Method for treating zinc-containing and carbon-containing industrial solid waste in steel production process
A technology for production process and industrial solid waste, applied in fluidized bed furnaces and other directions, can solve the problems of high reduction temperature, large process energy consumption, long reduction time, etc., and achieve high temperature reactivity, low temperature, and energy consumption. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] In this example, blast furnace dust is used as zinc-containing carbon-containing industrial solid waste. The main components of blast furnace dust include: Fe: 35%, Zn: 3.53%, C: 20.6%, and the rest are impurities. The molar ratio of C / Zn in blast furnace dust is 32.6.
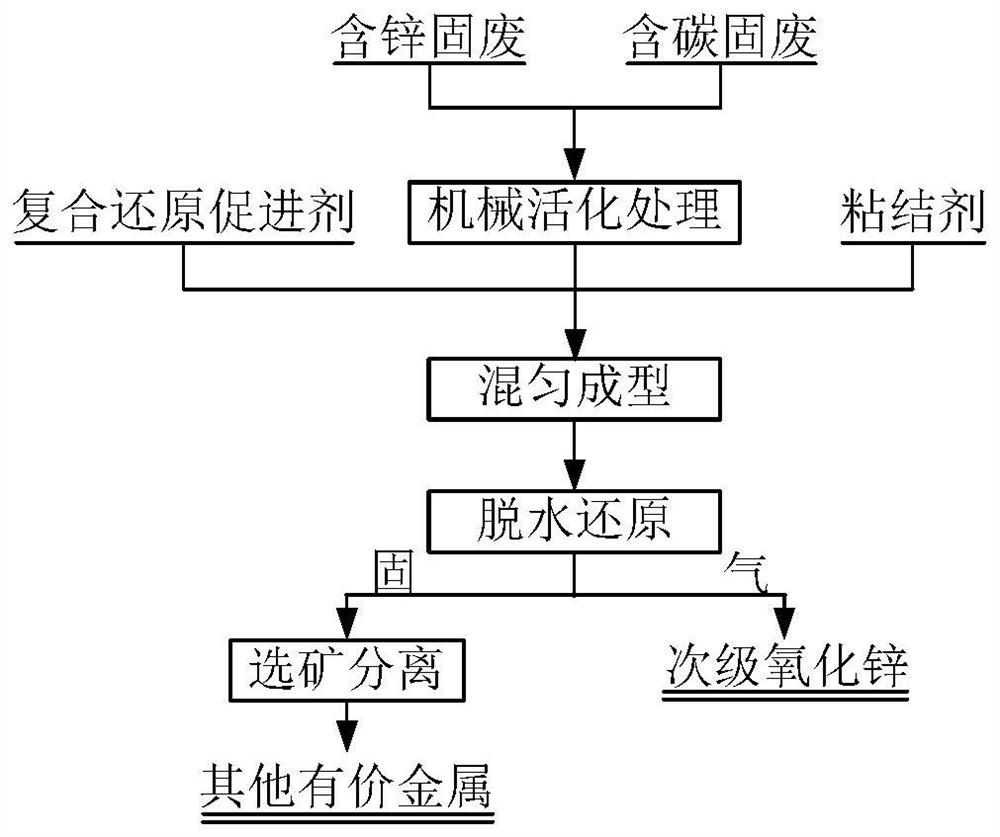
[0037] In this embodiment, the method for treating industrial solid waste containing zinc and carbon in the iron and steel production process specifically includes the following steps:
[0038] (1) Mechanically activate the above-mentioned blast furnace dust removal ash, and the particle size of the blast furnace dust removal dust after mechanical activation treatment is not more than 160 mesh;
[0039] (2) CaCO 31. Mix the blast furnace dust, bentonite and a small amount of water after mechanical activation treatment, and the mixed sample is pressed and formed by a press;
[0040] (3) drying the compressed mixed material at 150°C;
[0041] (4) Reducing the bulk material obtained in step (3) at a hig...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The method for processing zinc-containing solid waste and carbon-containing solid waste in the iron and steel production process in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0047] (1) Mechanically activate the above-mentioned blast furnace dedusting ash and electric furnace dedusting ash, and the particle size of the blast furnace dedusting ash after mechanical activation treatment is not more than 160 mesh;
[0048] (2) CaCO 3 , MgCO 3 and BaCO 3 According to the mass ratio of 6:3:1, the composite reduction accelerator obtained by mixing, the mixture of blast furnace dedusting ash and electric furnace dedusting ash after mechanical activation treatment, bentonite and a small amount of water are mixed evenly, and the mixed sample is pressed into shape by a press;
[0049] (3) drying the compressed mixed material at 110°C;
[0050] (4) Reducing the bulk material obtained in step (3) at a high temperature of 950° C. for 25 minutes, and recovering th...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The method for processing zinc-containing solid waste and carbon-containing solid waste in the iron and steel production process in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0055] (1) Mechanically activate the above-mentioned blast furnace dedusting ash and electric furnace dedusting ash, and the particle size of the blast furnace dedusting ash after mechanical activation treatment is not more than 160 mesh;
[0056] (2) CaCO 3 and MgCO 3 Mix the composite reduction accelerator obtained by mixing according to the mass ratio of 7:3, the mixture of blast furnace dedusting ash and electric furnace dedusting ash after mechanical activation treatment, diatom mud and a small amount of water, and mix evenly, and the mixed sample is pressed into shape by a press;
[0057] (3) drying the compressed mixed material at 200°C;
[0058] (4) Reducing the bulk material obtained in step (3) at a high temperature of 1050° C. for 10 minutes, and recovering the reduce...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com