Method for rapidly and continuously preparing high-toughness natural polymer bioplastics
A technology for natural polymers and bioplastics, which is applied in the field of rapid and continuous preparation of high-toughness natural polymer bioplastics, and can solve the problems of stubborn cellulose or chitin molecules, inability to large-scale continuous production, and difficulty in melting or dissolving. , to achieve the effect of good mechanical properties, low cost and excellent product performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
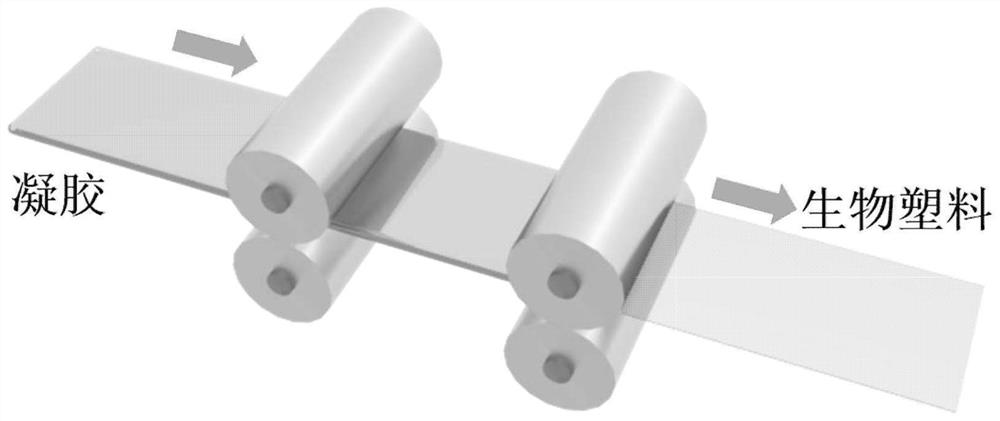
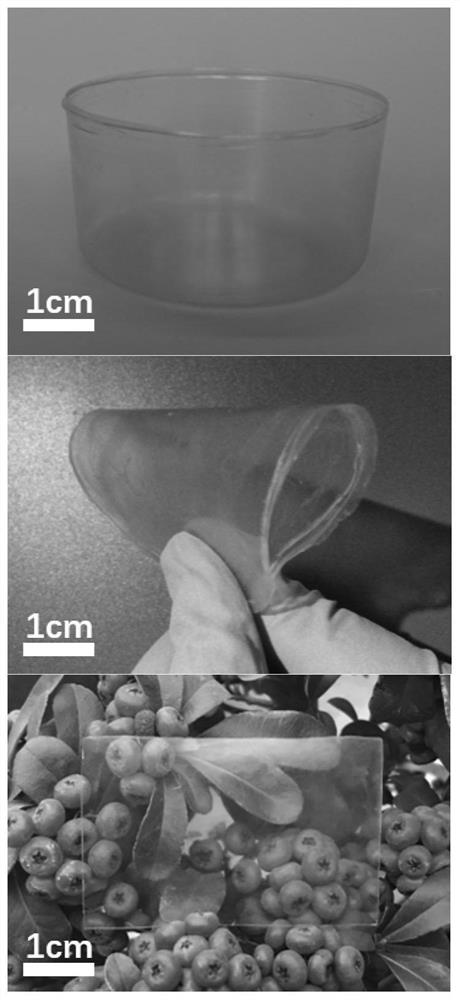
[0030] Prepare 7wt% NaOH, 12wt% urea and the rest of water as a solvent, add cotton linter pulp with a degree of polymerization of 500, stir and freeze overnight below freezing point, stir and thaw to obtain a cellulose solution with a concentration of 2wt%. After degassing, the solution was cast on the surface of a glass plate, and then directly immersed in ethanol for regeneration for 2 hours, and washed with deionized water to obtain a cellulose hydrogel. This hydrogel was substituted with ethanol to obtain a cellulose ethanol gel. The hydrogel was carried out as figure 1 The shown roll-to-roll thermocompression drying yields cellulosic bioplastics.
Embodiment 2
[0032]Prepare 7wt% NaOH, 12wt% urea and the rest of water as a solvent, add bamboo pulp with a degree of polymerization of 800, stir and freeze overnight below freezing point, and obtain a cellulose solution with a concentration of 2wt% after stirring and thawing. Add epichlorohydrin at -15~25°C according to the molar ratio of crosslinking agent to cellulose is 4:1, stir evenly and put it in the mold for 12 hours to obtain a partially chemically crosslinked cellulose gel, then The gel was placed in 75% ethanol aqueous solution for regeneration at room temperature, and washed with water until neutral after 2 hours to obtain a transparent cellulose hydrogel. The hydrogel is directly frozen at -20°C and then freeze-dried to obtain the cellulose airgel. The airgel is carried out as figure 1 The shown roll-to-roll thermocompression drying yields crosslinked cellulose bioplastics.
Embodiment 3
[0034] Prepare a solvent with 7wt% NaOH, 12wt% urea and the rest of water, add cotton linter pulp with a degree of polymerization of 500, stir and freeze overnight below freezing point, stir and thaw to obtain a cellulose solution with a concentration of 4wt%. Add epichlorohydrin at -15~25°C according to the molar ratio of crosslinking agent to cellulose is 4:1, stir evenly and put it in the mold for 12 hours to obtain a partially chemically crosslinked cellulose gel, then The gel was placed in 75% ethanol aqueous solution for regeneration at room temperature, and washed with water until neutral after 2 hours to obtain a transparent cross-linked cellulose hydrogel. The hydrogel was carried out as figure 1 The shown roll-to-roll thermocompression drying yields crosslinked cellulose bioplastics.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com