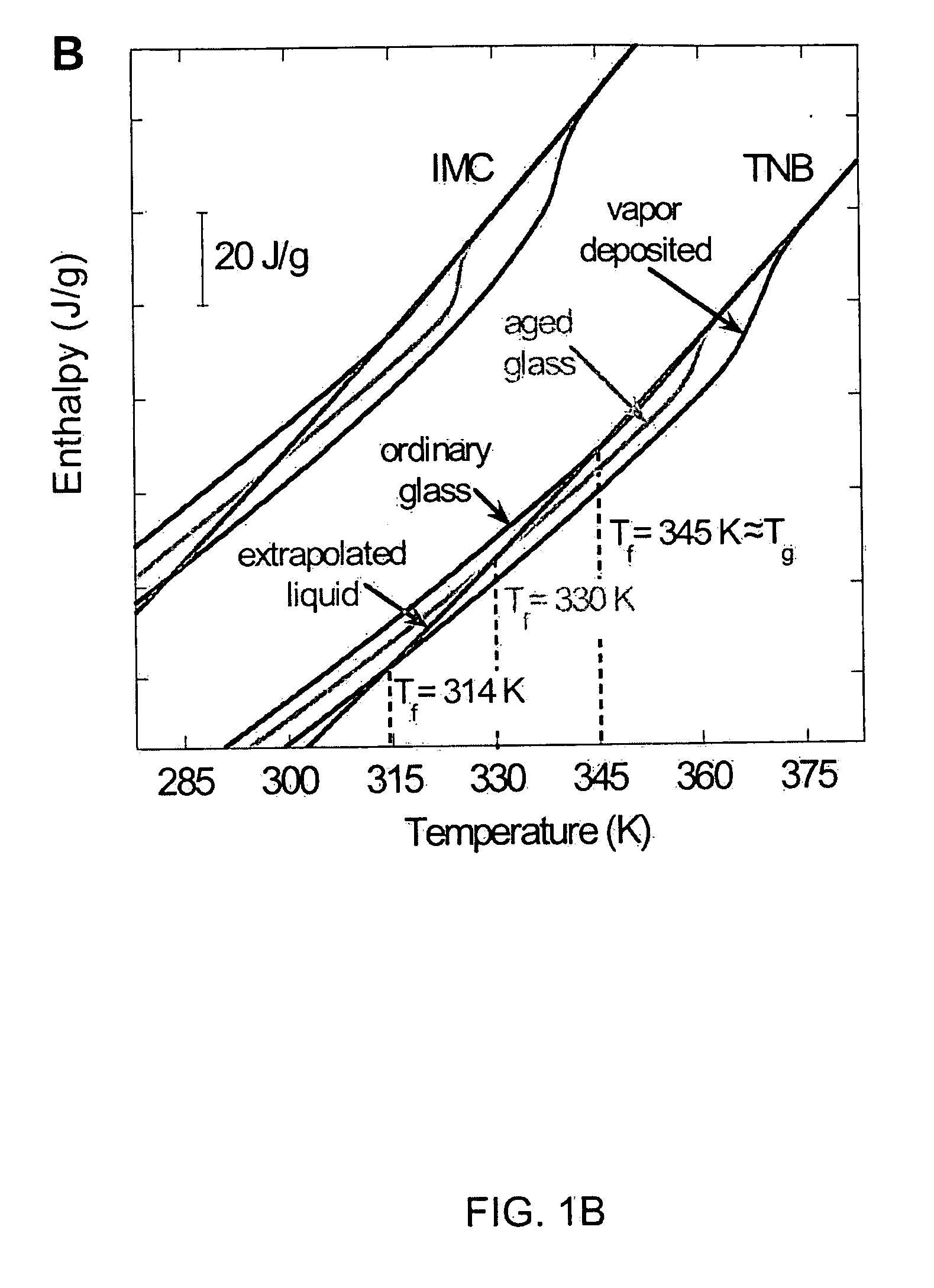
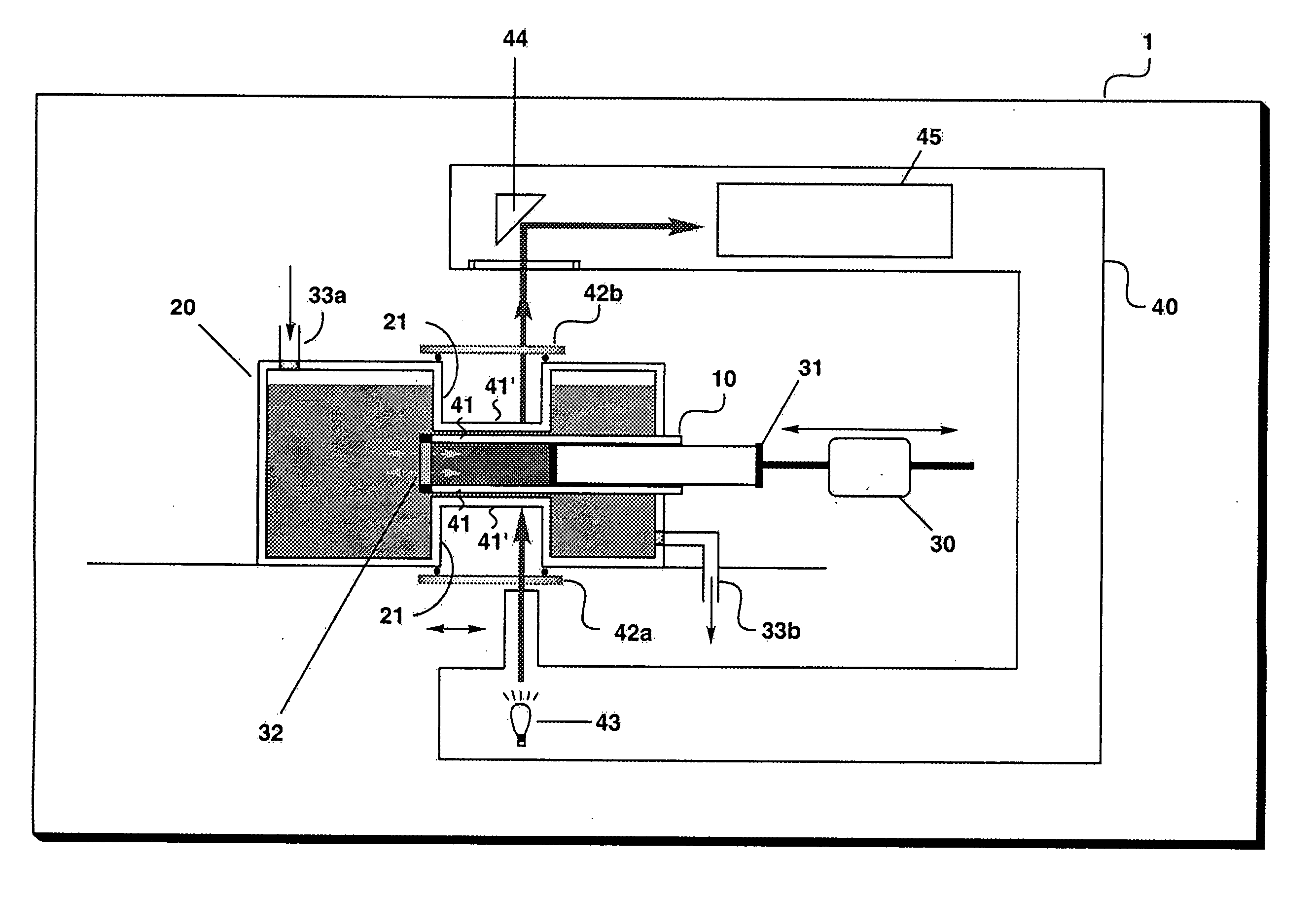
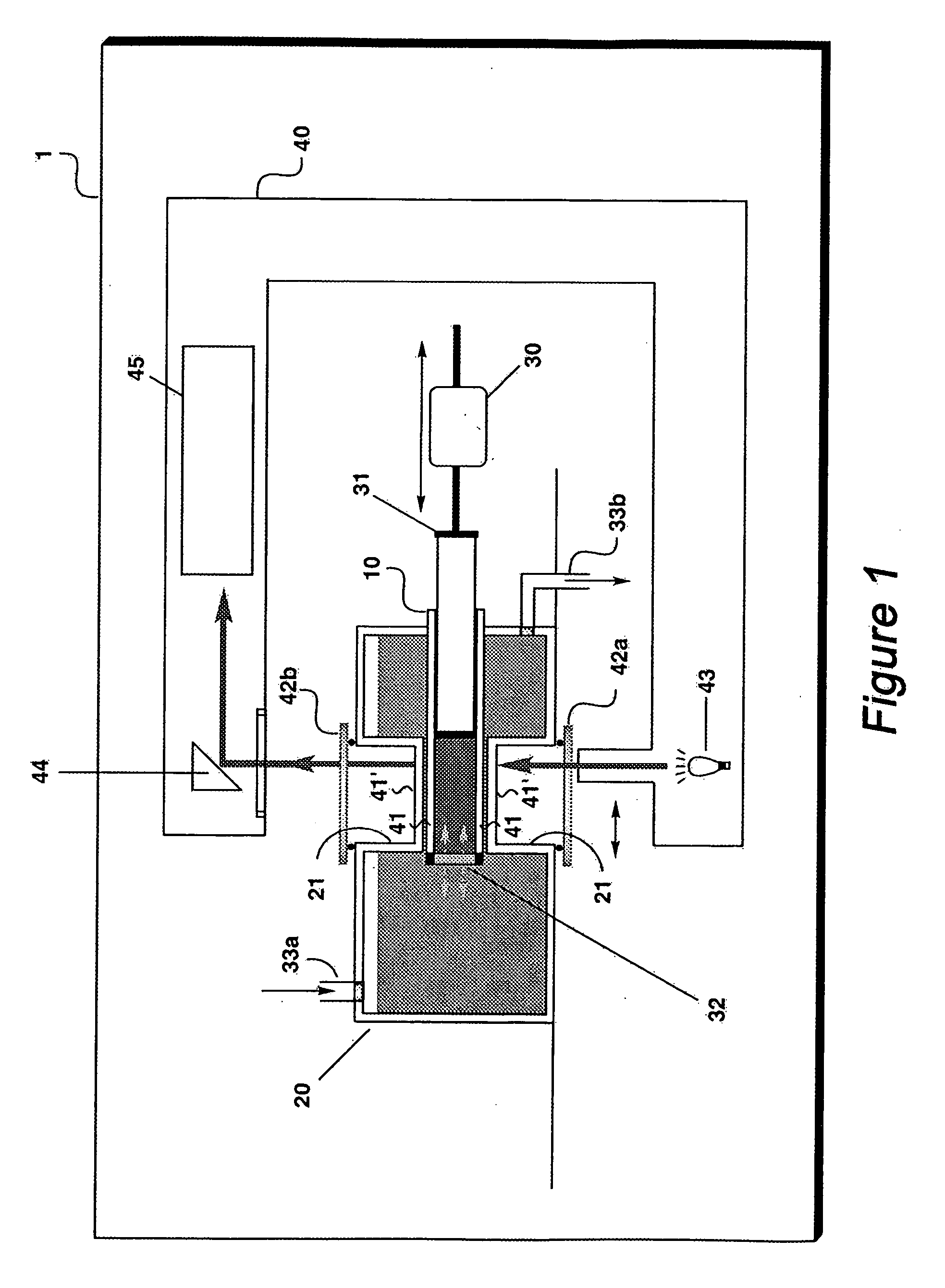
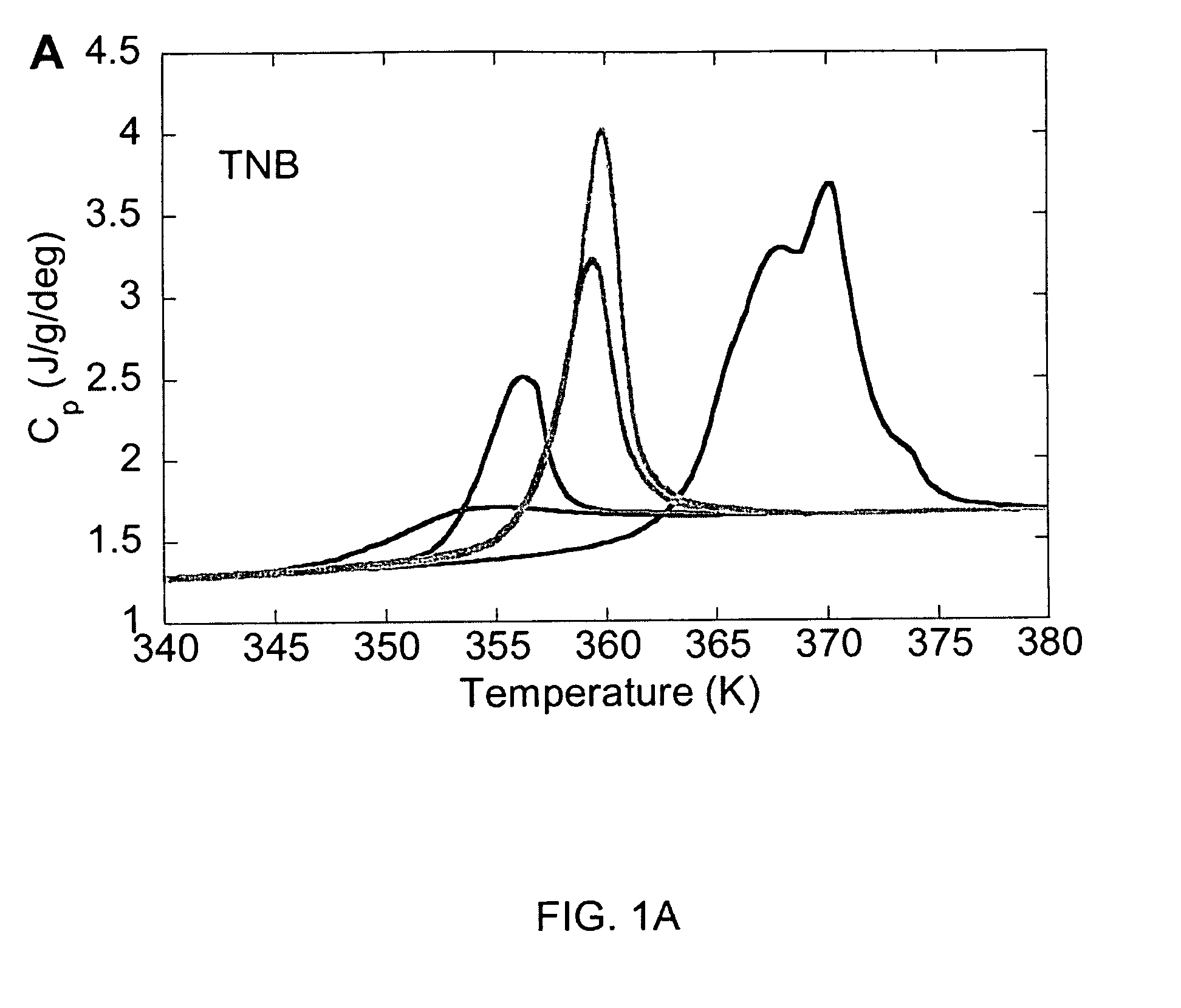
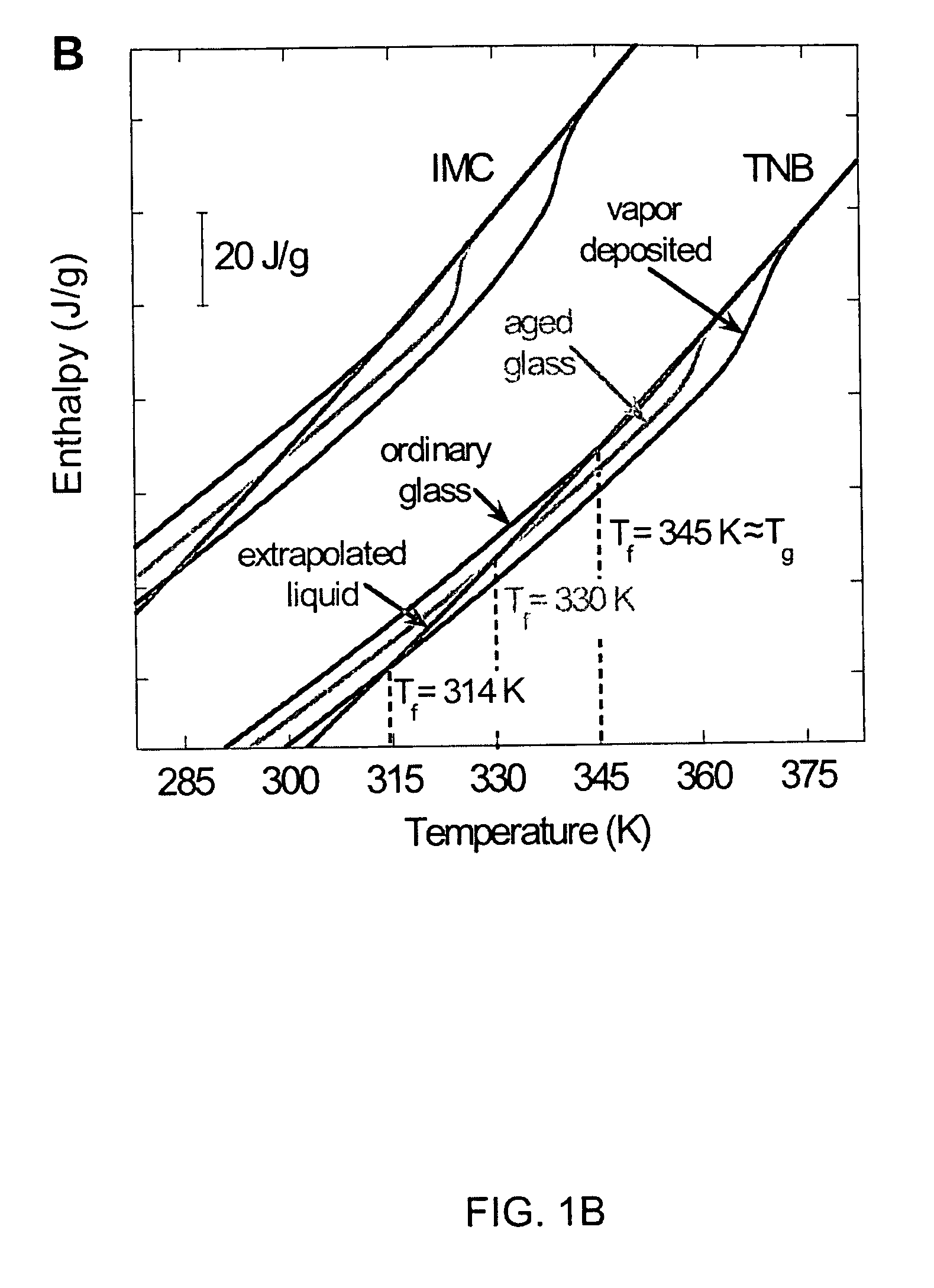
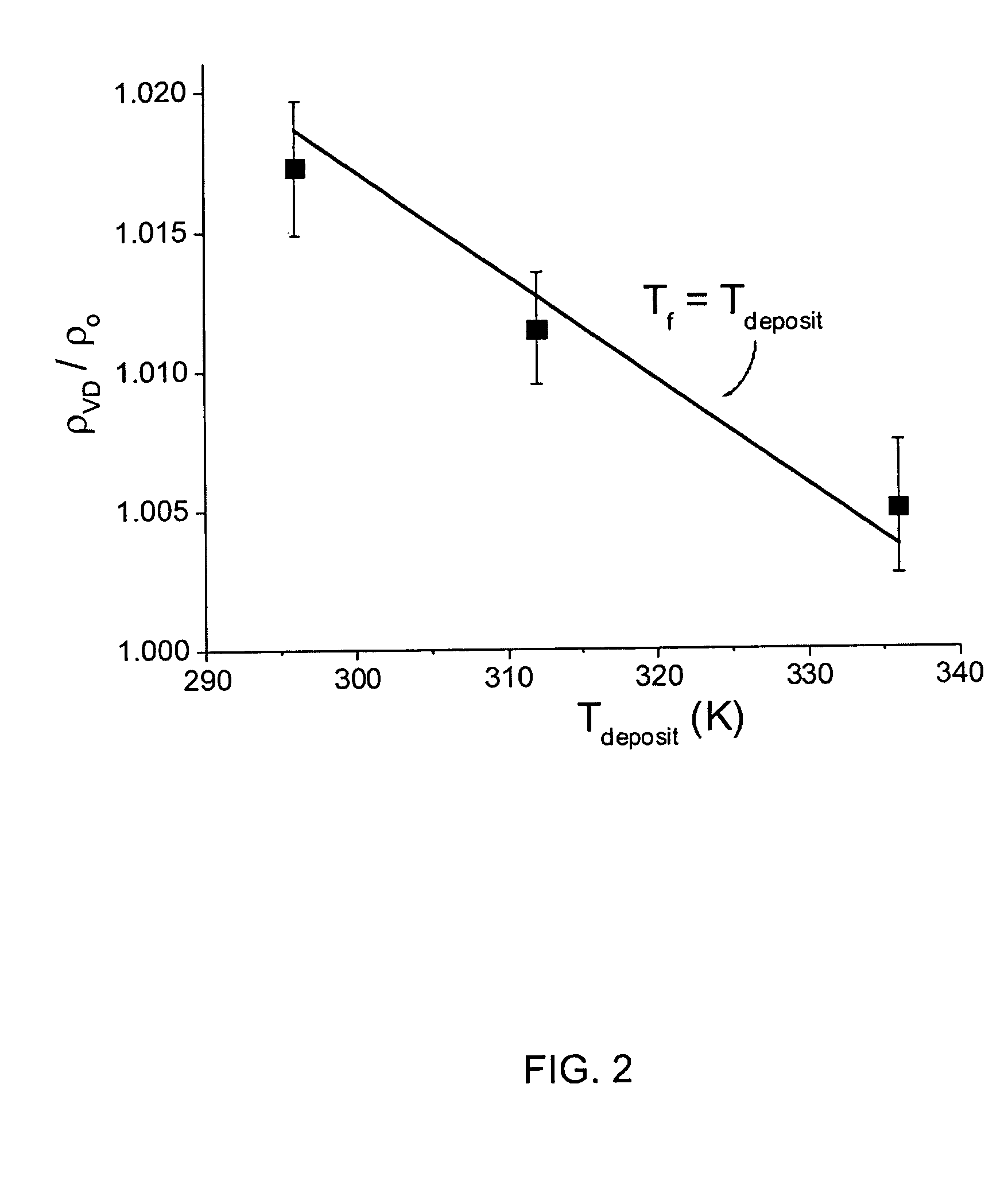
Unusually stable glasses and methods for forming same
ActiveUS20080213365A1High densityExtraordinary kinetic stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsVacuum evaporation coatingPresent methodMolecular solid
The present invention provides vapor deposition-methods that overcome the kinetic restrictions imposed by more conventional vapor deposition processes and liquid-cooling techniques to form amorphous molecular solids with greatly enhanced-stabilities. The present methods produce amorphous molecular solids having stabilities, as measured by fictive temperature, that cannot be achieved using liquid-cooling methods.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
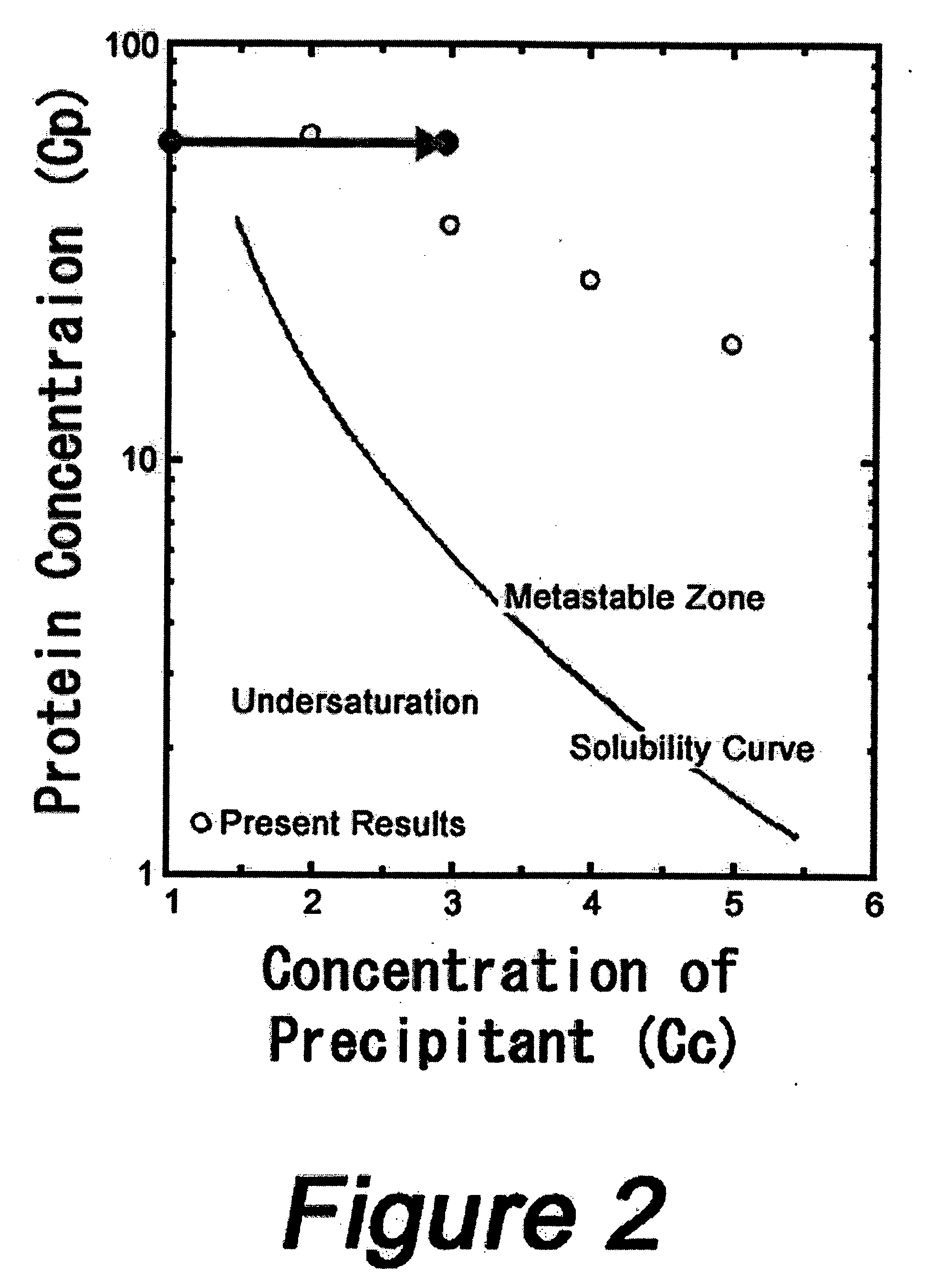
Apparatus for crystal growth of biomacromolecules
InactiveUS20060236924A1Efficient preparationOptimizationAfter-treatment apparatusBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological macromoleculeSolubility
A method comprising the steps of continuously changing the concentrations in solution of a biomacromolecule to be crystallized and a precipitant, thereby constructing a crystal phase diagram containing a solubility curve, searching for optimum conditions of crystallization on the basis of the constructed crystal phase diagram, and performing efficient growth of the crystal of the biomacromolecule. Also disclosed is an apparatus for implementing the method.
Owner:JAPAN ATOM ENERGY RES INST
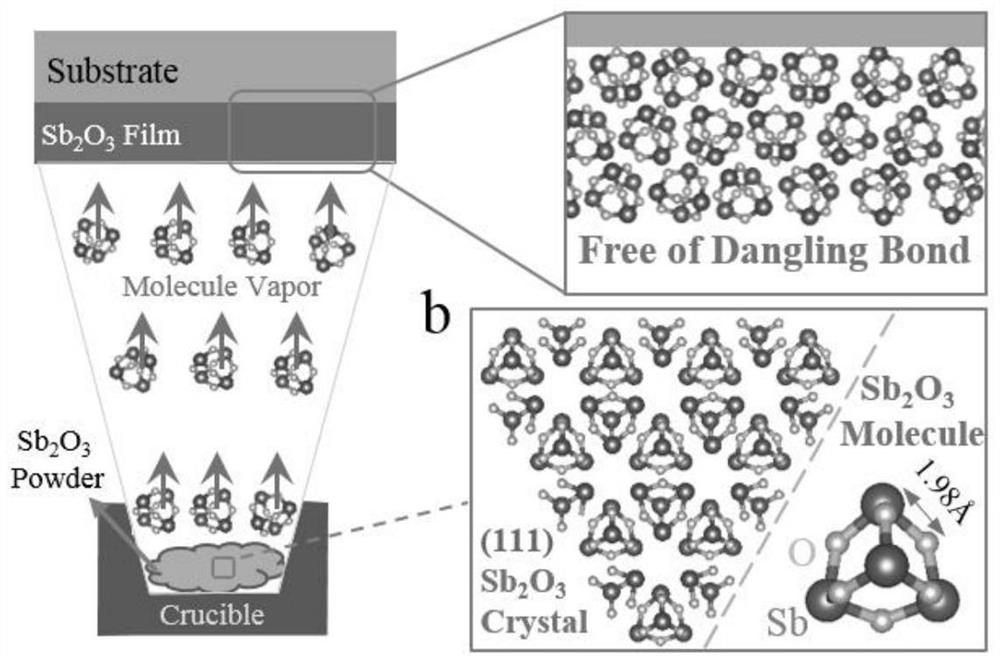
VDW dielectric material and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN111621746AEasy to integrateImprove insulation performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDielectricMolecular solid
