Candida albicans attenuated strain with deletion of ARP1 gene and application of candida albicans attenuated strain
A technology for Candida albicans and deletion strains, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of increased mycelium production capacity of Candida albicans, and achieve the effects of reduced toxicity, reduced colonization ability, and weakened proliferation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
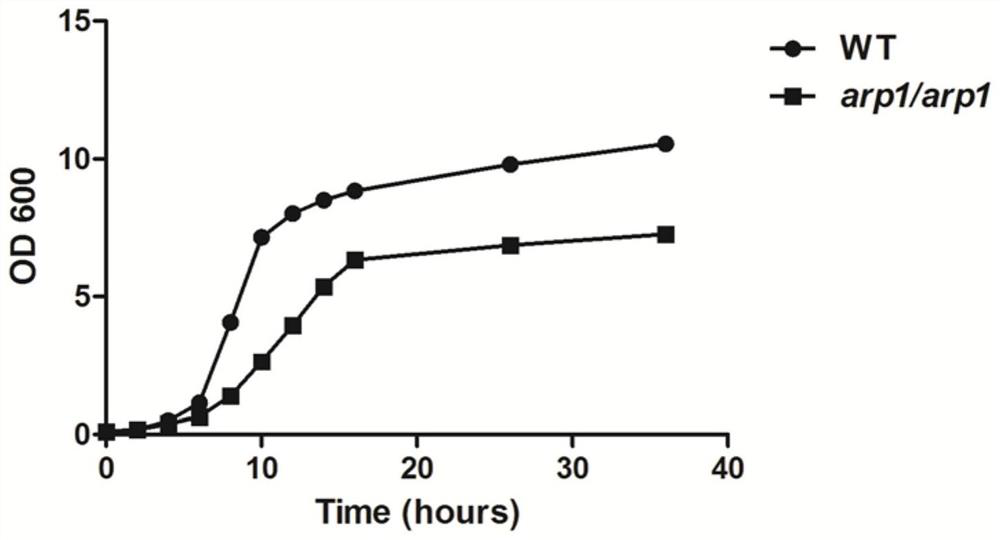
[0036] Example 1 Effect of ARP1 Gene Deletion on Candida Albicans Cell Proliferation
[0037]In order to prove the role of ARP1 deletion in the proliferation of Candida albicans, the present invention carried out the growth curve detection experiment of Candida albicans. Inoculate the wild-type strain of Candida albicans and the ARP1 deletion strain into liquid YPD medium respectively, and after culturing overnight at 30°C, transfer to fresh YPD medium at a ratio of 1 / 100, take samples every two hours to detect OD600, and draw the growth curve , and according to the OD value of the logarithmic phase culture solution, calculate the generation time of the wild-type strain and the ARP1 deletion strain.
[0038] The results are as follows: After Candida albicans was transferred to fresh YPD medium, the OD value of the ARP1 deletion strain at the same time point was significantly smaller than that of the wild-type strain at the same time; the doubling time of the wild-type strain w...
Embodiment 2
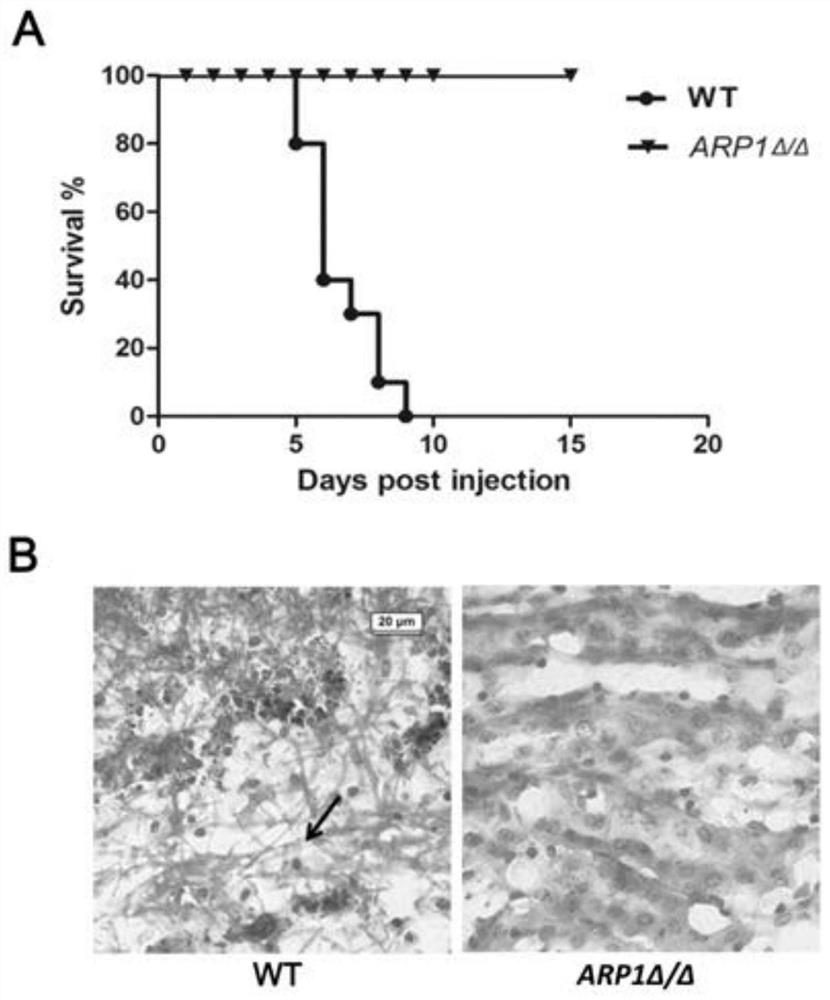
[0040] Example 2 The toxicity of Candida albicans with ARP1 deletion is significantly reduced
[0041] In order to prove the influence of ARP1 deletion on the regulation of virulence, the present invention carried out a mouse toxicity experiment. 1.2×10 6 Candida albicans wild strain and ARP1 deletion strain cells were injected into ICR mice, and the survival rate was observed. figure 2 A shows the survival curve of the mice infected with Candida albicans. It was found that the wild-type strain died from the 5th day, and all the mice infected with the wild-type strain died on the 9th day, showing that the average survival time was 6 days; and All mice infected with the ARP1-deficient strain survived up to 15 days, showing no toxicity.
