Soft polyvinyl chloride-based copolymer, method for producing soft polyvinyl chloride-based copolymer, composition comprising soft polyvinyl chloride-based copolymer, and resin product produced from composition
A vinyl chloride-based resin and vinyl chloride technology, applied in the field of resin products, including its composition, soft vinyl chloride-based copolymer, and its preparation method, can solve the problem of no industrial application value, low industrial practical value, It is difficult to achieve self-plasticization and other problems, and achieve the effects of avoiding the performance degradation of resin products, good biocompatibility, and excellent mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0124]
[0125] The preparation method of the soft vinyl chloride copolymer of the present invention is the preparation method of the above soft vinyl chloride copolymer, which comprises: comprising vinyl chloride, the monomer represented by the above formula (1) and the optional above formula The raw materials of the monomers shown in (2) are copolymerized.
[0126] The details of vinyl chloride, the monomer represented by formula (1), the monomer represented by formula (2) and other monomers have been described above, and will not be repeated here.
[0127] Examples of copolymerization reactions of the present invention include, without limitation, block polymerization, random polymerization, graft polymerization, gradient polymerization. Among them, random polymerization is preferable from the viewpoint of expressing the technical effect of the present application more favorably, that is, the molecular chain of the flexible vinyl chloride copolymer of the present inventio...
