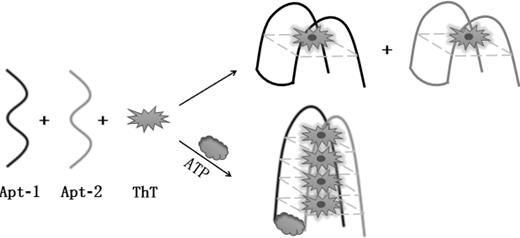
Method for detecting ATP (adenosine triphosphate) based on resolution type nucleic acid aptamer and thioflavin T
A nucleic acid aptamer, thioflavin technology, applied in the field of biosensing and analysis, can solve the problems of limited use, low specificity, false positive signals, etc., and achieve the effect of rapid method and improved sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1: Feasibility analysis of ATP detection
[0035] 1) DNA pretreatment: In order to remove the secondary structure of the ATP aptamer, the aptamer was pretreated before use. First, heat Apt-1 and Apt-2 with a volume of 4 µL and a concentration of 10 µM and 42 µL of buffer solution II at 90-95°C for 5-10 minutes, and then incubate on ice for 10-15 minutes.
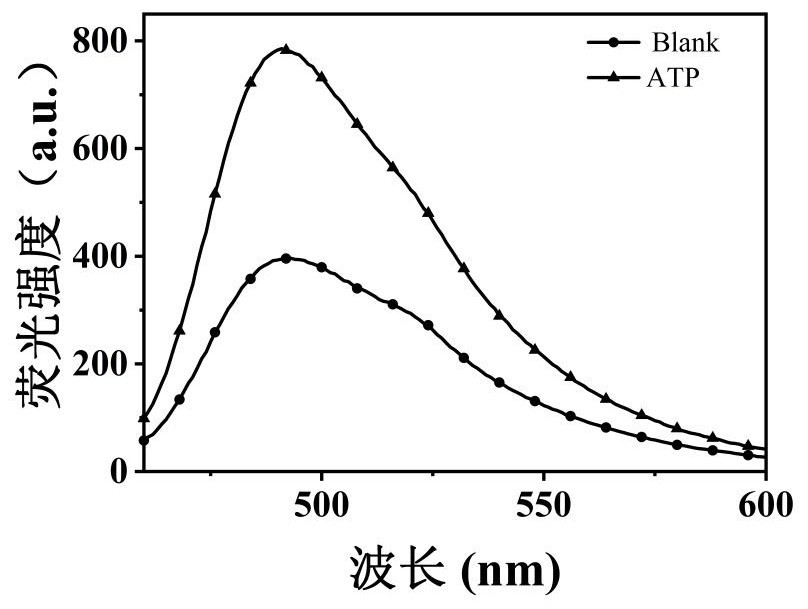
[0036] 2) Add 4 µL of 100 µM ThT solution to the pretreated solutions containing Apt-1 and Apt-2, and react at 36~38°C for 50~60 minutes. One group was used as a blank control, and the other group was added with 4 µL of 100 mM ATP as a positive control.
[0037] Such as figure 2 As shown, the blank group has weak fluorescence, and the positive control group has obvious fluorescence enhancement signal, which is about 2 times stronger, which fully demonstrates the feasibility of the scheme.
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: The specificity analysis that ATP detects
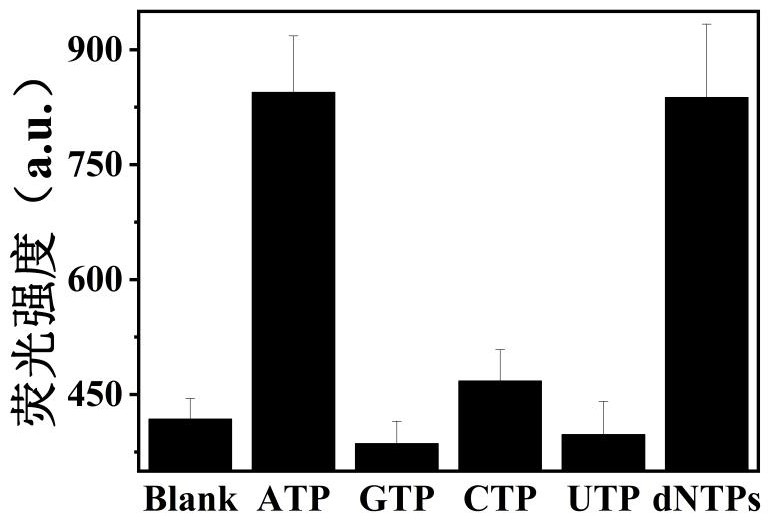
[0039] Add 4 µL of ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP and dNTPs at a concentration of 100 mM to the pretreated solutions containing Apt-1 and Apt-2, and then add 4 µL of a ThT solution at a concentration of 100 µM, and finally add the buffer solution Ⅱ After the total volume of the solution reaches 100 µL, react at 36-38°C for 50-60 minutes. Samples containing only Apt-1, Apt-2 and ThT served as blank controls.
[0040] Such as image 3 As shown, the fluorescence intensities of the blank, GTP, CTP and UTP systems are relatively weak. Similar to the system with the addition of ATP, the fluorescence intensity of the system after the addition of dNTPs is also significantly enhanced. This is because the dNTPs also contain the same concentration of ATP in addition to the analogs containing ATP, so they have a significant fluorescence response. The results show that this method has Good specificity.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: the sensitivity analysis of ATP detection
[0042] Add different volumes (0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.5, 2, 3, 4 µL, 100 mM) of ATP solution to the pretreated solutions containing Apt-1 and Apt-2, and then add 4 µL of 100 µM ThT solution, finally add buffer solution II until the total volume of the solution is 100 µL, then react at 36~38°C for 50~60 minutes.
[0043] Such as Figure 4 As shown, as the concentration of ATP gradually increased in the range of 0-1000 μM, the fluorescence signal intensity also gradually increased. Moreover, within the range of ATP concentration of 0-500 µM, there is a good linear relationship between the fluorescence signal intensity and the ATP concentration, and its linear regression equation is y=0.66x+364.38 (R 2 =0.96398), where y represents the fluorescence intensity value, and x represents the concentration of ATP in the system (µM). According to the 3σ rule, the limit of detection (LOD) of ATP in the buffer solution system was c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com