[0042] By detecting kidney sections of dying mice, figure 2 B shows the results of glycogen staining (PAS) of kidney sections of dying mice caused by Candida albicans infection, and the arrows show mycelial cells, showing that the wild-typ...
Embodiment 3
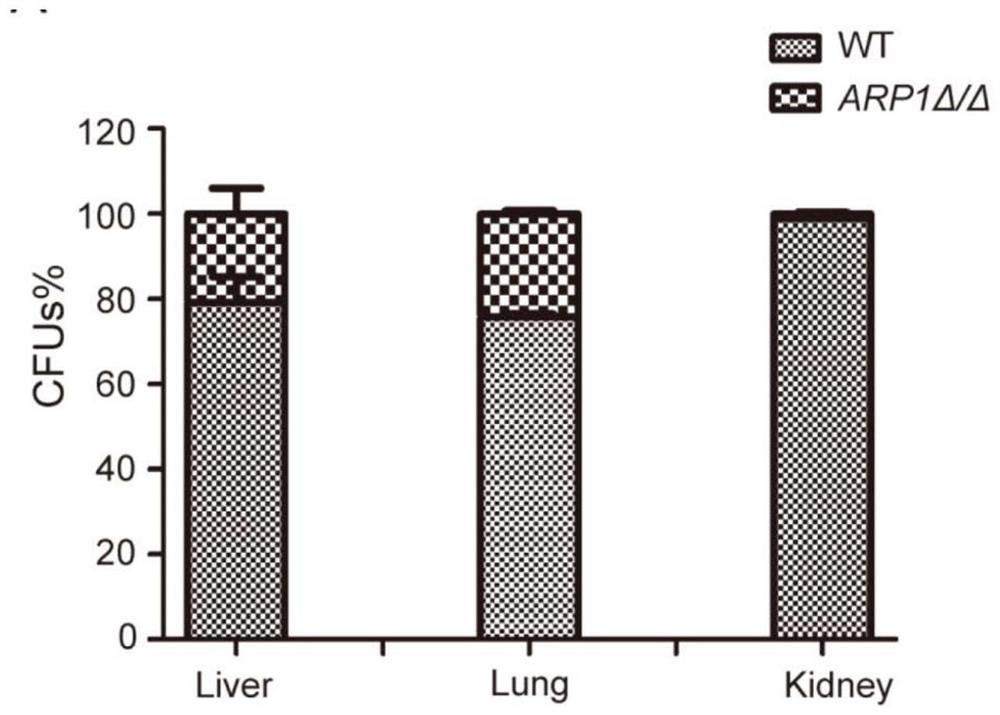
[0043] Example 3 Deletion of the ARP1 gene affects the colonization of Candida albicans in the kidney
[0044] To demonstrate the effect of the ARP1 gene on visceral colonization by Candida albicans. 1×10 6 Candida albicans wild strain and ARP1 deletion strain cells were mixed and injected into 4 six-week-old ICR mice. After 48 hours, kidneys, livers and lungs were collected, ground and homogenized, diluted appropriately and spread on YPD plates and SD-His plates. 30 Count the number of colonies after 2 days of incubation at °C. The result is as image 3 As shown, the proportion of ARP1-deficient strains in liver and lung was 20.8% and 24.3% respectively; while the proportion of ARP1-deficient strains in kidney was only 1.1%. This result indicated that the deletion of the ARP1 gene significantly affected the colonization ability of Candida albicans in the kidney.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com