Controlled-release fertilizer for corn and preparation method of controlled-release fertilizer
A technology for controlled release fertilizers and corn, applied in fertilizer mixtures, layered/coated fertilizers, nitrogen fertilizers, etc., can solve problems such as increasing labor costs, and achieve the effects of low production costs, improved controlled release period, and low dissolution rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
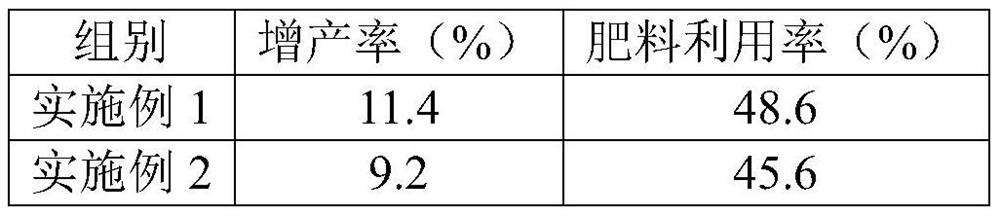
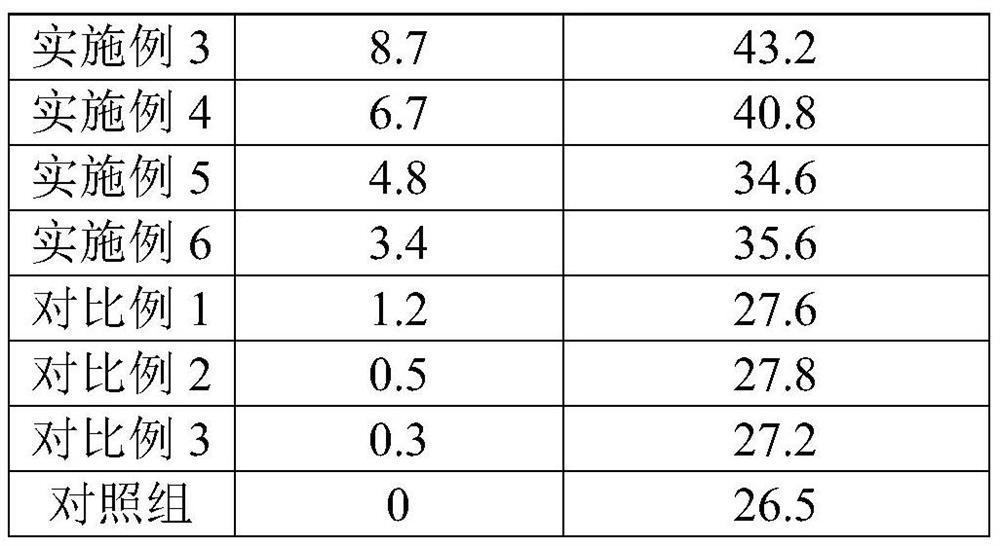
Examples
preparation example 1
[0043] This preparation example provides a kind of controlled-release urea, and the preparation method is as follows:
[0044] Mix 20 parts of carboxymethyl cellulose, 100 parts of polyethylene oxide polyol, 10 parts of ethylene glycol, and 5 parts of sulfuric acid, then quickly heat up to 160°C and react for 90 minutes, and wait until the solvent turns into a brown-black liquid and cool to 25°C That is to realize the graft copolymerization of cellulose and polyether polyol to obtain liquefied cellulose. At 85°C, pour 480g of urea into the fluidized bed to preheat for 15 minutes. After the preheating is completed, add 3mL of liquid paraffin, and then slowly drop 25g of a mixture containing toluene diisocyanate and liquefied cellulose (n(NCO):n(OH)=1:1) into the fluidized bed for urea coating reaction. The reaction is completed in 15 minutes, and the controlled-release urea is prepared after the urea particles are completely coated.
preparation example 2
[0046] This preparation example provides a kind of controlled-release urea, and the preparation method is as follows:
[0047] After mixing 10 parts of carboxylated cellulose nanofibers, 110 parts of polyoxypropylene polyol, 5 parts of glycerin, and 8 parts of phosphoric acid, the temperature was quickly raised to 160 ° C for 90 minutes, and the solvent turned into a brown-black liquid and cooled to 25 °C to achieve graft copolymerization of cellulose and polyether polyol to obtain liquefied cellulose. At 85°C, pour 500g of urea into the fluidized bed to preheat for 15 minutes. After the preheating is completed, add 5mL of liquid paraffin, and then slowly drop 30g of the mixture containing p-phenylene diisocyanate and liquefied cellulose (n(NCO):n(OH)=1:1) into the fluidized bed for the coating reaction of urea . The reaction is completed in 15 minutes, and the controlled-release urea is prepared after the urea particles are completely coated.
preparation example 3
[0049] This preparation example provides a kind of controlled-release urea, and the preparation method is as follows:
[0050] Mix 30 parts of methyl propyl cellulose, 90 parts of polytetrahydrofuran, 15 parts of butanediol, and 3 parts of nitric acid, then quickly heat up to 160°C and react for 90 minutes, and wait until the solvent turns into a brown-black liquid and cool to 25°C. Liquefied cellulose is obtained by grafting and copolymerizing cellulose and polyether polyol. At 85°C, pour 450g of urea into the fluidized bed to preheat for 15 minutes. After preheating is completed, add 1mL of liquid paraffin, and then slowly drop 15g of a mixture containing diphenylmethane diisocyanate and liquefied cellulose (n(NCO):n(OH)=1:1) into the fluidized bed for urea coating. Membrane reaction. The reaction is completed in 15 minutes, and the controlled-release urea is prepared after the urea particles are completely coated.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com