Wheeled leg robot and driving method thereof
A technology of wheel-legged robots and thighs, which is applied in the fields of motor vehicles, transportation and packaging, etc. It can solve the problems of system power loss, small output torque of joint drive devices, partial overflow loss of pumping stations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
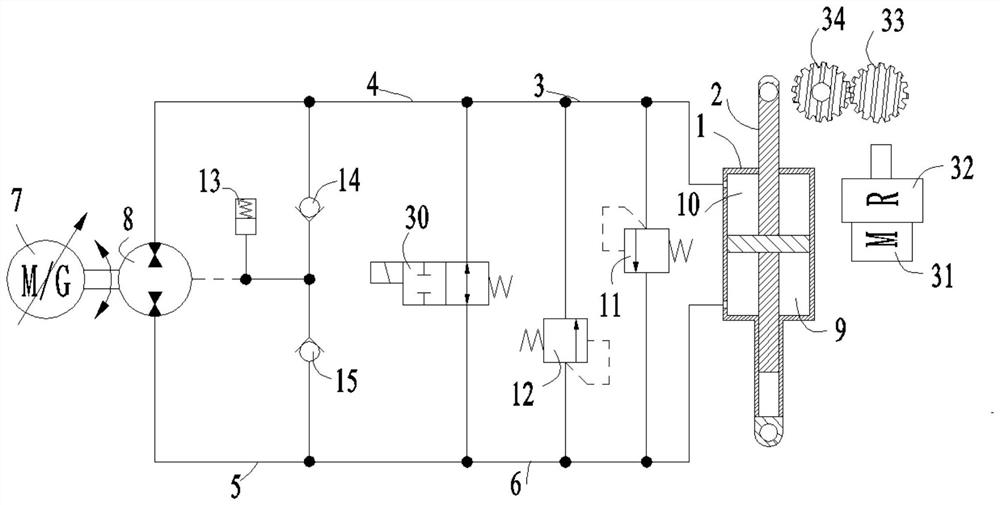
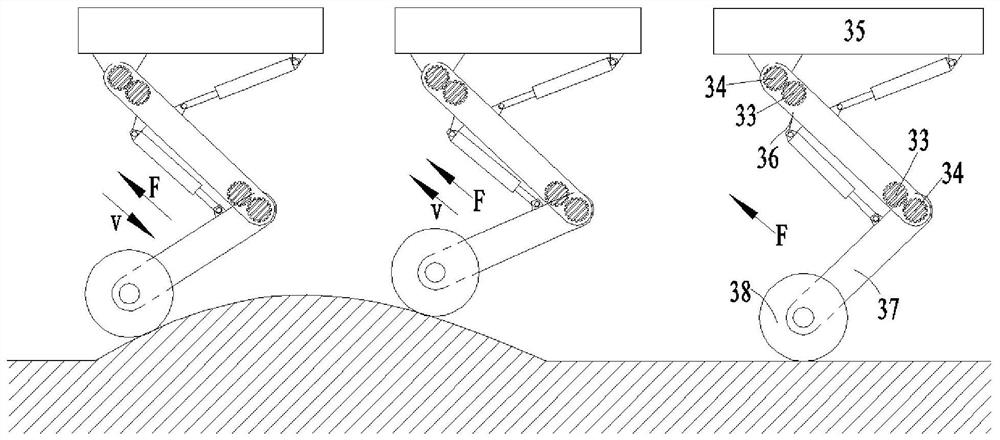
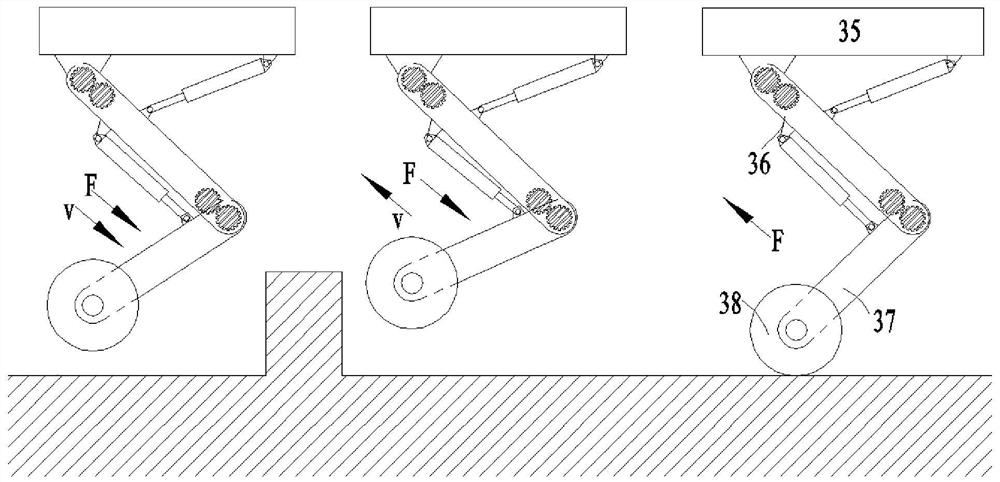
[0028] See attached Figure 1~3. A wheel-legged robot comprises a car body 35, a thigh 36, a calf 37, a wheel 38 and two hydraulic control systems; one end of the thigh 36 is hinged to the car body 35, and the other end of the thigh 36 is hinged to one end of the calf 37; the calf The other end of 37 is provided with a wheel 38; the hydraulic control system includes a hydraulic cylinder 1, a piston rod 2 and a motor gear control system; the hydraulic cylinder 1 is provided with a bearing chamber 9 and a non-bearing chamber 10; Bearing chamber 9 and non-bearing chamber 10; one hydraulic control system controls the angle between the car body 35 and the thigh 36 by controlling the elongation of the piston rod 2 relative to the hydraulic cylinder 1 or through the motor gear control system; the other hydraulic control system The control system controls the angle between the thigh 36 and the lower leg 37 by controlling the elongation of the piston rod 2 relative to the hydraulic cy...
Embodiment 2
[0030] See attached Figure 1~3 . On the basis of Embodiment 1, the hydraulic control system also includes a main oil circuit, a secondary oil circuit, a servo motor 7 and a hydraulic pump 8; the servo motor 7 is used to drive the hydraulic pump 8; the non-bearing chamber 10, The