Rapid and ultrahigh-sensitivity DNA fusion gene detection method
A technology that combines genes and genes, applied in the field of bioinformatics analysis, can solve problems such as excessive false positive information, consumption of computing resources, and insufficient sensitivity, to achieve high sensitivity, reduce computing resource consumption, and shorten running time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
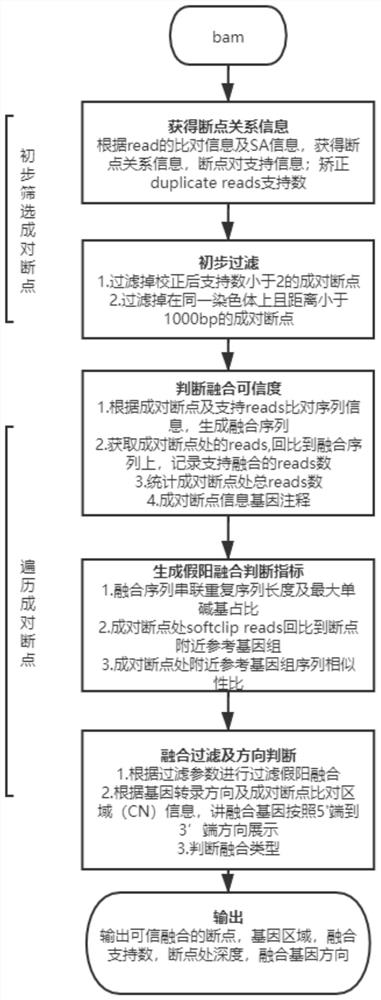
[0080] Embodiment 1 method is established
[0081] (1) Breakpoint search and preliminary screening
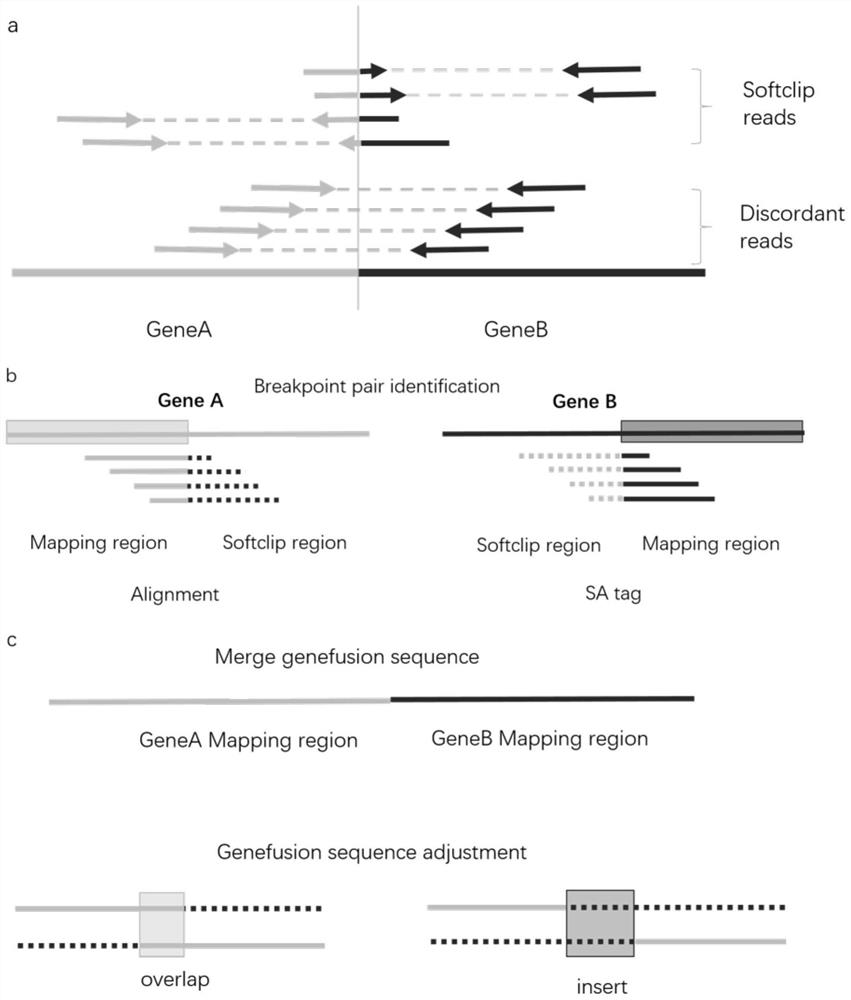
[0082] a. Paired breakpoint search: directly search for reads with soft clip areas in the BAM file, and obtain all paired breakpoint information at one time: I. Determine the breakpoint 1 through the main comparison position and cigar value of soft clipped reads Position and CN region; II. Determine the position and CN region of breakpoint 2 according to the comparison position and cigar value of the secondary comparison information (SA tag) of soft clipped read; III. Statistics have the same paired breakpoint and CN region The number of reads is the number of Supply_Support support for paired breakpoints.
