Preparation method of cellulose polyether polyol
A technology of polyether polyol and cellulose, applied in the field of modification of polyether polyol, can solve the problems of unseen, insoluble cellulose, etc., to ensure no pulverization, low shrinkage, and high conversion rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
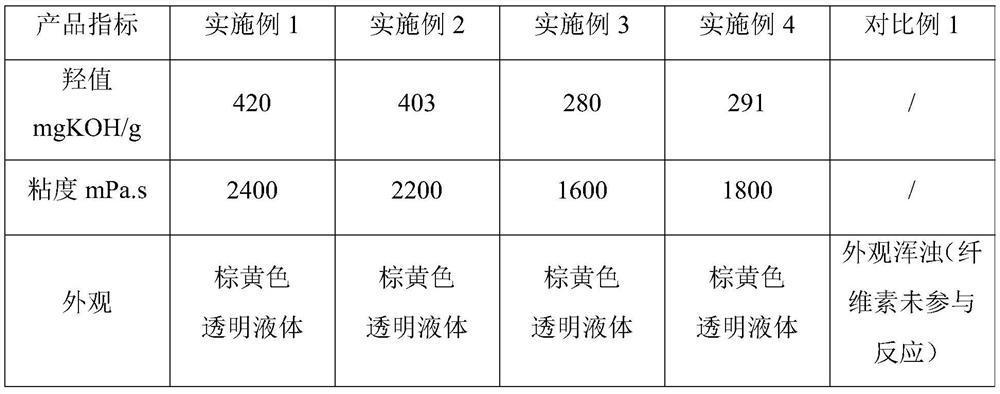
[0030] Put 25g of cellulose (molecular weight 0.7*10^5) into 500g water solvent system of 8wt% NaOH and 12wt% urea, and dissolve it in a freezing environment of 10±5°C to obtain an aqueous solution of NaOH, urea, and cellulose. Add this solution to a 2.5L polymerization reactor, then add 26g of diethylene glycol, and check the stamping of the polymerization reactor to ensure good sealing. After nitrogen replacement, vacuumize to the minimum vacuum degree of -0.093MPa, and control the temperature at 80± Add propylene oxide dropwise at 5°C until the amount of propylene oxide added is 360g, stop feeding propylene oxide, after the aging is completed, raise the temperature to 100±5°C, vacuumize and bubble nitrogen to remove the Moisture; after dehydration is completed, control the temperature at 108±2°C, continue to drop 220g of propylene oxide, and mature after the dropwise addition to obtain crude polyether; then the crude polyether is neutralized with phosphoric acid until the pH...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Put 20g of cellulose (molecular weight 0.7*10^5) into 500g of water solvent system of 8wt% NaOH and 12wt% urea, and dissolve it in a freezing environment at 5±5°C to obtain an aqueous solution of NaOH, urea, and cellulose. Add this solution to a 2.5L polymerization reactor, then add 26g of diethylene glycol, and check the stamping of the polymerization reactor to ensure good sealing. After nitrogen replacement, vacuumize to the minimum vacuum degree of -0.093MPa, and control the temperature at 80± Add propylene oxide dropwise at 5°C until the amount of propylene oxide added is 360g, stop feeding propylene oxide, after the aging is completed, raise the temperature to 95±5°C, vacuumize and bubble nitrogen to remove the Moisture; after dehydration is completed, control the temperature at 108±2°C, continue to drop 220g of propylene oxide, and mature after the dropwise addition to obtain crude polyether; then the crude polyether is neutralized with phosphoric acid until the p...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Put 15g of cellulose (molecular mass 0.7*10^5) into 500g water solvent system of 8wt% NaOH and 12wt% urea, and dissolve it in a freezing environment at -5±5°C to obtain an aqueous solution of NaOH, urea, and cellulose. Add this solution to a 2.5L polymerization reactor, then add 26g of diethylene glycol, and check the stamping of the polymerization reactor to ensure good sealing. After nitrogen replacement, vacuumize to the minimum vacuum degree of -0.093MPa, and control the temperature at 80± Add propylene oxide dropwise at 5°C until the amount of propylene oxide added is 360g, stop feeding propylene oxide, after the aging is completed, raise the temperature to 95±5°C, vacuumize and bubble nitrogen to remove the Moisture; after dehydration is completed, control the temperature at 108±2°C, continue to drop 520g of propylene oxide, and mature after the dropwise addition to obtain crude polyether; then the crude polyether is neutralized with phosphoric acid until the pH is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com