Method for determining carbon isotope content of soil microorganisms
A technology of soil microorganisms and carbon isotopes, which is applied in the field of soil microbial carbon measurement, can solve the problems of large error in detection results, complex technology, and undetectable results, and achieve the effects of increasing content, high sensitivity, and reducing volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A method for measuring soil microbial carbon isotope content, comprising the steps of:
[0034] S1: Collect 0-15cm soil samples from the field of Yangtian Village Experimental Base in Zengcheng District, Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province. After removing stones and plant roots, air-dry and pass through a 4mm sieve for later use. At the same time, fumigation and non-fumigation treatments were set, and 10 g of soil samples (by dry weight) were added to a single parallel sample. The fumigated samples were placed in a chloroform environment and cultured in a closed environment for 24 hours. Then use 50mL0.5mol / L K 2 SO 4 The solution extracts the dissolved organic carbon in the soil, and the extraction conditions are as follows: the temperature is 25° C., the rotation speed is 200 rpm, and the extraction time is 2 hours. Do not fumigate the sample directly with 50mL0.5mol / L K 2 SO 4 Solution extraction. Each treatment has 3 parallels.
[0035] S2: Take 10 mL of the f...
Embodiment 2
[0043] A method for measuring soil microbial carbon isotope content, comprising the steps of:
[0044] S1: Collect 0-15cm soil samples from the experimental base of Liuge Village, Dongli Town, Leizhou City, Zhanjiang City, Guangdong Province. After removing stones and plant roots, air-dry and pass through a 4mm sieve for later use. At the same time, fumigation and