Acid-resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae and application thereof in preparation of organic acid
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and organic acid, which is applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of resource waste environment, increase the cost and process of product separation and purification, pollution, etc., and achieve the effects of saving costs, reducing separation and purification processes, and super acid resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1: Evolution and screening of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells
[0047] Specific steps are as follows:
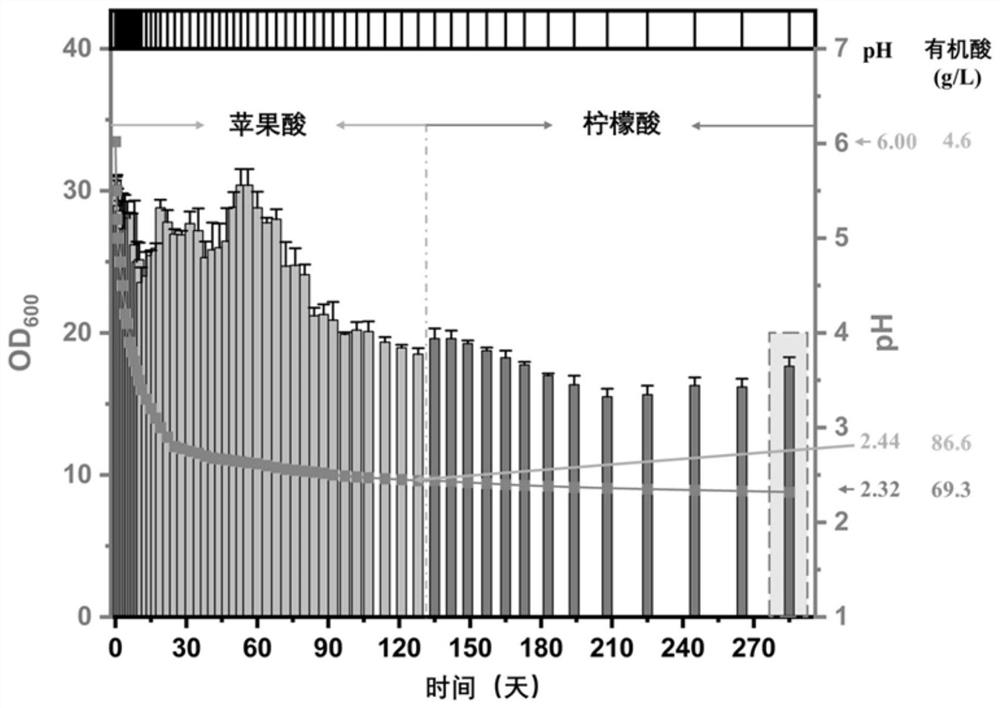
[0048] (1) Using Saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2-1C as the starting strain, malic acid was used as the selection pressure in the first stage, and different concentrations of malic acid were added exogenously, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae tolerant to lower pH was screened by directed evolution mutant strain. By adding different concentrations of malic acid, the pH is controlled to decrease step by step (starting from pH 6.0, the amount of exogenous malic acid added is 4.6g / L), and after the cells in each pH level have evolved to be able to grow, flat culture is carried out for enrichment (The target is the OD of the cells at 48h at this pH 600 Stability is reached, and there is no significant increase in the first two times; the purpose is to increase the number of mutant cells and make cell growth more stable at this pH) before proceeding to the evolution of...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Analysis of cell stability of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CTPth-2
[0054] In order to verify the stability of the obtained Saccharomyces cerevisiae CTPth-2 under low pH conditions, the specific steps are as follows:
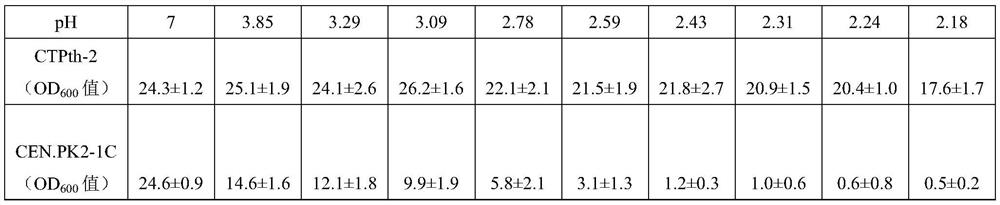
[0055] After Saccharomyces cerevisiae CTPth-2 was continuously passaged for 50 times, Saccharomyces cerevisiae CTPth-2 and the starting strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2-1C were inoculated into YPD medium respectively. In the case of growth comparison. The added concentration (g / L) of exogenous citric acid is 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, and the pH values are 7.0, 3.85, 3.29, 3.09, 2.78 , 2.59, 2.43, 2.31, 2.24, 2.18; samples were taken every 12 hours until 72 hours, and the growth status of the strain was determined. The results are shown in Table 1, wherein Saccharomyces cerevisiae CTPth-2 is abbreviated as CTPth-2; the starting strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae CEN.PK2-1C is abbreviated as CEN.PK2-1C.