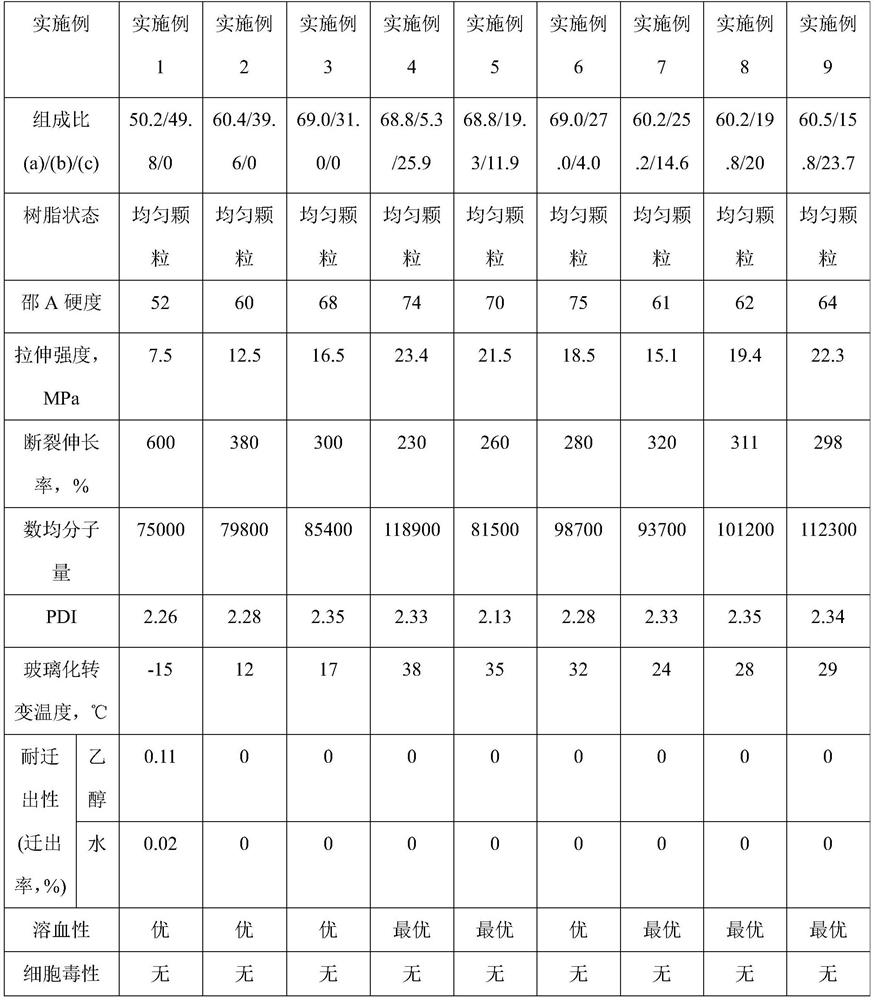
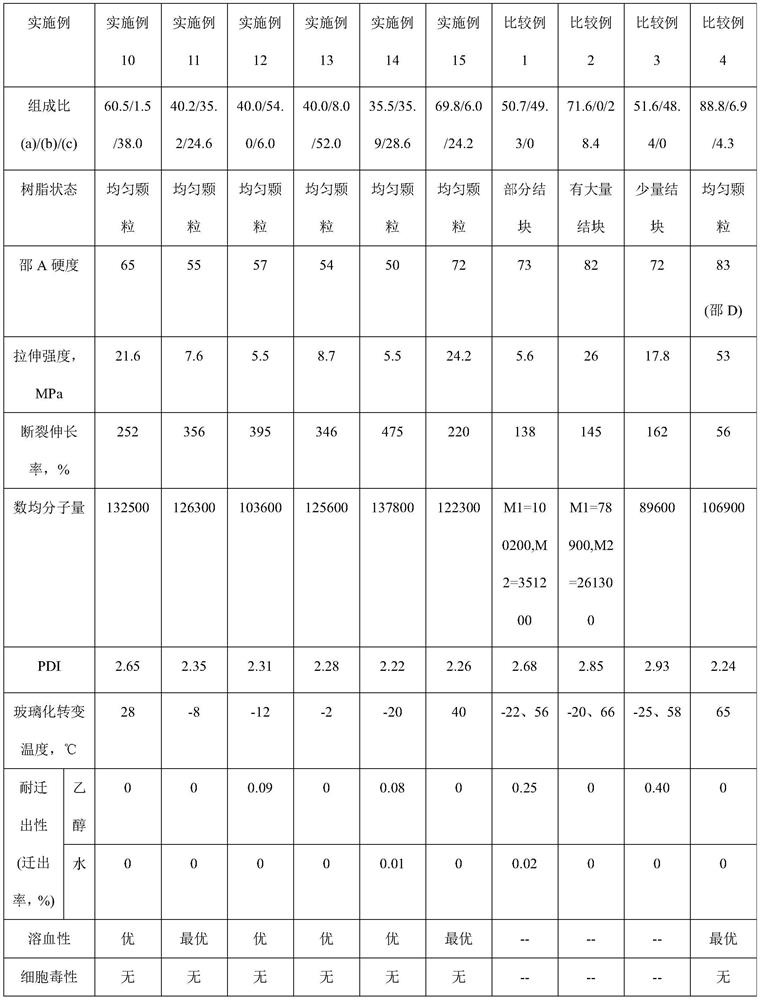
Embodiment 1
[0184] In a stainless steel micro-reactor with an internal volume of 200ml of stirring blades, 100g of deionized water, 10.4g of 2 mass % PVA aqueous solution, 0.042g of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose, 0.05g of azobisisobutyronitrile, 27g of polypropylene glycol monomethacrylate with a molecular weight of 375 (PPGMA-375, in the case of x=5 in the formula (1)), was filled with nitrogen for 5 minutes to replace the air in the reactor. Then feed VC monomer 27g in the reactor. After pre-stirring for 60 minutes, the temperature was raised to 70°C to start polymerization. It should be noted that the monomer feeding mass ratio VC:PPGMA-375=50:50, and the polymerization reaction time was 8.5 hours. After the completion of the polymerization reaction, unreacted VC monomer was reclaimed, and the polymerization product was alternately washed with a large amount of deionized water and ethanol to obtain 48.2 g of the vinyl chloride copolymer of white solid particles, and its composition: rel...
Embodiment 2
[0186] Change the feed mass ratio of VC and PPGMA-375 to be VC:PPGMA-375=60:40 and the polymerization reaction time is 8.0 hours, except that, obtain the vinyl chloride series copolymerization of white solid particles in the same way as in Example 1 49.5 g of the product, the composition: the content of the structural unit (a) was 60.4% by mass, and the content of the structural unit (b) was 39.6% by mass based on the total mass of the vinyl chloride-based copolymer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com