Preparation method and application of biomass porous carbon material based on castor seed residues
A porous carbon material, biomass technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, carbon compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of influence, poor chemical functionality, high viscosity, etc., to achieve widespread application value, simple preparation method, excellent Effects of Capacitance Characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] 1. Mix castor bean residue (0.5g), concentrated sulfuric acid (10mL) and deionized water (30mL), seal in a 100mL reaction kettle, and heat at 180°C for 12 hours. The resulting mixture was filtered, and the filtered product was washed with deionized water several times, and dried at 80°C.
[0038] 2. the product after step (1) drying and K 2 FeO 4 Add deionized water at different mass ratios of 1:1, stir at room temperature for 8 hours, and dry at 80°C overnight after the reaction is complete to obtain a solid mixture.
[0039] 3. Heat the solid mixture to 600°C in a tube furnace, 2 Under the atmosphere, the heating rate was 5°C / min and kept for 2h. Then, the solid mixture was washed with 3M hydrochloric acid and deionized water until the solution became neutral. Finally, dry at 100°C to obtain a porous carbon material derived from castor bean residue.
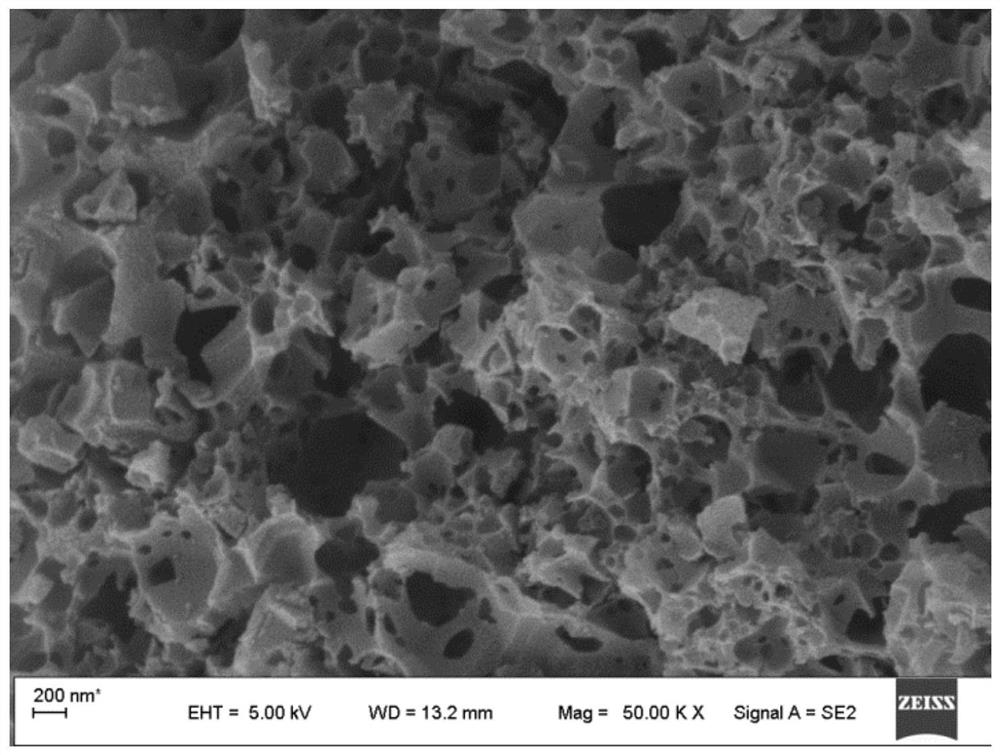
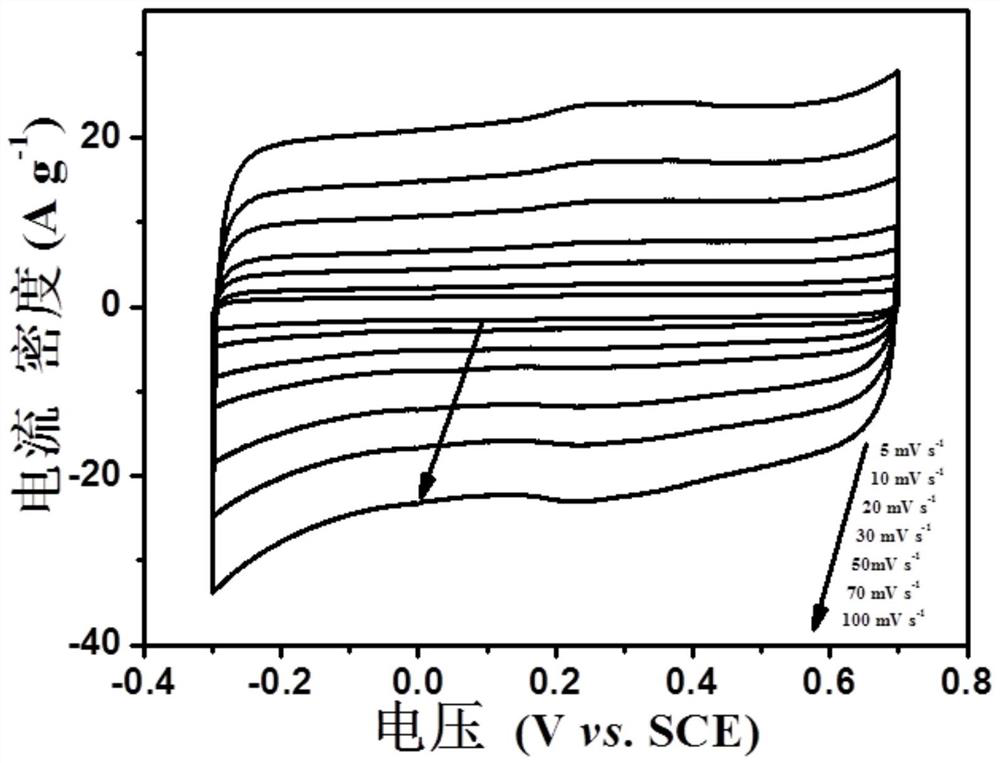
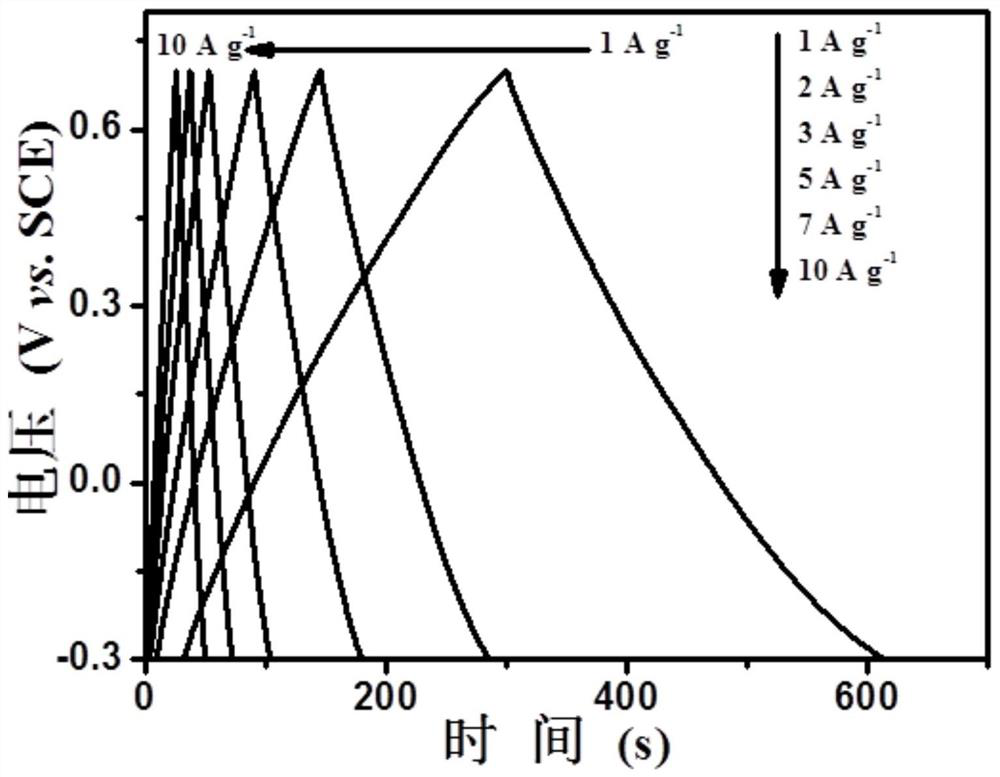
[0040] Morphological characterization of castor bean residue-derived porous carbon materials:
[0041] The morph...
Embodiment 2