non-fumigation treatments were set, and 10 g of soil samples (by dry weight) were added to a single parallel sample. The fumigated samples were placed in a chloroform environment and cultured in a closed environment for 24 hours. Then with 50mL 0.5mol / L K 2 SO 4 The solution extracts the dissolved organic carbon in the soil, and the extraction conditions are as follows: the temperature is 25° C., the rotation speed is 200 rpm, and the extraction time is 2 hours. Do not fumigate the sample directly with 50mL 0.5mol / L K 2 SO 4 Solution extraction. Each treatment has 3 parallels.
[0045] S2: Take 10 mL of the fi...
Embodiment 3
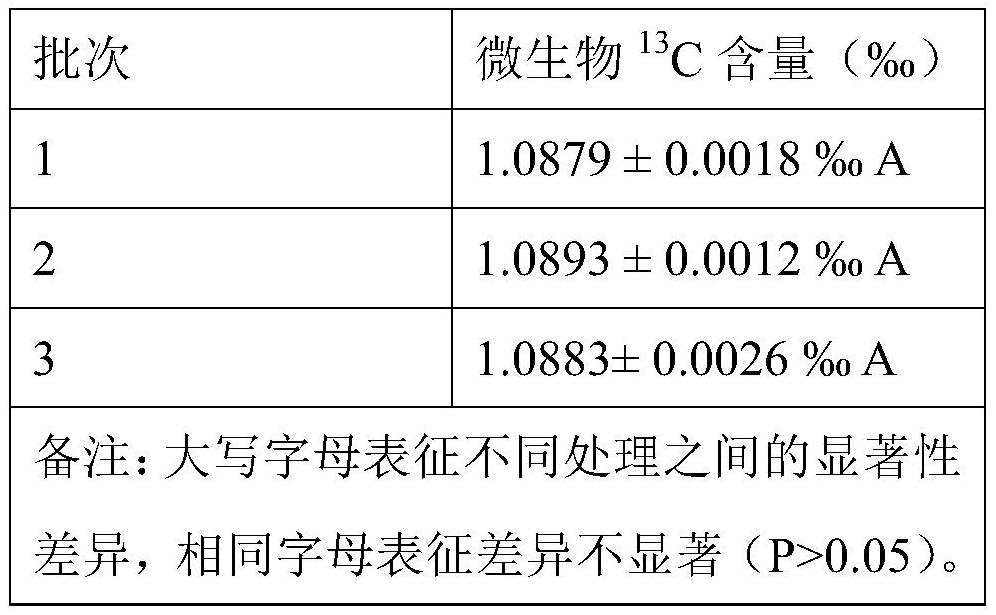
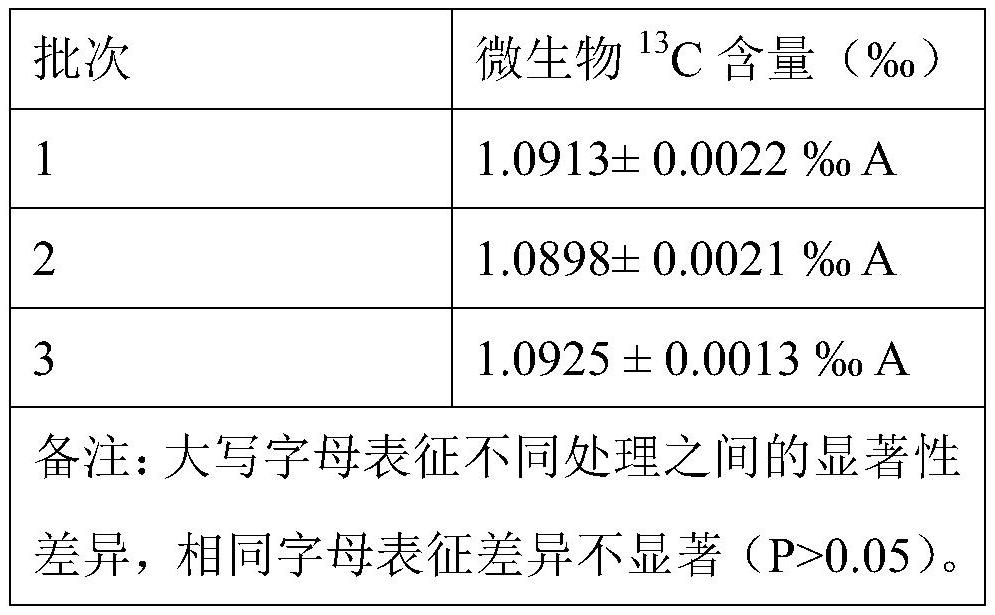
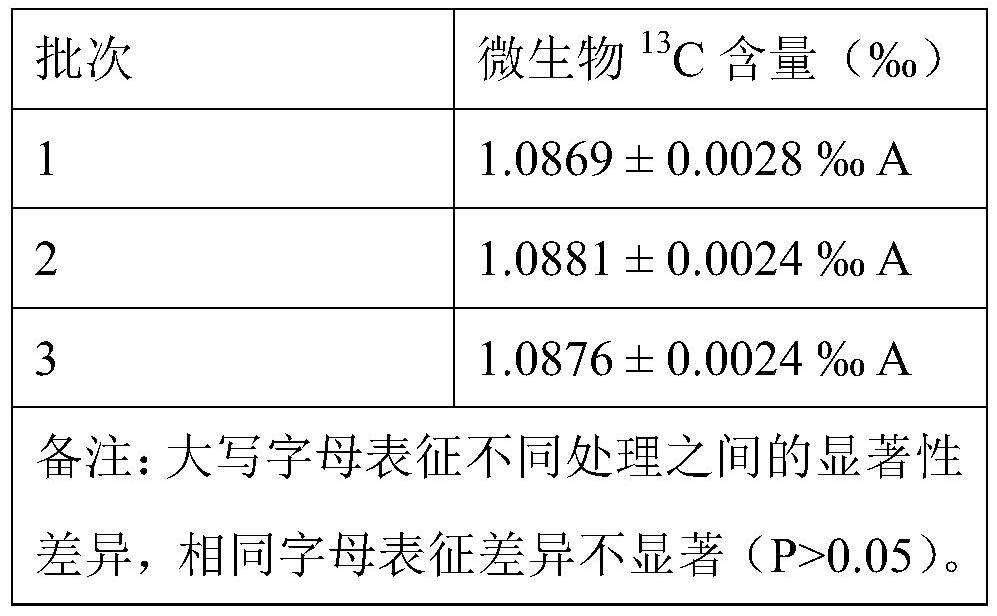
[0069] Embodiment 3 Sensitivity detection
[0070] 1: Using commercial glucose as carbon source ( 13 The C content is 1.0977±0.0011‰), respectively set 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 30mg / L (in terms of carbon, the carbon content in the solution) multiple treatments, each treatment Set up 3 parallel samples. Glucose was dissolved in 50 mL of 0.5 mol / L K 2 SO 4 In the solution, simulate the extracted solution, and use mg / L (calculated as carbon) as the background value control.
[0071] 2: Put the solution obtained above into a plastic centrifuge tube, seal the mouth of the tube with a sealing strip, and pierce 3 to 4 small holes on the sealing strip of the mouth of the tube with a fine needle. Immediately use a freeze dryer for dehydration (-80°C, 72h). Immediately after the dehydration treatment, the obtained powder was placed in a sealed sample tube and stored at -20°C for future testing. During the test, take out 0.8 ~ 1.2mg of powder, add it to the tin cup for te...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com