System for single-molecule isolation for cell populations and single cells, and methods and uses thereof
A cell and molecular technology, applied in the field of protein and/or cell detection, can solve the problems that are not widely used, easy to be destroyed, and cannot be used in ordinary biological laboratories
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
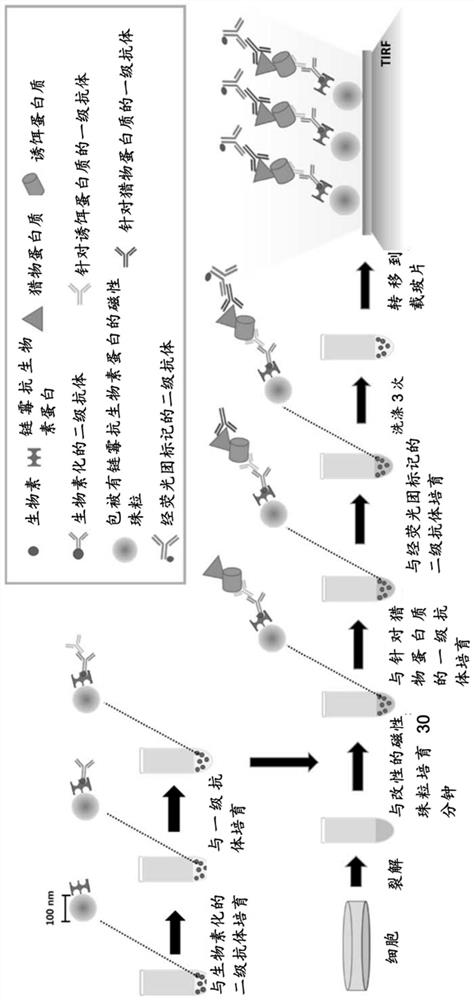
[0109]General representative method for single cell separation and analysis based on nanobeads for cell populations
[0110]The streptavidin-coated magnetic nanobeads are modified by immobilizing a primary antibody on their surface and are used to capture the target protein (bait protein) (as described in the Examples herein). The cells are lysed and magnetic nanobeads are added to the lysate and incubated for 30 minutes, and after the prey protein is captured by the beads, the protein is detected using a specific primary antibody and a fluorescently labeled secondary antibody. The nanobeads were washed three times to remove non-specifically bound proteins, transferred to a glass slide and covered with a cover slip, and imaged using a TIRF microscope. In some embodiments, the bait protein or prey protein is fluorescently labeled for direct visualization. (figure 1 )
Embodiment 2
[0112]Nanobead-based SiMPull for green fluorescent protein (GFP) pull-down in cell populations
[0113]The SiMPull method based on nanobeads first verifies protein pulldown by pulling down GFP, because GFP can be directly visualized without immunostaining, which simplifies verification and, more importantly, because GFP can be used in photobleaching experiments to evaluate the fluorescence of pulldown The single-molecule state of the spot.
[0114]Use magnetic nanobeads to pull down the ectopic GFP in HEK293T cells (figure 2 a). In contrast, in the negative control experiment, very few GFP molecules were pulled down (figure 2 a), and the calculated measured signal-to-noise (SN) ratio is about 10-20 (figure 2 b). The SN ratio is equivalent to or better than the original SiMPull method of Jain et al. By applying the algorithm previously used by Jain et al.,figure 2 About 95% of the fluorescent spots in a show Gaussian distribution. A photobleaching experiment was performed on these fluoresc...
Embodiment 3
[0116]Pull down the cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) complex in the cell population
[0117]The holoenzyme or complex of PKA (one of the most widely studied protein kinases) exists as a heterotetramer comprising a regulatory (R) subunit dimer and two catalytic (C) subunits (image 3 a); cAMP can bind to the R subunit and release the C subunit from the PKA complex at physiological levels (image 3 a). We used the well-characterized interaction between the PKA-R subunit and the PKA-C subunit to validate the nanobead-based SiMPull assay used to study PPI.
[0118]The expression vectors used in this study are pEGFP-n1 (Addgene catalog number 6085-1) for GFP expression, pcDNA3-mouse PKA-C-α-mEGFP (Addgene catalog number 45521) and pcDNA3-mouse PKA-RII -α-mEGFP (Addgene catalog number 45527). By replacing the GFP sequence in pcDNA3-PKA-C-α-mEGFP with the mCherry sequence, pcDNA3-PKA-C-α-mCherry was constructed.
[0119]The interaction of PKA-C-eGFP and PKA-R-mCherry was detected in HEK293T cell...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com