The invention belongs to the field of two-dimensional material preparing, and particularly discloses a VDW dielectric material and a preparing method and application thereof. The method comprise the following steps that an inorganic molecular crystal serves as an evaporation source, a heat evaporation method is adopted, the inorganic molecular crystal is subjected to sublimation under the high vacuum, meanwhile, a perfect molecular structure of the crystal can be kept, evaporation is carried out, and a VDW film is obtained. Due to the fact that unsaturated chemical bonds do not exist in inorganic molecules, the VDW film surface has no suspension bonds, and preparing of the VDW dielectric material can be finished. The prepared VDW film can serve as a dielectric material of a two-dimensionalmaterial electronic device, the scattering source of carriers in a two-dimensional groove material can be obviously reduced, it is ensured that a two-dimensional material has the high migration rate,meanwhile, a preparing technology and a semiconductor preparing technology are compatible, and scale preparing and integrating are easy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
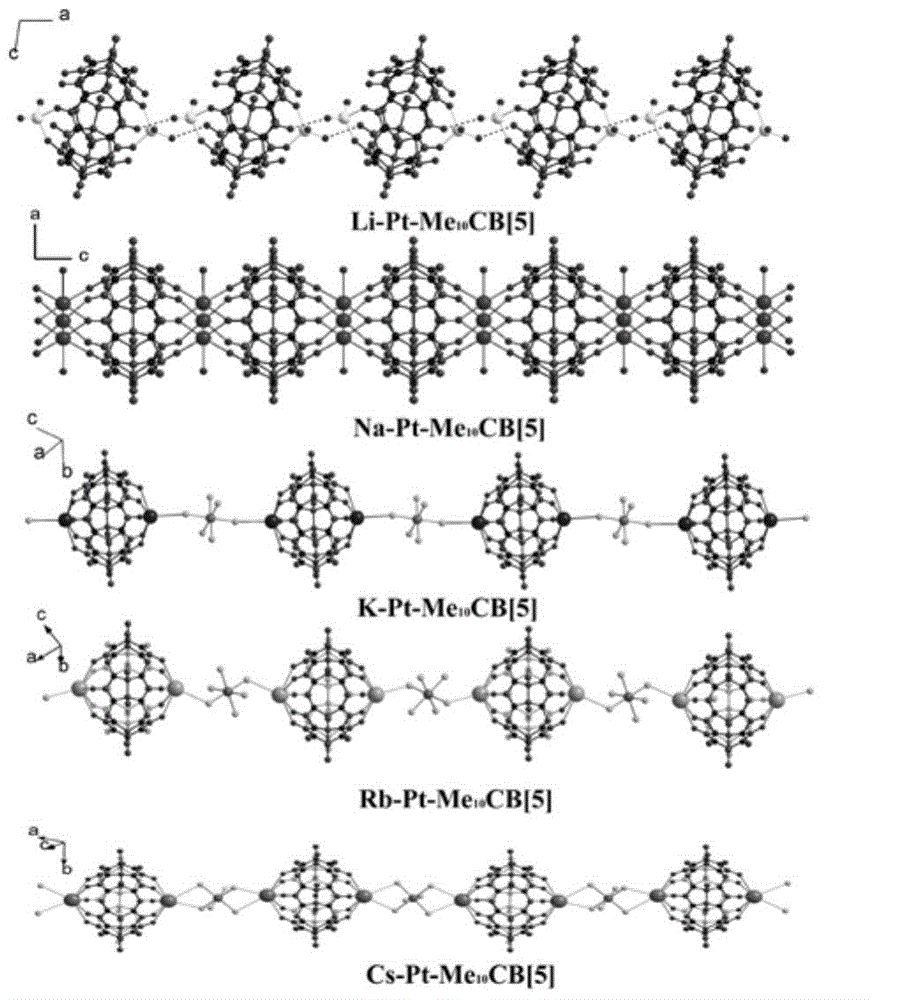
Supermolecule crystal material based platinum nano-catalyst and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN104368389AEvenly distributedImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDiffusion methodsNano catalyst
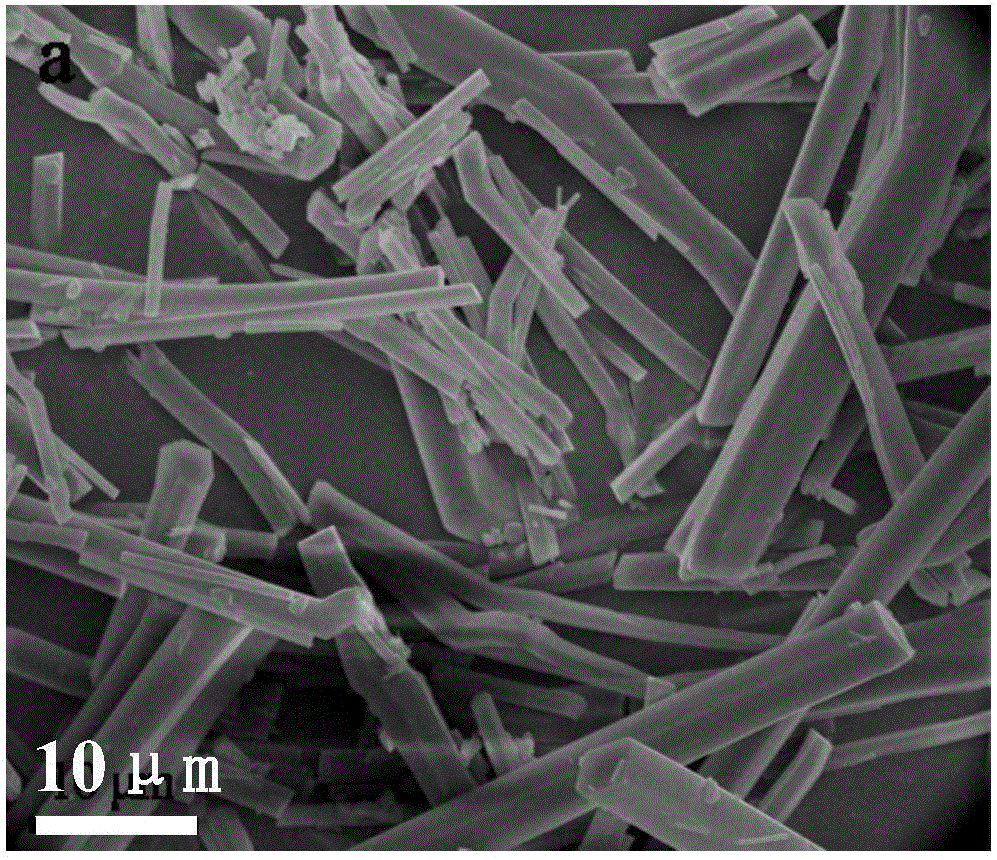
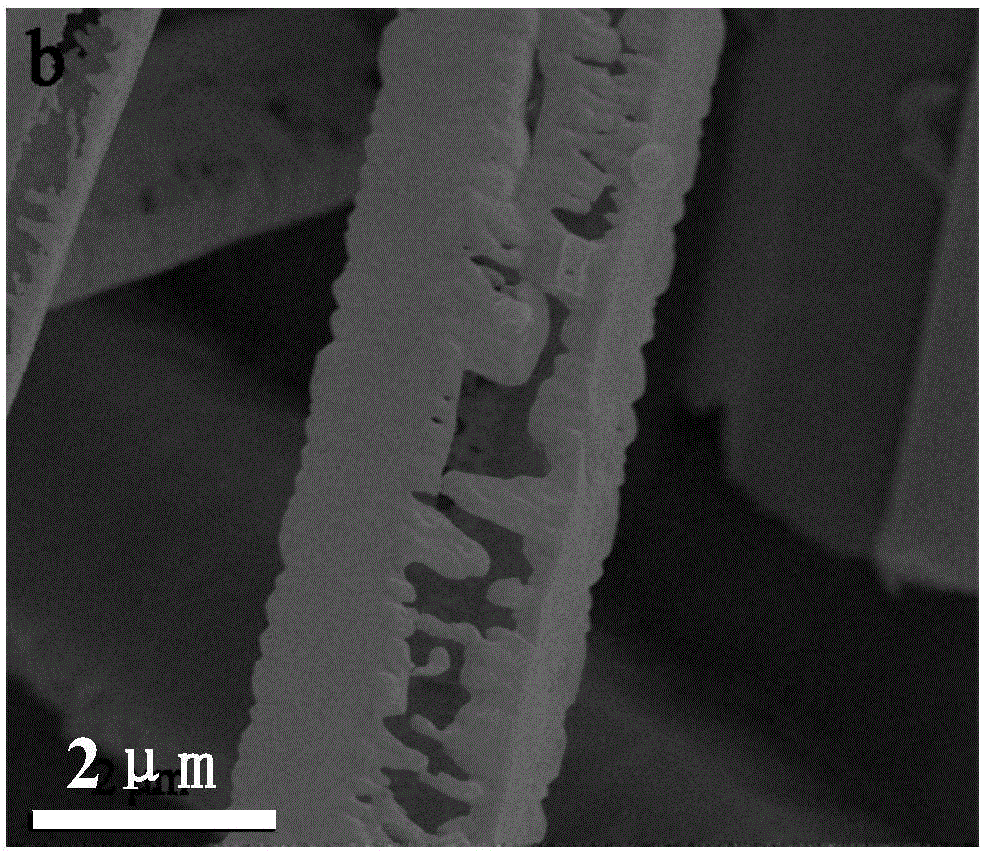
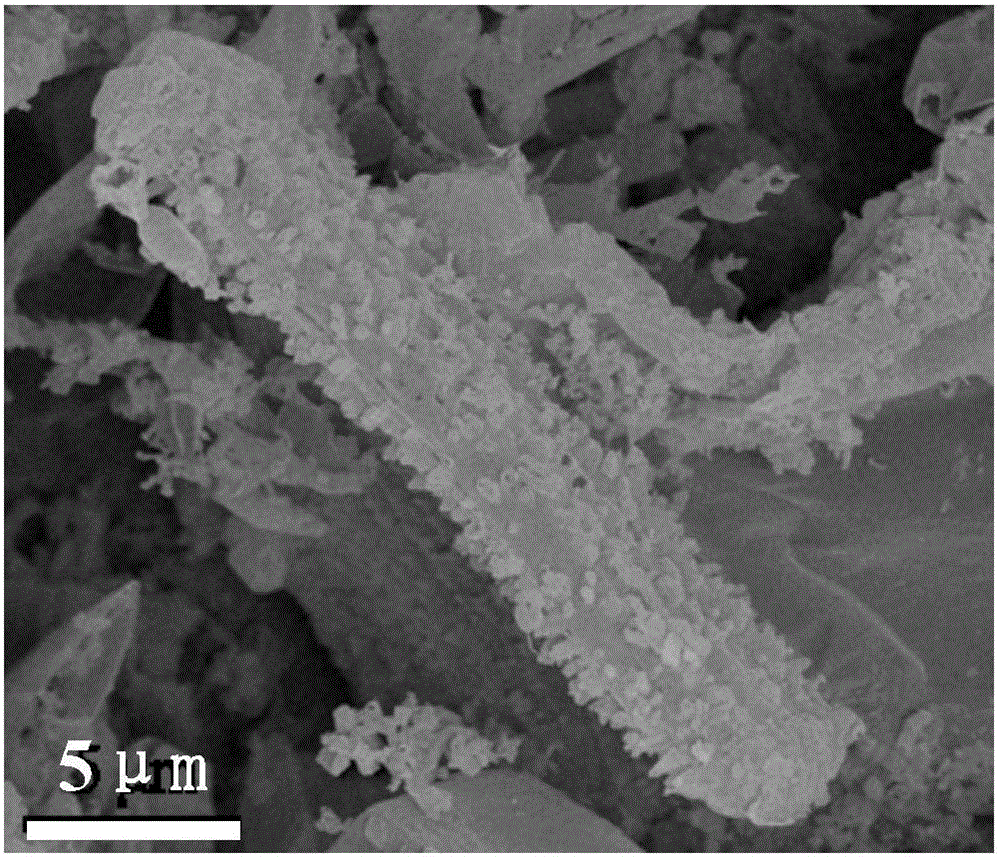
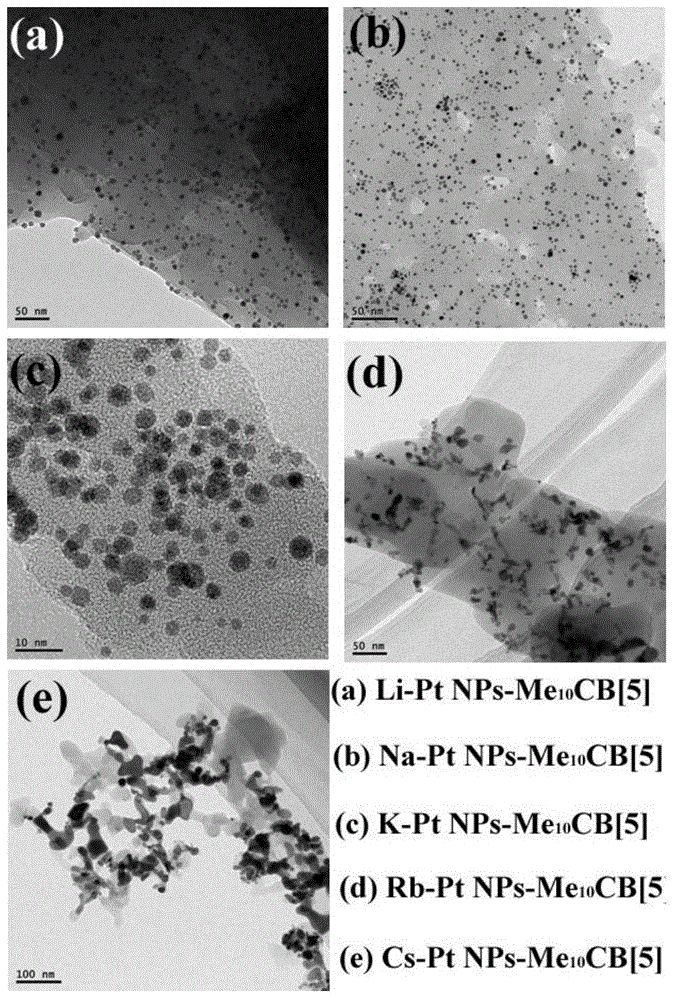