[0053] 1. Mix castor bean residue (1.8g), concentrated sulfuric acid (3mL) and deionized water (40mL), seal in a 100mL reaction kettle, and heat at 120°C for 6 hours. The resulting mixture was filtered, and the filtered product was washed with deionized water several times, and dried at 80°C.
[0054] 2. the product after step (1) drying and K 2 FeO 4 Add deionized water at different mass ratios of 1:3, stir at room temperature for 10 h, and dry at 100°C overnight after the reaction is complete to obtain a solid mixture.
[0055] 3. Heat the solid mixture to 900°C in a tube furnace, 2 Under the atmosphere, the heating rate was 10°C / min and kept for 6h. Then, the solid mixture was washed with 1M hydrochloric acid and deionized water until the solution became neutral. Finally, dry at 80°C to obtain a porous carbon material derived from castor bean residue.
Embodiment 3
[0057] 1. Mix castor bean residue (1.2g), concentrated sulfuric acid (8mL) and deionized water (60mL), seal in a 100mL reactor, and heat at 160°C for 10 hours. The resulting mixture was filtered, and the filtered product was washed with deionized water several times, and dried at 80°C.
[0058] 2. the product after step (1) drying and K 2 FeO 4 Add deionized water at different mass ratios of 1:2, stir at room temperature for 12 h, and dry at 90°C overnight after the reaction is complete to obtain a solid mixture.
[0059] 3. Heat the solid mixture to 800°C in a tube furnace, 2 Under the atmosphere, the heating rate was 8°C / min and kept for 4h. Then, the solid mixture was washed with 2M hydrochloric acid and deionized water until the solution became neutral. Finally, dry at 90°C to obtain a porous carbon material derived from castor bean residue.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com