Method for promoting nodulation and nitrogen fixation of root system of tumorous stem mustard by using azorhizobium caulinodans
A technology of nitrogen-fixing rhizobia and stem mustard, applied in horticultural methods, botany equipment and methods, applications, etc., to achieve great application value, increase crop yield, and reduce environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
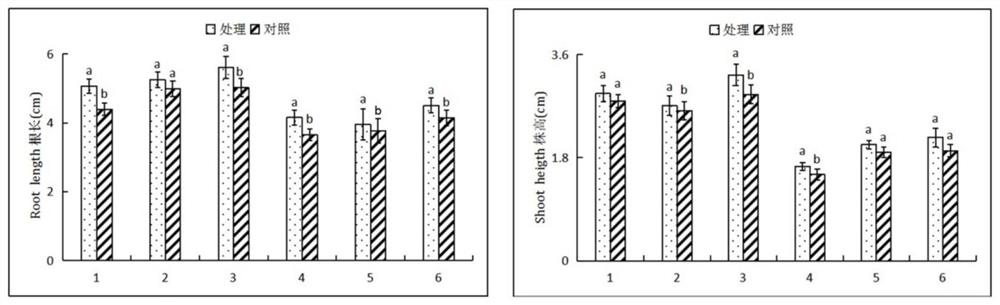
[0033] Example 1: Research on the Growth-promoting Effect of Rhizobium on Stem Mustard
[0034] 1. Seed treatment and bacterial solution configuration
[0035] Select uniform and plump mustard seeds with roughly the same particle size and place them in 2ml centrifuge tubes, place the centrifuge tubes in an ultra-clean workbench, soak the seeds with 50% NaClO for 10 minutes, shake the centrifuge tubes during soaking to ensure that all the seeds are soaked, pour out the cleaning solution Use a pipette gun to draw sterile water to rinse and disinfect the surface. The rinsing solution is replaced with a pipette gun with a sterilized 1ml tip. The surface-sterilized seeds were placed in a tissue culture bottle, and the surface of a high-temperature sterilized agar-water solid medium (hereinafter referred to as the medium) was poured into the tissue culture bottle for limited bacterial culture. Placed on a conventional culture rack for cultivation.
[0036]Activation and expansion...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 Different concentrations of rhizobia infecting the tuber mustard infection experiment
[0042] Disinfect the surface of the seeds of Fuza No. 2 in the same way as above, place them on agar-water solid medium for bacterial culture at the upper limit, and when the seeds germinate to the stage of two leaves and one heart, remove the ungerminated seeds with tweezers, leaving seedlings with roughly the same growth status. Put the rhizobia bacteria liquid in the logarithmic growth phase in a 50ml centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 4500r / m for 10min to collect the bacteria, and dilute them with PBS buffer to 1.0×10 9 cfu / mL, 1.0×10 8 cfu / mL, 1.0×10 7 cfu / mL, 1.0×10 6 Four different concentrations of cfu / mL are available for use. Pipette 1ml of rhizobia bacteria solution at different concentrations to the surface of the culture medium, set 4 replicates for each concentration, 10 grains per bottle, and connect the same amount of PBS for parallel control, set 4 replicate...
Embodiment 3
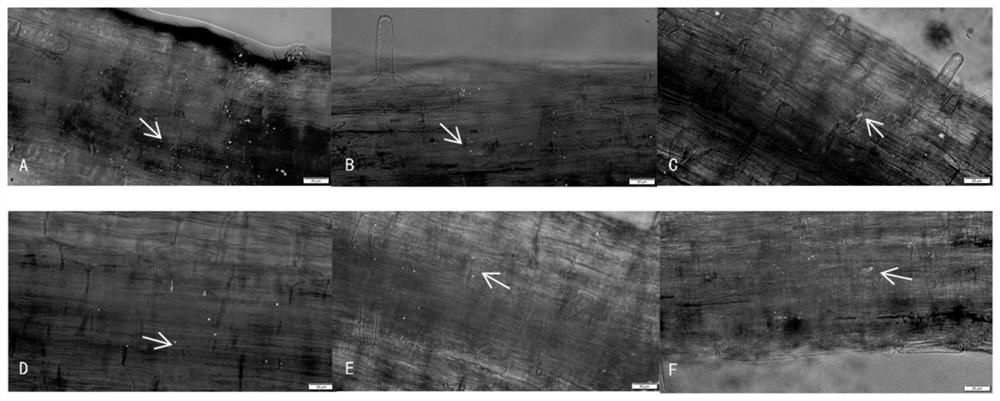
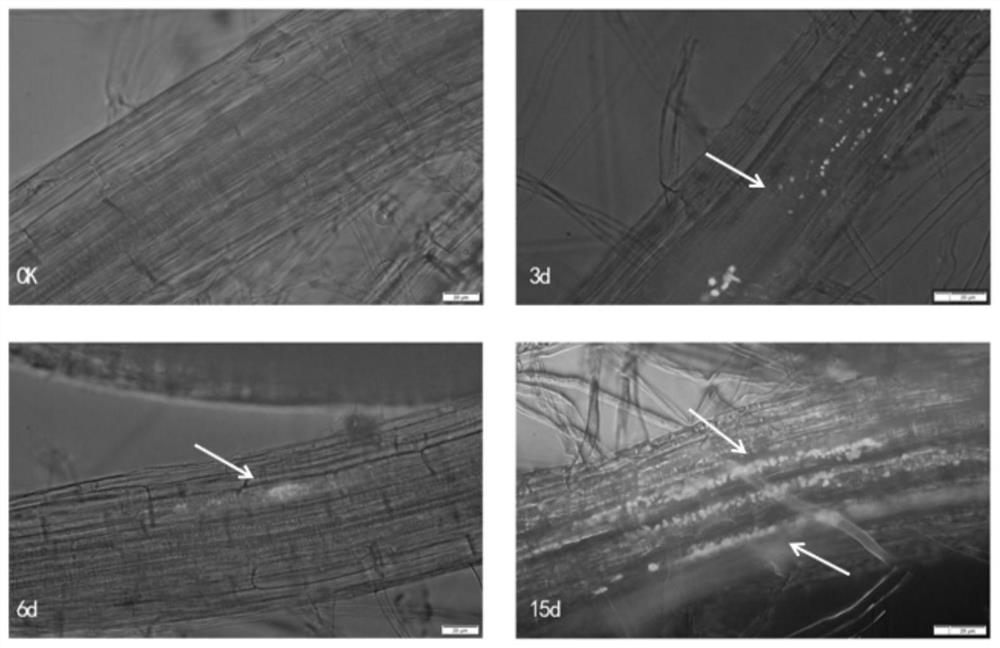
[0046] Example 3 Observation on the colonization of rhizobia in the root system of Stem mustard
[0047] Under indoor conditions, the plump seeds of Fuza No. 2 were used for surface disinfection, and the disinfection method was the same as above. Placed in agar-water solid medium for upper-limit bacterial culture, germinated to the stage of two leaves and one heart, each tissue culture bottle draws 1mL1.0×10 8 The cfu / mL PBS diluted bacterial solution was added to the surface of the agar-water solid medium to inoculate the tuber mustard seedlings. After inoculation, seal the tissue culture vials with parafilm to avoid contamination. Place conventional intelligent culture racks to limit bacterial culture. Set time gradients on the 3d, 6d, 9d, 12d, 15d, 18d, and 21d of inoculation, and regularly use a fluorescence microscope to detect the colonization of GFP-labeled A. caulinodans in the roots of the stem mustard seedlings.
[0048] Pick representative tuber mustard seedlings...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com