Biomarker for typing non-small cell lung cancer, and application thereof
A non-small cell lung cancer, biomarker technology, applied in the field of medical detection, can solve the problem of pathological judgment error, poor differentiation and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Based on the public database, the preliminary screening of variant gene markers for pathological subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer includes the following steps:
[0045] 1. Screening of candidate mutation sites.
[0046] Whole-genome sequencing data of tumor tissues of patients with non-small cell tumors were obtained from the TCGA database (https: / / portal.gdc.cancer.gov / ): In this study, a total of 561 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (including 286 cases of adenocarcinoma and 286 cases of adenocarcinoma) were downloaded. 275 cases of squamous cell carcinoma) whole genome sequencing data, four different software (mutect, varscan, muse and somaticsniper) were used to calculate the mutation sites respectively, and at least two of the four mutation software were used to simultaneously call the mutation sites in the samples as candidates mutation site.
[0047] 2. Potential marker screening.
[0048] Difference analysis was performed based on the adenocarcin...
Embodiment 2
[0053] In this embodiment, the potential markers obtained above are analyzed and verified on clinical samples, including the following steps:
[0054] 1. Tissue sample acquisition:
[0055] The related FFPE section samples of 374 cases of non-small cell lung cancer (191 cases of adenocarcinoma and 183 cases of squamous cell carcinoma) were collected from Jinan University.
[0056] 2. Sample sequencing analysis:
[0057] FFPE tissue samples were analyzed by whole genome sequencing by a third party (Clearcode Biotechnology).
[0058] 3. Model establishment.
[0059] 3.1 The model is initially established.
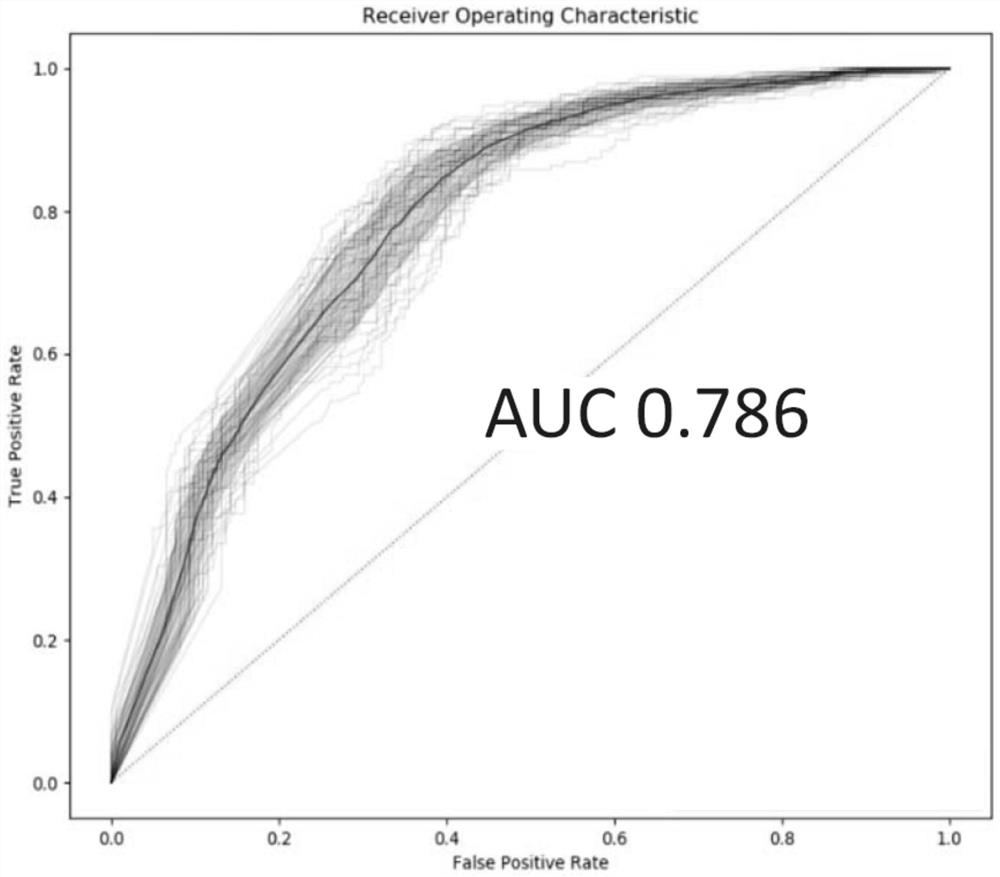
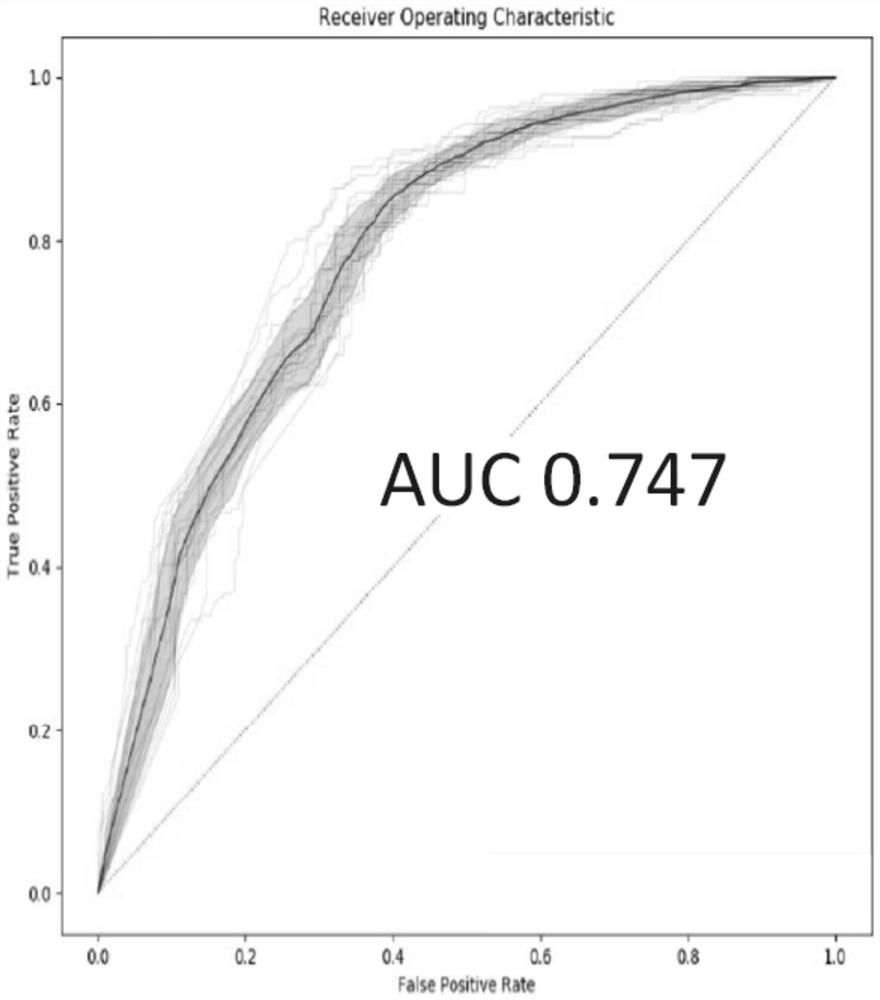
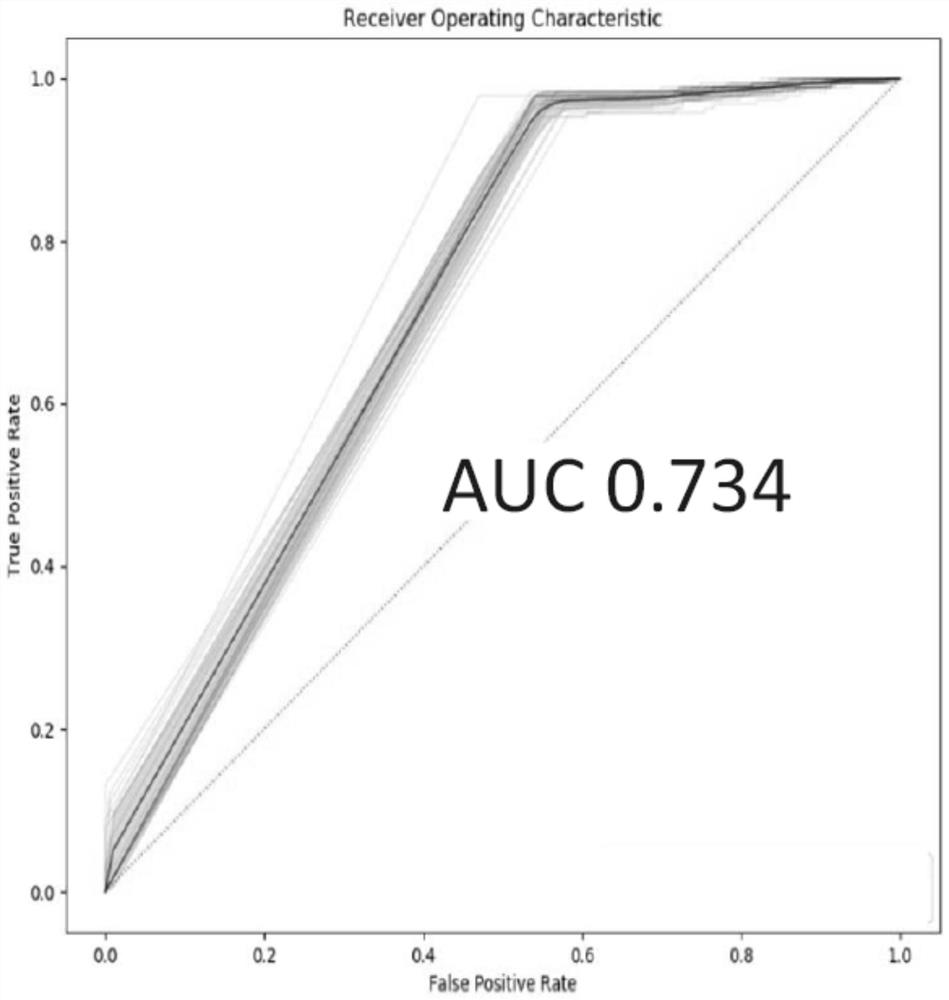
[0060] Using all the potential markers obtained in Example 1 above, the independent verification set, that is, the above-mentioned 191 cases of adenocarcinoma and 183 cases of squamous cell carcinoma of non-small cell lung cancer patient tissue samples were detected and judged, and the random forest model was used for modeling analysis ( R package randomForest), according...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Select 13 cases of non-small cell lung cancer clinically judged as non-small cell lung cancer samples from Jinan University, which are different from the sample set in Example 2, and use the 20 MARKER combined models established in Example 2 above for analysis, and compare the analysis results with clinical experts The judgment results are compared, and the results are shown in the table below.
[0069] Table 2. Clinical validation results
[0070] cases Model typing results Expert Judgment Results number 1 Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma number 2 squamous cell carcinoma squamous cell carcinoma number 3 Adenocarcinoma squamous cell carcinoma No 4 squamous cell carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Number 5 Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma number 6 Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma Number 7 squamous cell carcinoma squamous cell carcinoma number 8 Adenocarcinoma Adenocarcinoma No.9 squamous cell carcino...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com