[0083] b. Fusion Supply_Support support number correction: Correct the false positive fusion problem caused by the high support number caused by PCR duplicate, and record it as the dupcount support number.
[0084] c. Preliminary filtering of breakpoints: It is generally ...
Embodiment 2
[0117] Embodiment 2 tissue sample simulation test
[0118] The specific fusion information of the positive standard product in this embodiment is shown in Table 2 below. In this embodiment, a total of 10 cases of HD753 were used as gDNA standard products to simulate fresh tissue samples to test the detection effect of this method. DNA sequencing data were obtained for all samples using targeted capture, and the target capture range covered the fusion breakpoint position in the standard. The sequencing depth is 2500X.
[0119] Table 2 Standard product fusion gene information
[0120]
[0121] The sequencing data of 10 samples were compared and analyzed using the BWA (v0.7.17) MEM algorithm, and the "-Y" parameter was set to retain the softclip region sequence for subsequent fusion sequence correction and fusion event verification. The rest of the parameters use the default parameters of the BWA MEM algorithm. The reference sequence uses the human reference genome version...
Embodiment 3
[0127] Example 3 Liquid biopsy sample simulation test
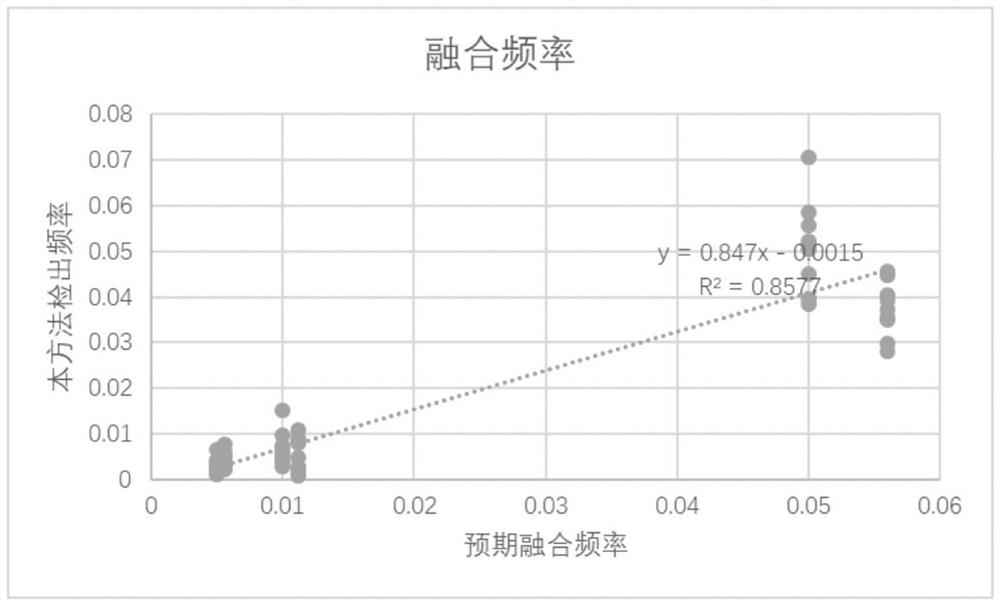
[0128] Liquid biopsy requires higher and higher sensitivity for fusion detection, so this example uses HD786 cfDNA standard for testing. There are SLC34A2-ROS1, CCDC6-RET fusions with a frequency of about 5% in the HD786 standard. In order to obtain a lower frequency of fusion-positive standards, HD786 standards were mixed with fusion-negative samples in different proportions, and fusion-positive cfDNA samples with expected frequencies of 1% and 0.5% were simulated. In this embodiment, three groups are set, each group has 10 repeated samples, and the information is shown in Table 5. The experimental sequencing depth was 10000X. The specific analysis process is the same as in Example 1, and this method is used for fusion analysis. The fusion detection results are shown in Table 6, all detected by this method. And the running time is significantly shortened under the same thread (20 threads), as shown in Table 7. The f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com