Distributed optical fiber light source control system suitable for wide temperature range
A distributed optical fiber and light source control technology, applied to thermometers, thermometers with physical/chemical changes, measuring devices, etc., to achieve the effects of reduced stability and simple temperature compensation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
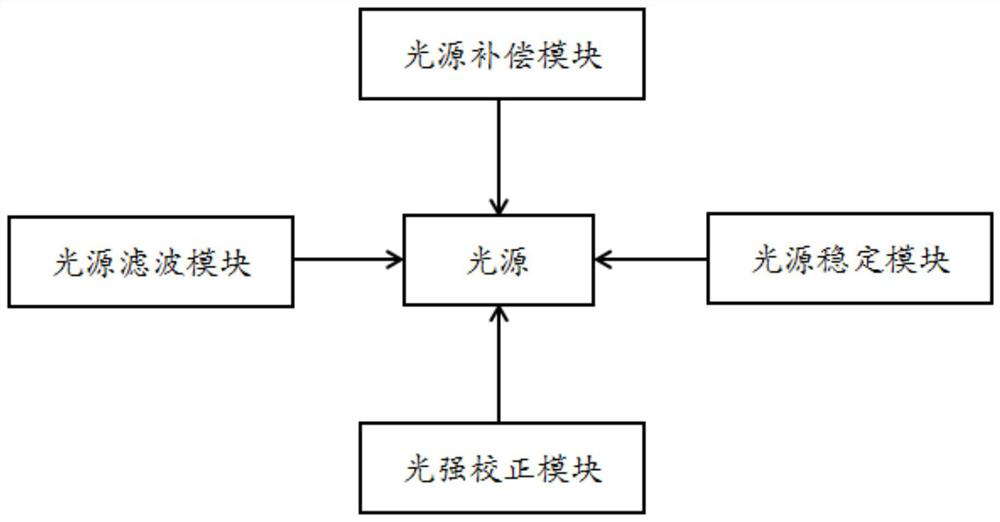
[0027] The embodiment is basically as attached figure 1 shown, including:
[0028] light source;
[0029] The light source filter module, the light source filter module includes a positive temperature coefficient long period fiber grating and a negative temperature coefficient long period fiber grating; wherein, the central wavelength of the positive temperature coefficient long period fiber grating increases with the temperature rise, and the average wavelength acting on the light source increases with the The decreasing interval when the temperature presents a parabolic change; the central wavelength of the long-period fiber grating with a negative temperature coefficient decreases as the temperature rises, and acts on the increasing area when the average wavelength of the light source presents a parabolic change with the temperature;
[0030] The light source compensation module is used to perform compensation calculation on each component of the light source according to ...
Embodiment 2
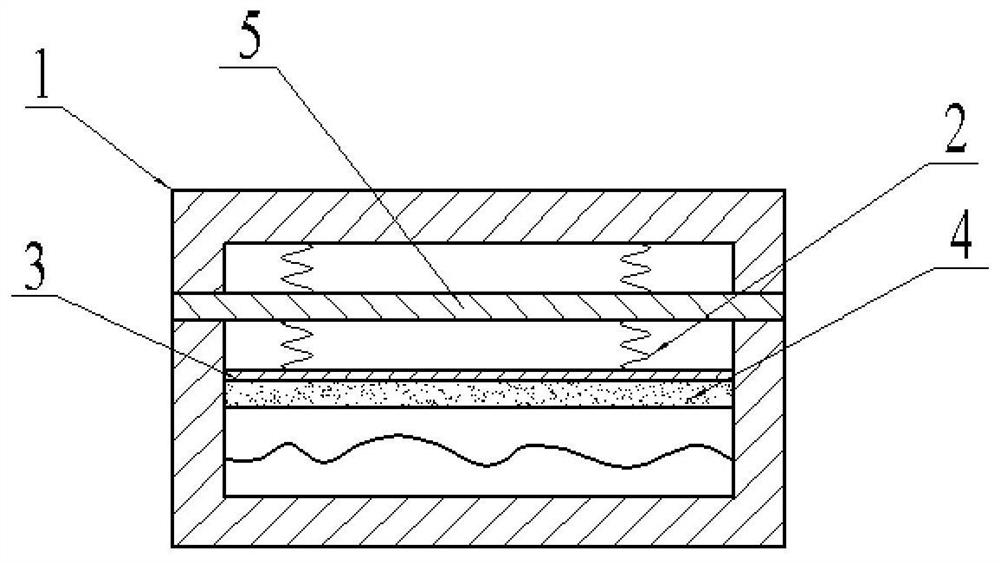
[0040] The only difference from Embodiment 1 is that it also includes a fixing groove and a protective shell, and the positive temperature coefficient long-period fiber grating and the negative temperature coefficient long-period fiber grating are fixed through the fixing groove, that is, the positive temperature coefficient long-period fiber grating and the negative temperature Coefficient long-period fiber gratings are fixed on the grooves to alleviate the effects of thermal expansion and contraction to prevent loosening. At the same time, a positive temperature coefficient long-period fiber grating and a negative temperature coefficient long-period fiber grating are arranged in sequence in the protective case, so as to protect the positive temperature coefficient long-period fiber grating and the negative temperature coefficient long-period fiber grating from water and dust. Protective effects.
Embodiment 3
[0042] The only difference from Embodiment 2 is that in this embodiment, the optical fiber 5 is used in winter in Northeast China, the daily temperature difference between day and night can be above 20-30°C, and the temperature change rate can reach 4-6°C / h; a part of the optical fiber 5 One is buried in the soil and the other is exposed to the air. Soil temperature will show seasonal fluctuations and diurnal changes with the change of air temperature near the surface; at the same time, due to the influence of periodic diurnal and annual changes in solar radiation, soil temperature will also change accordingly, making the annual change of soil temperature show It is a sinusoidal function, and the variation range of temperature decreases with the increase of soil depth. At a certain depth, the amplitude can be considered to be approximately zero. In addition, due to the different heat transfer coefficients of soil and air, the temperature of the soil is usually higher than that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com