The invention provides supermolecule crystal material based platinum nano-catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method is characterized by including steps of utilizing platinum and Me10CB [5] and preparing a series of M-Pt-Me10CB [5] (M=Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) supermolecule crystal materials under the induction action of different alkali metal by a conventional solution diffusion method. The supermolecule crystal materials can prepare platinum nanoparticles-Me10CB [5] nano-composite catalyst with different particle sizes under the condition of hydrogen reduction. The supermolecule crystal material based platinum nano-catalyst has high catalytic activity and stability, can catalyze hydrogenation reaction of nitrobenzene under the mild condition and can be repeatedly used. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity in process, low cost, convenience in operation, good application effect and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of meta-material dielectric substrate
InactiveCN102480051AExtended function applicationRich electromagnetic modulation functionAntennasMolecular solidDielectric substrate
The invention provides a preparation method of a meta-material dielectric substrate. Organic high molecular solids with different dielectric constants are formed in different regions of a porous material substrate with a centrifugal method, and non-uniform dielectric constant distribution of the meta-material dielectric substrate is realized, so that the meta-material dielectric substrate has richer electromagnetic modulating functions, and the functional applications of a meta-material are expanded.
Owner:KUANG CHI INST OF ADVANCED TECH +1
High molecular solid/solid phase changing material with net type and comb type mixed structure and its preparing method
InactiveCN1263821CHigh phase change enthalpyPhase transition temperature is suitableHeat-exchange elementsPhase change enthalpyPolyethylene glycol