[0056] Table 1: OD of ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of malic acid
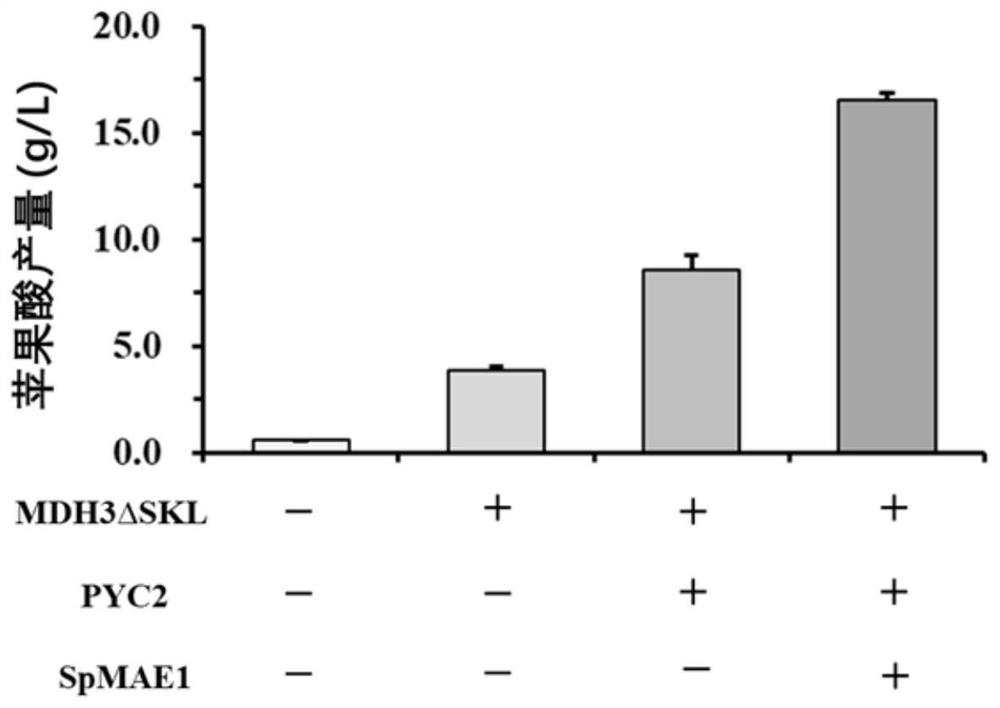
[0060] In order to better verify the potential of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CTPth-2 as a chassis cell to produce organic acids, in the present invention, taking malic acid as an example, the target product is synthesized through metabolic modification.
[0061] Specific steps are as follows:
[0062] 1. Construction of recombinant strains:
[0063] (1) Chemically synthesize the nucleotide sequence encoding malate dehydrogenase MDH3ΔSKL (malate dehydrogenase MDH3 removes the last three amino acids SKL), the nucleotide sequence encoding pyruvate carboxylase pyc2, and the nucleus encoding malate transporter SpMAE1 Nucleotide sequence (wherein, the nucleotide sequence encoding the MDH3 enzyme is shown in SEQ ID NO.2, the nucleotide sequence encoding the PYC2 enzyme is shown in SEQ ID NO.4, the encoding SpMAE1 enzyme The nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.6);
[0064] (2) Construction of the recombinant vector:
[0065] T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com