Oligonucleotides for modulating scn9a expression
A technology of oligonucleotides and nucleotides, used in recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragments, medical preparations with non-active ingredients, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0423] Oligonucleotide Synthesis
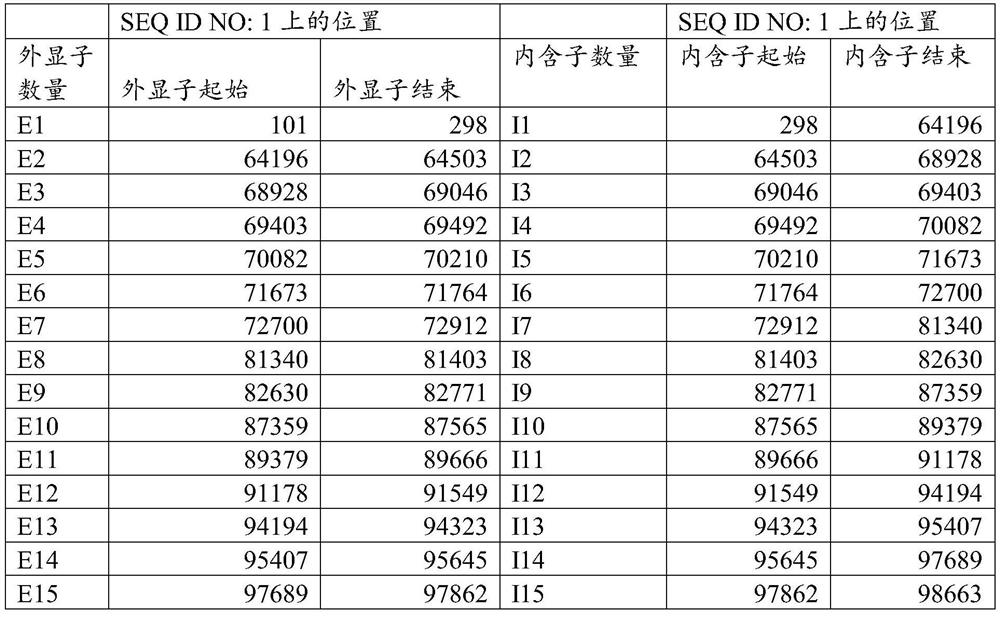
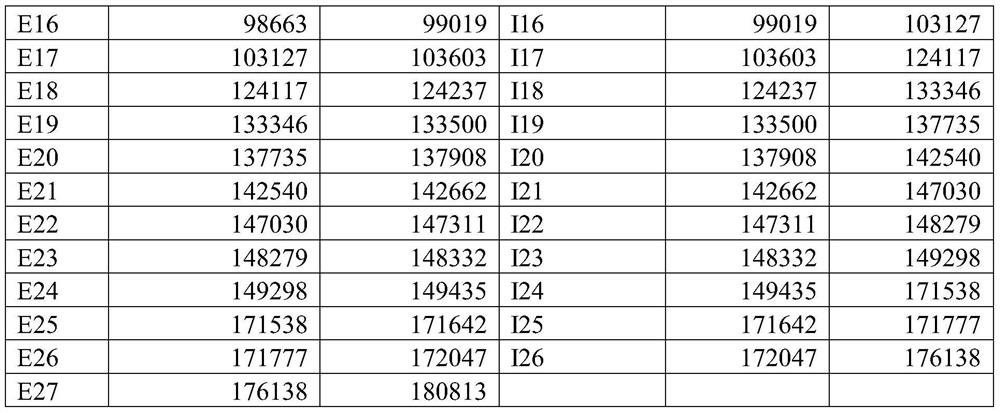
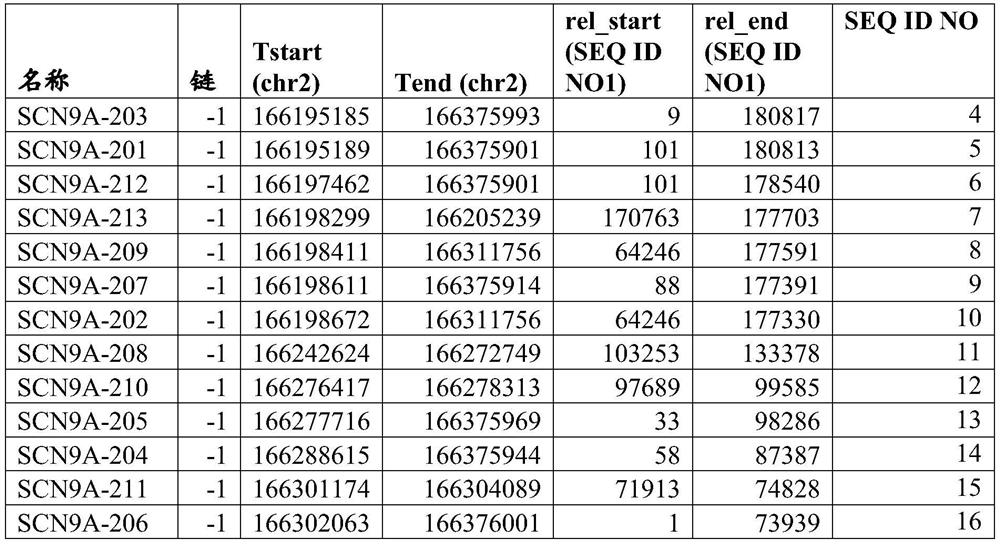
[0424] The compounds are listed in the compound table, which also shows the nucleobase sequence, complementary target sequence regions (start and end) on SEQ ID NO: 1, gap polymer design, Tm (dG) and after receiving the compound treatment The level of remaining mRNA in the cells (see Example 1 below).
[0425] Oligonucleotide synthesis is well known in the art. Below are scenarios that may apply. The oligonucleotides of the present invention can be produced by slightly different methods in terms of equipment, vectors and concentrations used.
[0426] Oligonucleotides were synthesized on an Oligomaker 48 using the phosphoramidite method on a uridine universal carrier at a 1 μmol scale. At the end of the synthesis, the oligonucleotides were cleaved from the solid support using ammonia at 60°C for 5-16 hours. Oligonucleotides were purified by reverse phase HPLC (RP-HPLC) or by solid phase extraction and characterized by UPLC and further conf...
example 1
[0443] Example 1: In vitro reduction of Nav1.7 in the SK-N-AS human cell line using oligonucleotides.