The present invention relates to a kind of high molecular solid / solid phase changing material with mixed net and comb structure, and features that polyglycol with two active end radical and polyglycol with one active end radical are fixed onto the high molecular skeleton material to form 3D mixed net and comb structure. The material of the present invention has relatively great phase change enthalpy up to 120 J / g, proper phase change temperature capable of being altered in 0-65 deg.c, stable solid state before and after phase change without supercooling, separating and other unstable phenomenon, high mechanical strength, high solvent resistance, good machining performance, no toxicity, no leakage, no corrosion, no pollution, long service life and other advantages. The present invention may be used widely in solar energy utilization, afterheat recovering, intelligent air conditioner and other fields.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
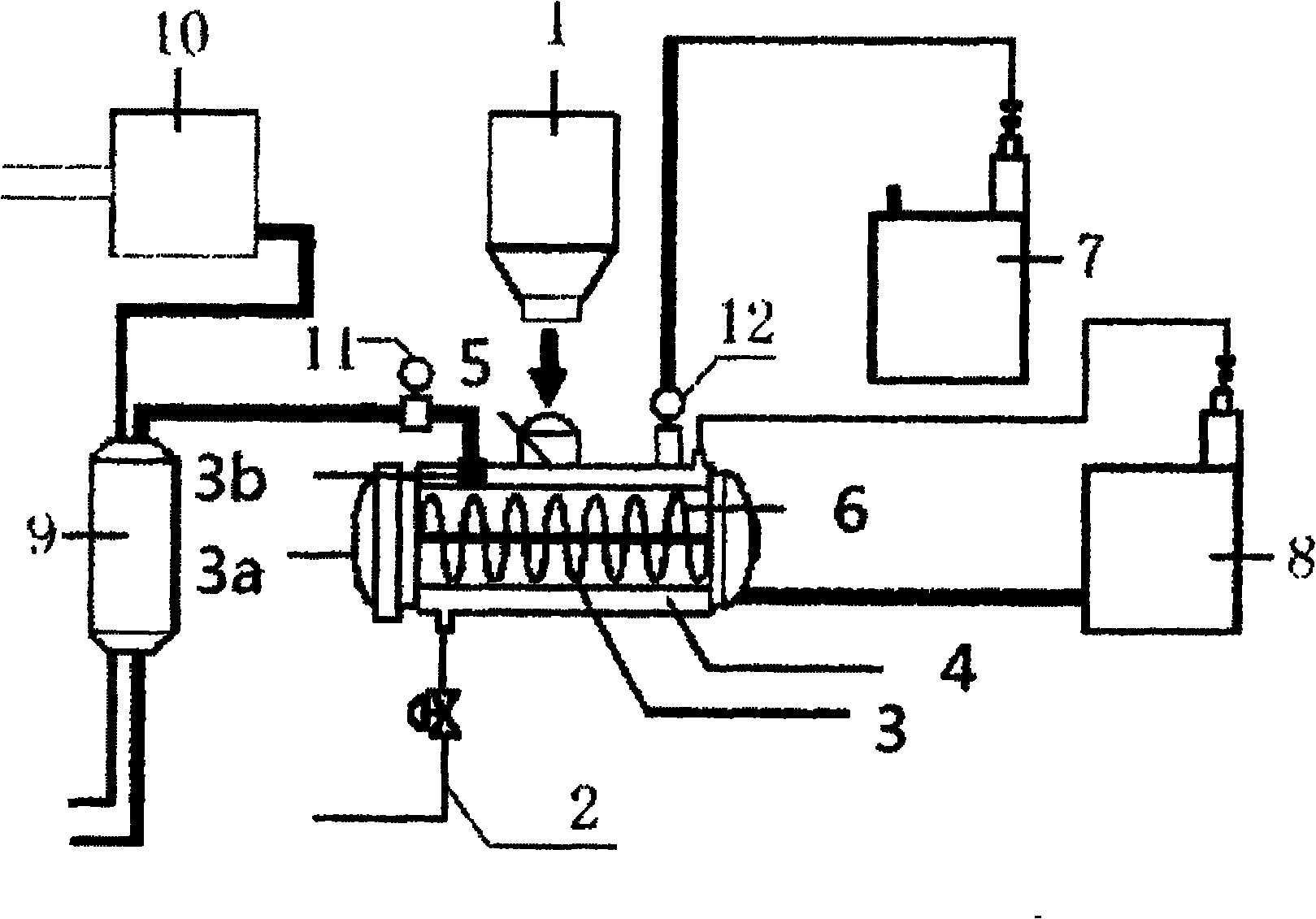
Medical waste subcritical hydrolysis processing apparatus
InactiveCN102039297AAddress aversive issuesNo impurity contentSolid waste disposalHeat carrierMolecular solid
The invention discloses a medical waste subcritical hydrolysis processing apparatus. The apparatus comprises: a raw material storage chamber, a subcritical hydrolysis processor, a heating casing, a steam concurrent boiler, an organic heat carrier boiler, an eddy flow deduster and a deodorizing unit. The apparatus is characterized in that: the outlet of the raw material storage chamber is connected with the inlet of the subcritical hydrolysis processor, the subcritical hydrolysis processor is connected with the eddy flow deduster via the outlet of the processor, the eddy flow deduster is connected with the deodorizing unit, the heating casing