Indirect time of flight range calculation apparatus and method of calculating a phase angle in accordance with an indirect time of flight range calculation technique
A time-of-flight, indirect technology, used in measurement devices, re-radiation of electromagnetic waves, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of doubling or doubling the number of samples, affecting the phase angle accuracy, etc., to reduce motion artifacts, large The effect of immunity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
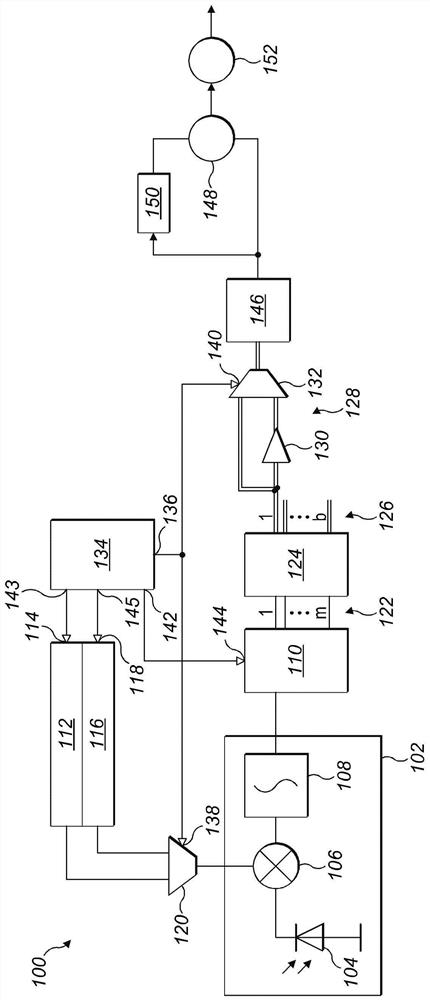
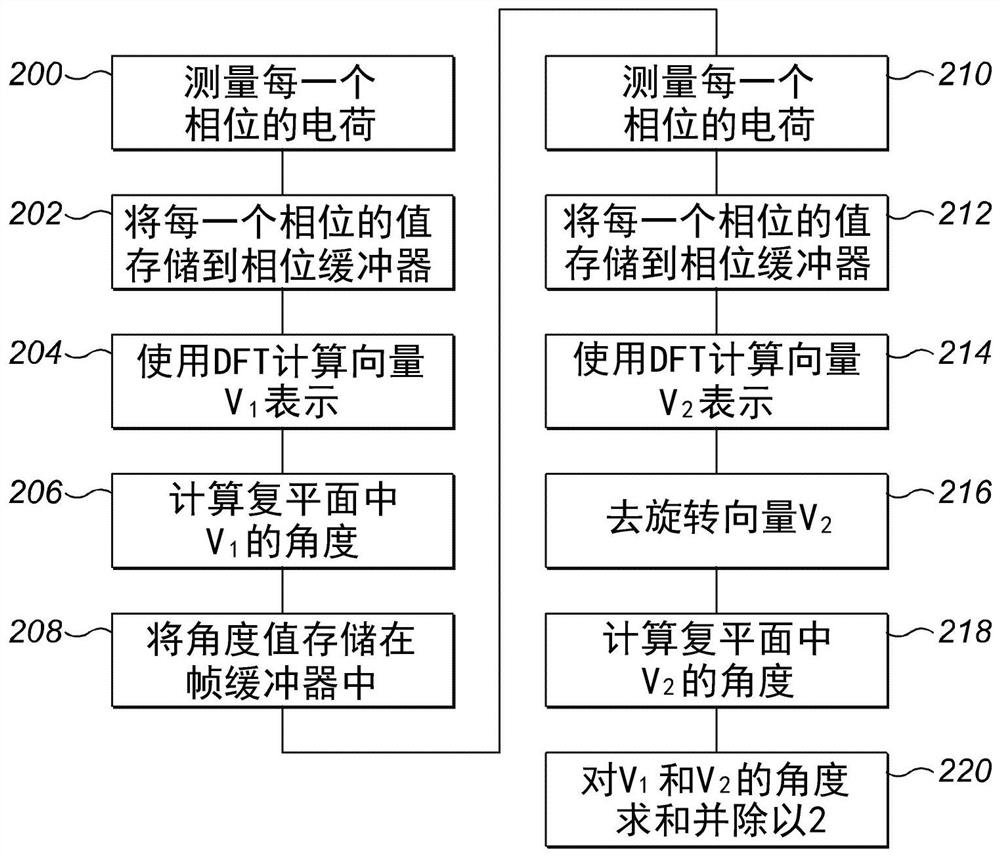
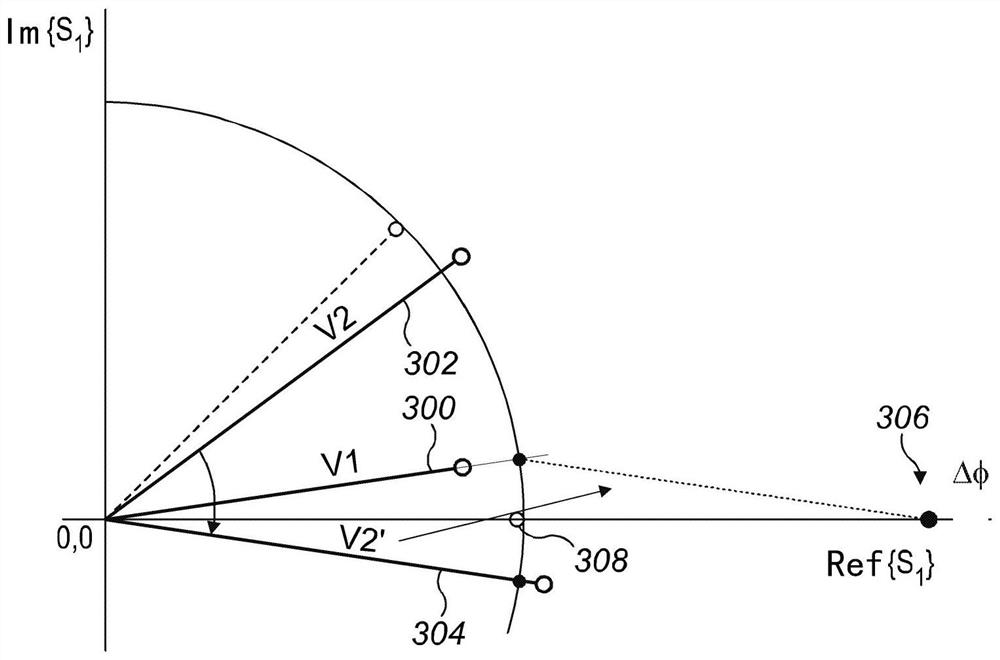
[0048] refer to figure 1 , the indirect time-of-flight distance calculation device 100 includes an electromagnetic radiation source (not shown), such as a laser diode (LD) or a light emitting diode (LED). In this example, the source of electromagnetic radiation is infrared light amplitude modulated for emission as a continuous wave optical signal according to an indirect time-of-flight measurement technique. The detection and ranging module of the apparatus includes an optical receiver photon mixer pixel device 102 that includes a photodiode 104 having an anode operatively coupled to ground potential and a coupling A cathode to a first input of a photon mixer 106 whose output is coupled to an input of an integrator 108 . The output of the integrator 108 is coupled to the input of a phase buffer 110 . In this example, a single photon mixer pixel device 102 is being described for simplicity and clarity of description. However, those skilled in the art will appreciate that the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com