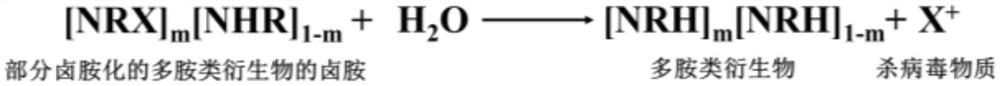Coating having virus killing function and formed on surface of article and coating method of coating
A virus-killing and article-killing technology, applied in botanical equipment and methods, devices for coating liquids on surfaces, coatings, etc., can solve the problem of preventing haloamine compounds from being retrieved, inability to complete the transcription process, and inability to produce specific proteins And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
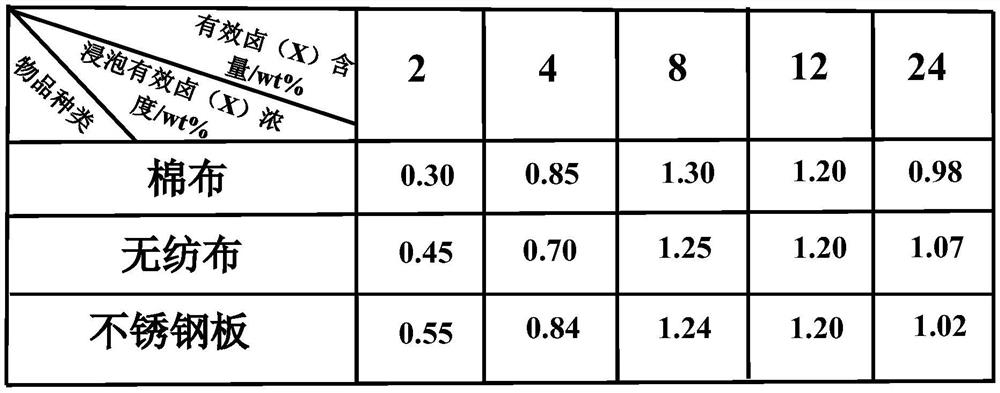
Embodiment 1
[0049] Step 1, prepare polyallylamine solution, the solution concentration is 100mg / mL;
[0050] Step 2, preparation of available chlorine cation (Cl + ) content is a chlorinating agent solution of 5.00wt%;
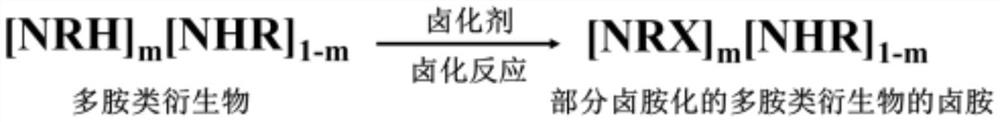
[0051] Step 3, when the molar fraction m of the monomer repeating unit of the amino group of haloamination in the polyallylamine solution is m=0.4, calculate the consumption of required available chlorine cation (Cl+), then step 2 The prepared chlorinating agent solution is added dropwise in the prepared solution of step 1, and stirred while adding dropwise to make it react uniformly;
[0052] Step 4. Dialyzing the solution prepared in Step 3 to obtain a partially chloraminated polyamine derivative solution. Its concentration is 50mg / mL, and its available chloride cation (Cl + ) content is 2.00wt%;
[0053] Step 5, select cotton cloth as the substrate article (material) of coating;
[0054] Step 6. Treat the cotton cloth in an oxygen environment of a plasma cleaner f...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Step 1, prepare polyethyleneimine solution, the solution concentration is 100mg / mL;
[0065] Step 2, preparation of available chlorine cation (Cl + ) content is a chlorinating agent solution of 5.00wt%;
[0066] Step 3, when the molar fraction m=0.4 of the monomer repeating unit of the amine group of chlorination in polyethyleneimine solution, calculate required available chlorine cation (Cl + ), then the chlorinating agent solution prepared in step 2 is added dropwise in the prepared solution of step 1, and stirred while adding dropwise, to make its uniform reaction;
[0067] Step 4. Dialyzing the solution prepared in Step 3 to obtain a partially chloraminated polyamine derivative solution. Its concentration is 100mg / mL, and its available chloride cation (Cl + ) content is 2.00wt%;
[0068] Step 5, select cotton cloth as the substrate article (material) of coating;
[0069] Step 6. Treat the cotton cloth in an oxygen environment of a plasma cleaner for 5 minutes t...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Step 1, prepare poly-N-methylformamide solution, the solution concentration is 100mg / mL;
[0078] Step 2, preparation of available chlorine cation (Cl + ) content is a chlorinating agent solution of 3.00wt%;
[0079] Step 3, when the molar fraction m=0.4 of the monomer repeating unit of the amino group of chloramination in the N-methylformamide solution, calculate the required available chlorine cation (Cl + ), then the chlorinating agent solution prepared in step 2 is added dropwise in the prepared solution of step 1, and stirred while adding dropwise, to make its uniform reaction;
[0080] Step 4. Dialyzing the solution prepared in Step 3 to obtain a partially chloraminated polyamine derivative solution. Its concentration is 60mg / mL, and its available chloride cation (Cl + ) content is 2.50wt%;
[0081] Step 5, select cotton cloth as the substrate article (material) of coating;
[0082] Step 6. Treat the cotton cloth in an oxygen environment of a plasma cleaner f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com