is installed on the lower portion of the subcritical hydrolysis processor, the steam concurrent boiler and the organic heat carrier boiler are connected with the subcritical hydrolysis processor and the heating casing respectively. The apparatus of the invention can be heated to the working temperature in a short time; achieves the advantages of low operation cost and low environment load; and can sterilize, damage, decrease, decompose a large amount of medical wastes completely under the high temperature and high pressure condition, and further dry and convert them into low molecular solid fuel with uniform texture, low content of impurity, no secondary pollution and gross calorific value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JINTAI NEW ENERGY ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH INC
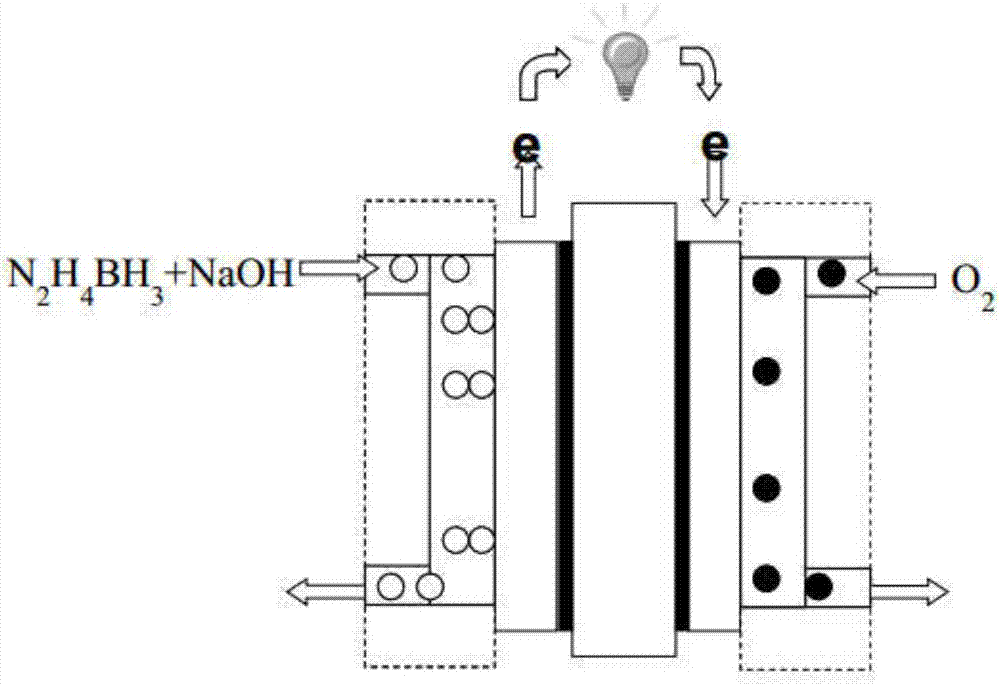
Direct hydrazion-borane fuel battery
ActiveCN106887609AImprove discharge performanceEasy to storeCell electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsMolecular solidHydrogen content
The invention relates to a direct type fuel battery, and provides a direct hydrazion-borane battery using hydrazion-borane as fuel. The fuel battery mainly comprises a liquid fuel, a cathode catalyst, an electrolyte membrane and an anode catalyst, wherein the fuel of the fuel battery is a hydrazion-borane solution. The hydrazion-borane (N2H4BH3, HB) is a stable and non-poisonous molecular solid, and has the characteristics that the hydrogen content is high, the transportation is convenient, the storage is safe, and the environment-friendly and non-pollution effects are realized. The direct hydrazion-borane fuel battery has the advantages that the output voltage, energy conversion efficiency and energy density are high, the storage is easy, the safety is good, and the direct hydrazion-borane battery can be used as a portable power source of mobile equipment.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
