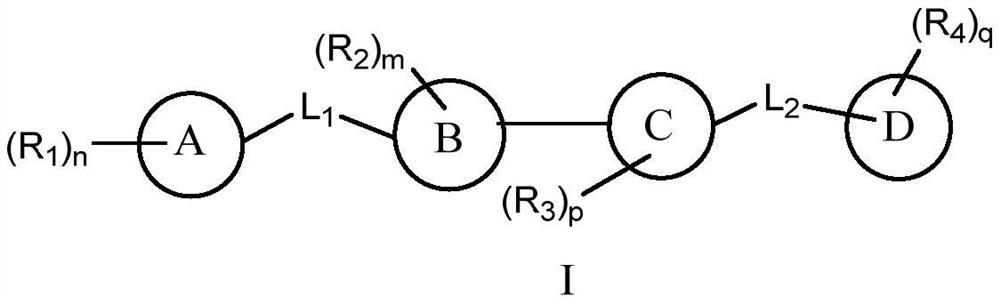
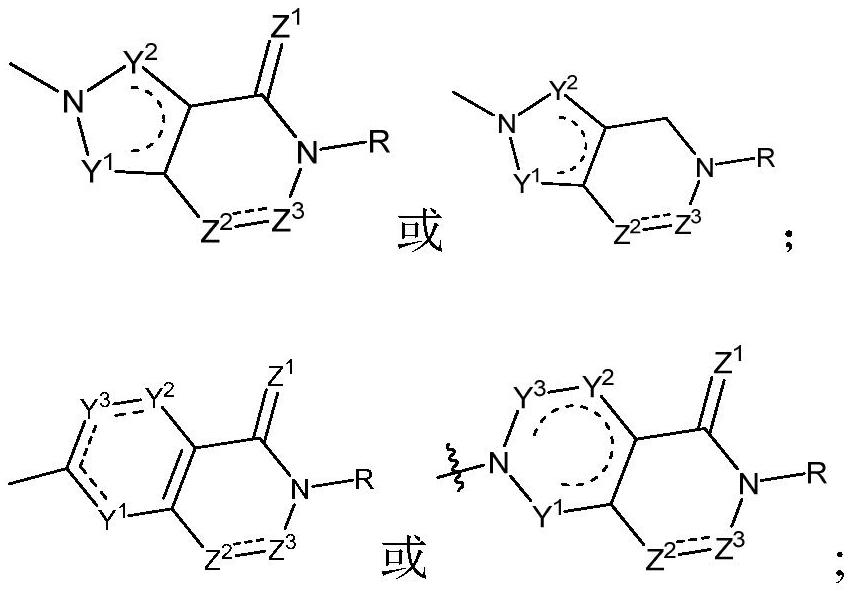
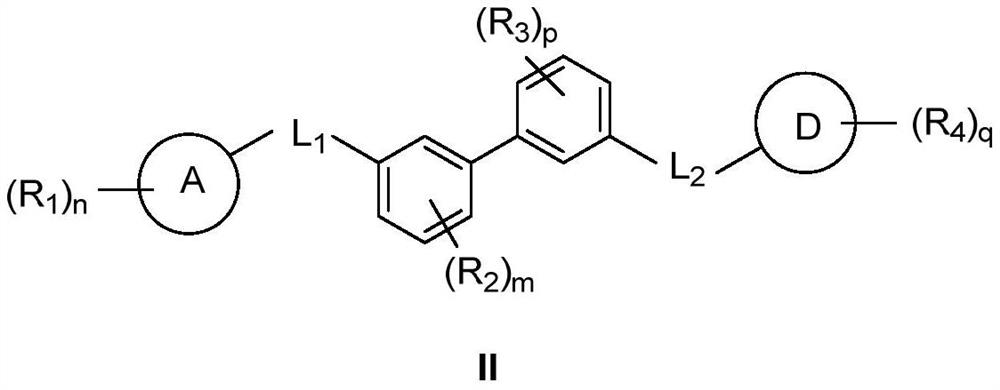
Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound as well as preparation method, pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
A technology of compounds and hydrates, applied in the field of small molecule drugs, can solve the problems of only injectable administration, not oral administration, and high production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0133] The preparation of formula I compound
[0134] In order to prepare the compound described in the general formula I of the present invention, according to the structure of the general formula I, the compound of the general formula I in the present invention can be obtained by the following method 1 or 2.
[0135] Method 1 includes the following steps:
[0136]
[0137] (a) Based on halide 1-1 and a suitable coupling reagent 1-2 (like boronic acid, borate ester, tin reagent or Grignard reagent), palladium or copper catalyzed coupling reaction (like Suzuki, Stille or Kumada coupling) to obtain intermediate compound 1-3;
[0138] (b) using intermediate 1-3 as a raw material, reacting with carboxylic acid 1-4 under the action of a condensing agent (like HATU, EDCI or HBTU) to obtain amide intermediate 1-5;
[0139] (c) using intermediate 1-5 as raw material, removing the protecting group (Boc) under acidic conditions to obtain intermediate 1-6;
[0140] (d) using interme...
Embodiment 1
[0185] The synthesis of embodiment 1 compound LW1005-001
[0186]
[0187] Step 1-1:
[0188]
[0189] Compound 1 (51g, Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2019, 62, 276-287), 2-methyl-3-bromobenzoic acid (95.56g) was sequentially added to PPA (500g), and the reaction was carried out under mechanical stirring at 140°C for 6 hours. After the reaction is complete, pour ice water into the reaction bottle, pour out the slurry after dilution for 30 minutes, and filter. Add 500ml of water to the filtered solid, add solid sodium hydroxide under mechanical stirring, adjust the water phase to pH=6-8, and filter. The filter cake solid was dried at 55° C. to obtain 80 g of off-white solid product. MS-APCI:305[M+H] + .
[0190] Step 1-2:
[0191]
[0192] 3 (2.0g), DMAP (805mg) was added to DMF (30mL), the turbid liquid was added to Boc2O, the solid was dissolved, and the reaction was heated at 40°C overnight. TLC showed a small amount of 1 remaining. The reaction solution was...
Embodiment 2
[0197] The synthesis of embodiment 2 compound LW1005-002
[0198]
[0199] Step 2-1:
[0200]
[0201] Compound 3 (10g) was dissolved in DMF (150ml), and 6 (14.3g; Macromolecules, 2015, 48, 1688-1702) and Cs2CO3 (21.4g) were added and reacted overnight at room temperature. TLC detects that the reaction is complete. After filtration, the filtrate was added with water and then extracted with EtOAc. The organic phase was spin-dried and slurried with HEP:EtOAc=10:1 to obtain 11 g of white solid 7. MS-APCI:587.1[M+H]+
[0202] 1H NMR (400MHz, Chloroform-d) δ8.05(dd, J=7.9, 1.3Hz, 1H), 7.75(dd, J=8.0, 1.3Hz, 1H), 7.54(dt, J=6.7, 1.5Hz, 4H),7.49(d,J=7.3Hz,1H),7.41–7.35(m,2H),7.34–7.27(m,4H),7.22(t,J=7.9Hz,1H),6.58(d,J =7.3Hz, 1H), 4.26(t, J=4.7Hz, 2H), 4.05(dd, J=5.5, 4.1Hz, 2H), 2.92(s, 3H), 1.05(s, 9H).
[0203] Step 2-2:
[0204]
[0205] 7 (11 g) was dissolved in THF (110 mL) at room temperature, 1NTBAF / THF (20.7 mL) was added, and reacted for 2 hours. TLC showed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com