Process for extracting cyclopentane by hydrofining crude benzene containing dicyclopentadiene
A dicyclopentadiene, hydrogenation and refining technology, applied in the field of coal chemical industry, can solve problems such as cyclopentane research that has not been reported, and achieve the effects of increasing added value, easy control of reaction heat, and avoiding coking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
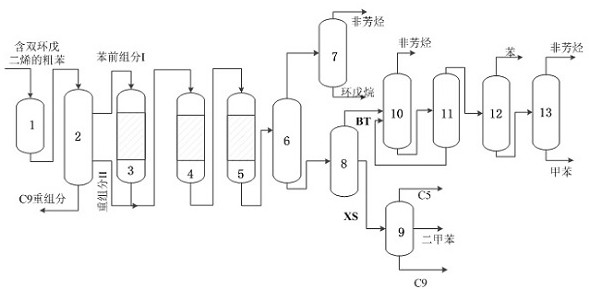
[0023] After the raw material is filtered, it enters the weight removal tower 2 from the buffer tank 1, removes heavy components above carbon 9 at the bottom of the weight removal tower 2, and simultaneously pyrolyzes dicyclopentadiene to generate cyclopentadiene, which is separated from the top of the weight removal tower 2 The After mixing with hydrogen, it enters the first-stage hydrogenation reactor 3 from top to bottom, and the first-stage hydrogenation becomes a Ni-S reduction catalyst at a reaction temperature of 10°C, a pressure of 4.0MPa, and a space velocity of 2.0h -1, the reaction is carried out under the condition of hydrogen oil volume ratio of 400:1, the diolefins in the pre-saturated benzene component I, and cyclopentadiene are hydrogenated to generate cyclopentene and cyclopentane; after hydrogenation, the pre-benzene component I and recombined Part II is mixed with hydrogen, heat exchanged by a heat exchanger, and then enters the second-stage hydrogenation re...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The raw material 2 enters the weight removal tower 2 from the buffer tank 1 after being filtered, and the heavy components above carbon 9 are removed in this unit, and at the same time, dicyclopentadiene is pyrolyzed to produce cyclopentadiene, which is separated by distillation and separated in the weight removal tower 2 The benzene pre-component I at -1 , the hydrogen oil volume ratio is 800:1 for the reaction, the diolefins in the pre-saturated benzene component I, cyclopentadiene are hydrogenated to generate cyclopentene and cyclopentane; after hydrogenation, the pre-benzene component I, heavy component II and Hydrogen is mixed, heat exchanged by a heat exchanger, and then enters the second-stage hydrogenation reactor 4 from top to bottom. The second-stage hydrogenation reaction is Ni-Mo in a sulfided state. The reaction conditions are temperature 190 ° C, pressure 2.0 MPa, space velocity 0.5h -1 , Hydrogenation at a volume ratio of 800:1 to hydrogen oil; the remain...
Embodiment 3
[0027] The raw material 3 enters the weight removal tower 2 from the buffer tank 1 after being filtered, and the heavy components above carbon 9 are removed in this unit, and at the same time, dicyclopentadiene is pyrolyzed to produce cyclopentadiene. The benzene pre-component I at -1 , the hydrogen oil volume ratio is 600:1 to react, the diolefins in the component I before saturated benzene, cyclopentadiene are hydrogenated to generate cyclopentene and cyclopentane; after hydrogenation, the component I before benzene, the heavy component II and Hydrogen is mixed, heat exchanged by a heat exchanger, and then enters the second-stage hydrogenation reactor 4 from top to bottom. The second-stage hydrogenation reaction is Ni-Mo in a sulfide state. The reaction conditions are temperature 170°C, pressure 3.0MPa, space velocity 1.0h -1 , Hydrogenation at a hydrogen oil volume ratio of 600:1; unsaturated olefins left in the saturated first-stage hydrogenation; the components after the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com