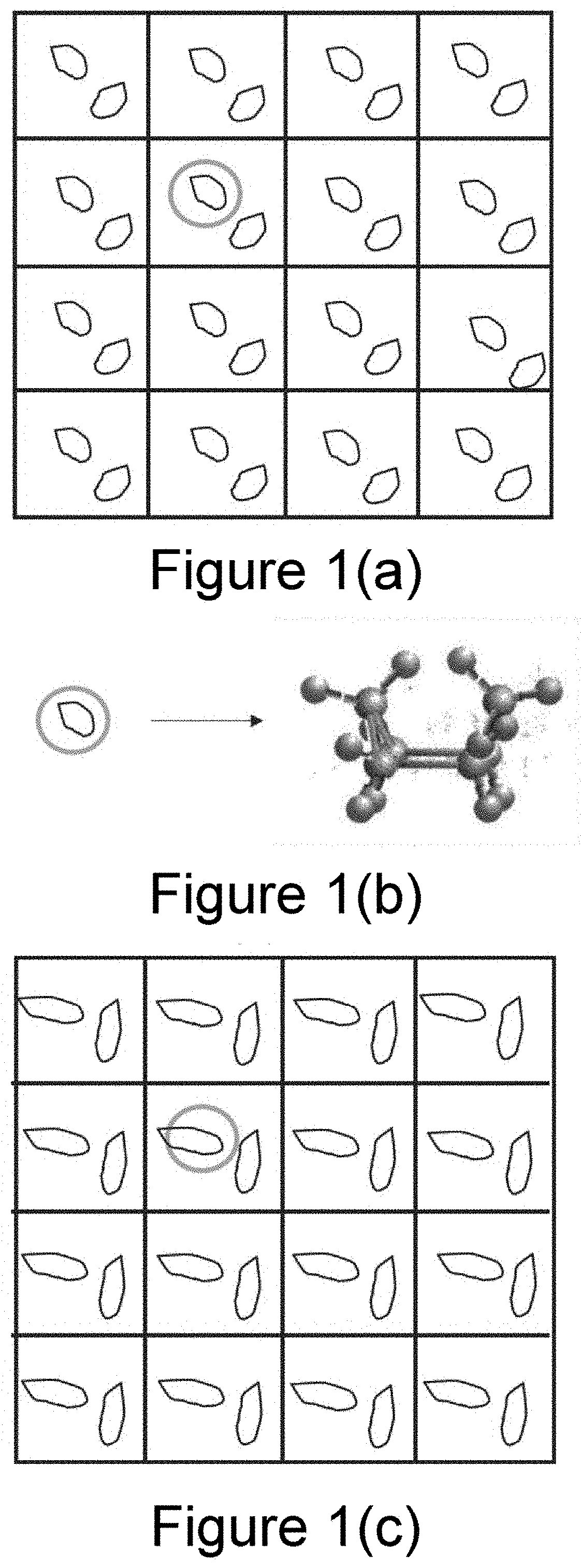
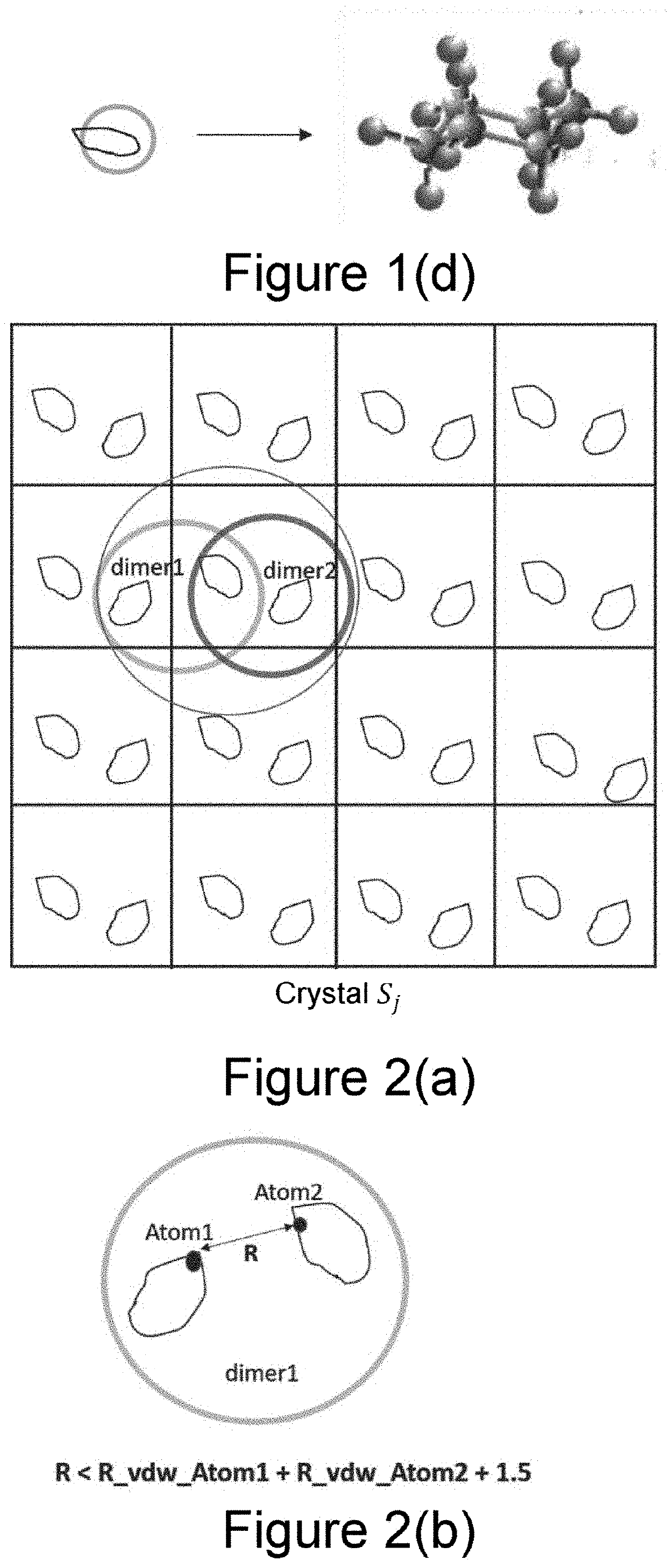
Double-layer neural network algorithm for high-precision energy calculation of organic molecular crystal structure
PendingUS20210375402A1Improve accuracyEasy to calculateChemical property predictionNeural architecturesChemical physicsMolecular solid
The invention pertains to the field of organic molecular crystal structure prediction, and particularly related to a double-layer neural network algorithm for high-precision energy calculation of organic molecular crystal structure, including the first round of conventional crystal structure prediction; extract all molecular conformations from existing crystals and calculate their energies; extract all molecular dimers within the Van der Waals radius of the central unit cell and calculate the intermolecular interaction energies; perform molecular conformation analysis to build a convolutional neural network of single-molecule conformational energies; build a molecular dimer energy-corrected convolutional neural network; calculate the total crystal energies. The invention improves the accuracy of energy calculation in the process of predicting the crystal structure of drug molecules while maintaining the calculation speed; fast and accurate energy calculation will guide the CSP process to quickly find a truly stable crystal form on the correct potential energy surface.
Owner:SHENZHEN JINGTAI TECH CO LTD