main oil circuit, the hydraulic pump 8, the secondary oil circuit and the bearing chamber 9 are connected in sequence; the elongation of the piston rod 2 relative to the hydraulic cylinder 1 changes with the change of the hydraulic oil capacity in the bearing chamber 9 and the non-bearing chamber 10 . It can be seen from the above structure that if the circuit formed by the non-bearing chamber 10, the main oil circuit, the hydraulic pump 8, the secondary oil circuit and the bearing chamber 9 is connected in sequence, the servo motor 7 will rotate forward, and the hydraulic oil in the bearing chamber 9 will be pumped by the hydraulic pump. 8 is sucked to the non-bearing cavity 10, the elongation of t...
Embodiment 3
[0038] See attached Figure 1~3 . A method for driving a wheel-legged robot, using the wheel-legged robot described in Embodiment 1, including an active vibration reduction step; the active vibration reduction step specifically includes: driving the wheel-legged robot to travel when the wheel 38 touches the ground and rotates; When the wheel-legged robot is running on a flat ground, there is no forced exchange of hydraulic oil between the bearing chamber 9 and the non-bearing chamber 10; the load force borne by the hydraulic cylinder 1 and the piston rod 2 has no fluctuation, and the car body 35 has no vibration. The relative elongation of piston rod 2 to hydraulic cylinder 1 remains constant, and the angle between car body 35 and thigh 36 and the angle between thigh 36 and shank 37 remain constant; When the ground is sloped, the load force borne by the hydraulic cylinder 1 and the piston rod 2 becomes larger, the hydraulic oil is forced to exchange between the bearing chambe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com