[0444] LNA-modified oligonucleotides targeting human Nav1.7 were tested for their ability to reduce Nav1.7 mRNA expression in human SK-N-AS neuroblastoma cells purchased from ATCC (CRL-2137). SK-N-AS cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (ECACC-94092302) supplemented with 0.1 mM non-essential amino acids (NEAA) and a final concentration of 10% fetal bovine serum. Cells were incubated in an active evaporation incubator (Thermo C10) at 37°C, 5% CO 2 and 95% humidity for cultivation. Cells were inoculated into 95 μL of SK-N-AS cell culture medium at a density of 9300 cells / well (96-well plate), and left in an incubator for 24 hours. Oligonucleotides diluted in PBS (5.0 μL) to a final concentration of 5 μM were then added to the cell cultures from precast 96-well dilution plates. The cell culture plates were incubated in the incubator for 96 hours.
[04...
example 2
[0452] Example 2: Reduction of Nav1.8 alone or in combination with reduction of Nav1.7 in a modified SK-N-AS human cell line (CRISPR activated Nav1.8) using oligonucleotides in vitro.
[0453] Activation of Nav1.8 expression in SK-N-AS cells:
[0454] SK-N-AS cells were transduced with hCMV-Blast-dCas9-VPR encoded lentiviral particles (#VCAS11918, Dharmacon) at 0.5 MOI and selected with 2 μg / mL elastin for 10 days. SK-N-AS stably expressing dCas9-VPR protein was subsequently engineered to express Nav1.8-specific sgRNA. Briefly, the expression cassette driven by the U6 promoter was synthesized as a gBlock and then subcloned in the PiggyBac vector (#PB511B-1, System Biosciences). The identity of the vector was verified by Sanger sequencing. Stable integration of the U6-driven cassette expressing the Nav1.8-specific sgRNA was obtained using a transposase expression plasmid (#PB210PA-1, System Biosciences) following the manufacturer's instructions. Cells stably expressing the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com