High-temperature-resistant epoxy adhesive composition and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106753114AWide variety of sourcesEasy to buyNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesEpoxy resin adhesivesMolecular solidPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a high-temperature-resistant epoxy adhesive composition and a preparation method thereof. The high-temperature-resistant epoxy adhesive composition comprises a component A consisting of epoxy resin, aluminum hydroxide and silicon dioxide, and a component B consisting of phosphoric acid, ethanediol and water. After mixing and glue regulating are performed in proportion, primary solidification is performed under a room temperature environment for hours, and the solidification is complete after 12 hours. Finished high-molecular solids can resist high temperature of 300 DEG C, and can resist instantaneous high temperature of 350 DEG C.
Owner:江苏芯锐传感科技有限公司
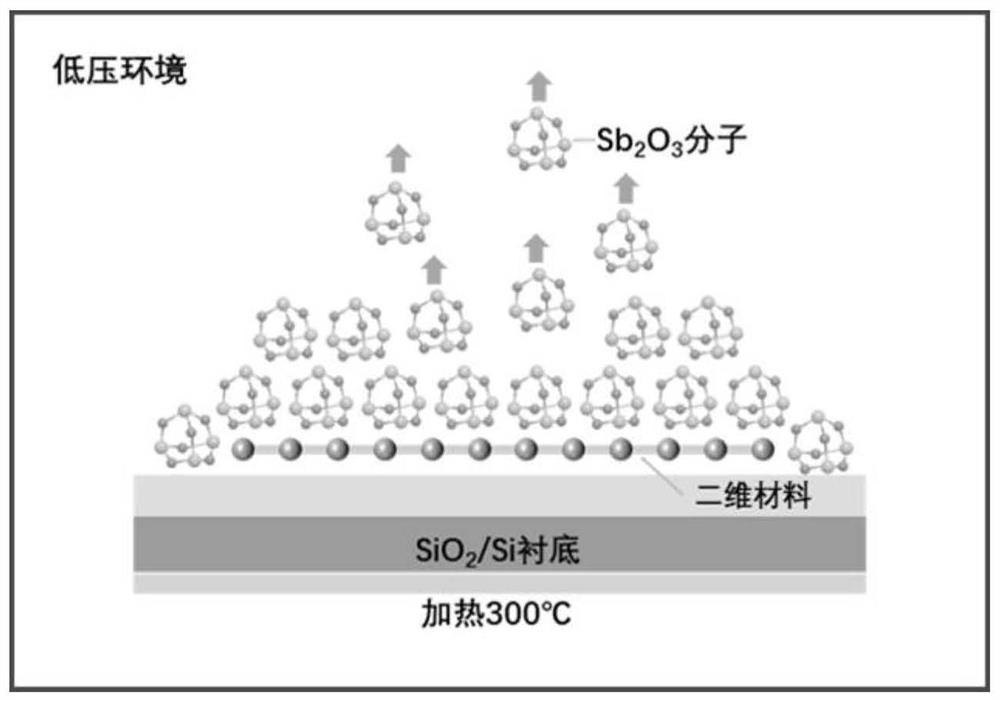
Structure for packaging two-dimensional material by using inorganic molecular crystal and packaging and de-packaging method thereof
PendingCN112185804AAchieve damage-free packagingAvoid changing the chemical state of the surfaceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMolecular solidChemistry
The invention belongs to the field of nano materials, and particularly relates to a structure for packaging a two-dimensional material by using an inorganic molecular crystal and a packaging and de-packaging method thereof. The packaging method comprises the following steps: (1) sublimating inorganic molecular crystals to form a gaseous inorganic molecular atmosphere; and (2) depositing gaseous inorganic molecules on the surface of the two-dimensional material to form a protective layer. An inorganic molecular crystal material is used as a sublimation source, due to weak acting force between molecular crystals, sublimation can be conducted in a high-vacuum environment at a low temperature, the molecular crystals are deposited on the surface of a two-dimensional material to be packaged, anobtained