Animal species identification method
An identification method and species technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbe determination/inspection, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as difficult identification of animal species
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
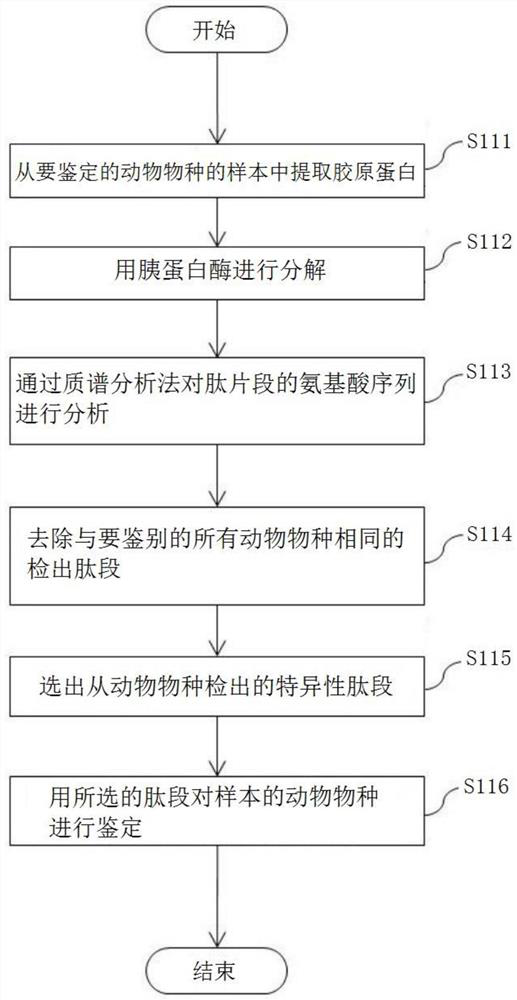
[0067] In this example, an example of identification of natural leather of 6 kinds of animals including cattle, horses, pigs, sheep, goats, and deer will be described.
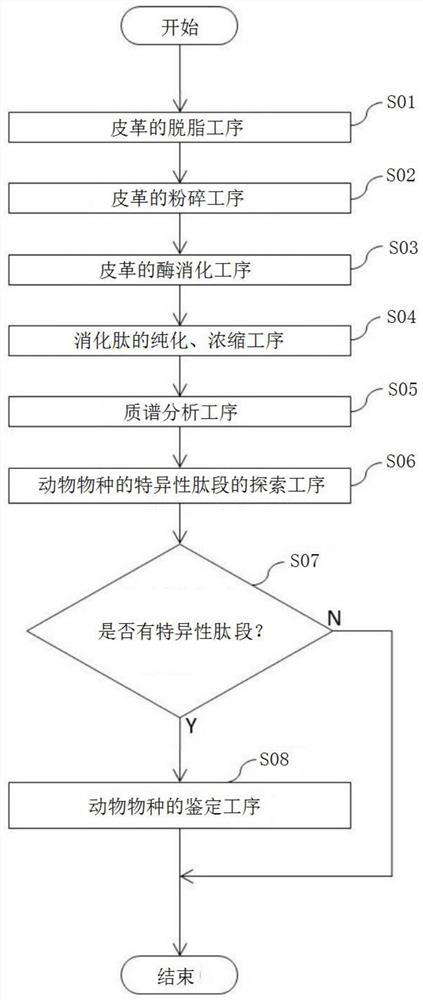
[0068]First, the tissue of the skin of an animal species of natural leather and the collagen of the main fiber will be described. Animal skin consists of the epidermis, dermis and underlying subcutaneous connective tissue. The epidermis is composed of 4 layers, including the cuticle and the granular layer, and the layers that are not used by leather are removed. In addition, the elastin fibers in the papillary layer and subcutaneous tissue are almost completely removed during mechanical manipulation or drug handling during manufacturing. In addition, keratin, which makes up hair, is useless when making leather except for fur, and is decomposed and removed by lime treatment. Therefore, the fibers that make up leather are mostly collagen fibers. The dermis is divided into the papillary layer (silver layer) an...
Embodiment 2
[0111] In this example, an example of identification of animal species of fur such as foxes, raccoons, and minks will be described.
[0112] About the process flow of the identification method of the animal species of the fur of fox, raccoon, mink etc., also same as embodiment 1, follow figure 1 process.
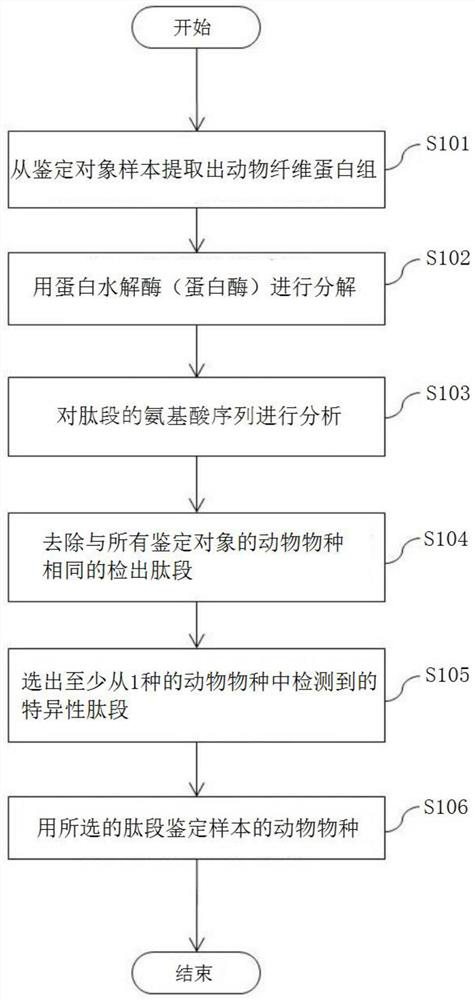
[0113] First, keratin is extracted from the fur of fox, raccoon, mink, etc. (step S101). The extracted keratin is decomposed with keratinase (step S102). As the keratin-decomposing enzyme, trypsin can be used.
[0114]Next, in the same manner as in Example 1, the amino acid sequences of the peptides are analyzed (step S103), the detected peptides that are identical to all identified animal species are removed (step S104), and the peptides detected from the animal species are selected. specific peptides (step S105). Then, use the selected peptides to identify the animal species of the sample (step S106).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com