packaging layer is connected with the two-dimensional material through Van der Waals' force, and the chemical state of the surface of the two-dimensional material is prevented from being changed; and the two-dimensional material packaging method can realize nondestructive packaging of the two-dimensional material, is easy to realize large-scale preparation and device integration, fully utilizes the performance of the inorganic molecular crystal, can realize packaging of different two-dimensional materials, has universality, and has a wide market prospect.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Luminescent and dispersible hybrid materials combining ionic and coordinate bonds in molecular crystals
ActiveUS20200263085A1High Luminous Quantum EfficiencyImprove stabilityGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMolecular solidMolecular cluster
Inorganic-organic hybrid structures having both ionic and coordinate bonds in a molecular cluster possessing the features of structural diversity, high luminescence and stability, and excellent dispersibility, suitable for use as lighting phosphors.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Unusually stable glasses and methods for forming same
ActiveUS8329218B2High densityLow on energy landscapeSynthetic resin layered productsVacuum evaporation coatingPresent methodMolecular solid
The present invention provides vapor deposition methods that overcome the kinetic restrictions imposed by more conventional vapor deposition processes and liquid-cooling techniques to form amorphous molecular solids with greatly enhanced stabilities. The present methods produce amorphous molecular solids having stabilities, as measured by fictive temperature, that cannot be achieved using liquid-cooling methods.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com