Control method and system for dead-beat current prediction of permanent magnet motor without position sensor
A permanent magnet motor and current prediction technology, which is applied in the control system, motor control, vector control system, etc., can solve the problems of low current prediction accuracy, large system size, weight, and high maintenance cost, and achieve improved system robustness, Solve the effects of phase lag and sensitivity reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
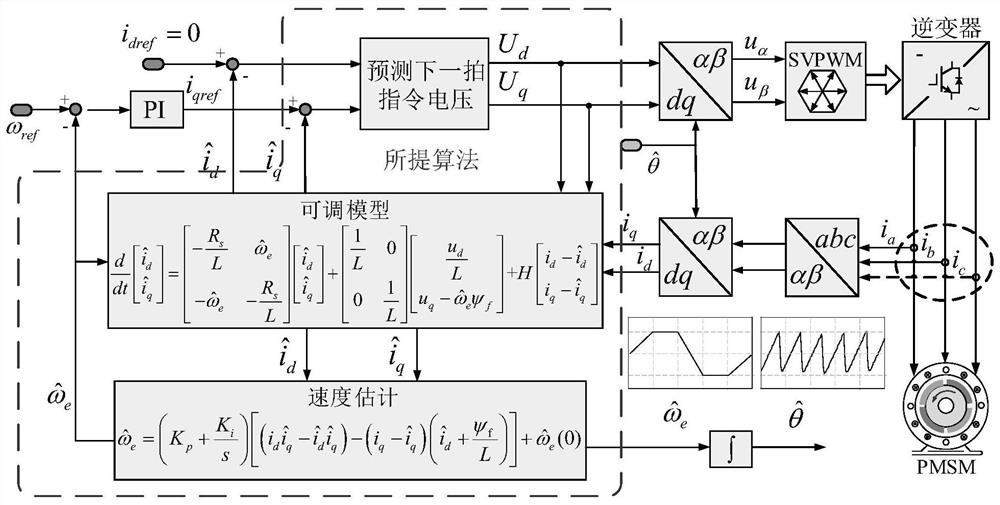
[0057] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 This embodiment will be described. A control method for deadbeat current prediction of a position sensorless permanent magnet motor described in this embodiment, the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0058] Step 1. Rewrite the stator voltage flux equation in the motor rotating coordinate system into the stator current form, and use the stator current form equation as a reference model, and use the deadbeat current prediction equation including the feedback gain matrix as an adjustable model, and Build an adaptive observer according to the reference model and the adjustable model;
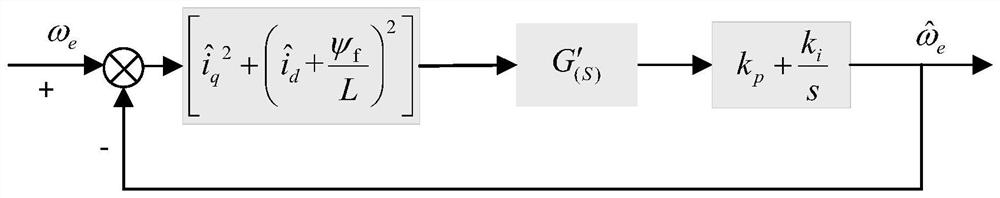
[0059] Step 2, based on the adaptive observer constructed in step 1, obtain the estimated values of the rotor electrical angular velocity and the rotor position angle;
[0060] Using the estimated value of the rotor electrical angular velocity, the rotor electrical angular velocity estimation process is sorted into a s...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0066] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that in the first step, the stator voltage flux equation under the motor rotating coordinate system is rewritten into the stator current form, and the specific process is as follows:
[0067] The expression of the stator voltage flux equation is shown in formula (1):
[0068]
[0069] Among them: u d is the actual stator voltage in the d-axis coordinate system, u q is the actual stator voltage in the q-axis coordinate system; i d is the actual stator current in the d-axis coordinate system, i q is the actual stator current in the q-axis coordinate system; R s is the stator resistance; L d is the inductance in the d-axis coordinate system, L q is the inductance in the q-axis coordinate system; ψ d is the stator flux linkage in the d-axis coordinate system, ψ q is the stator flux linkage in the q-axis coordinate system; ω e is the rotor electrical angular velocity; ψ ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
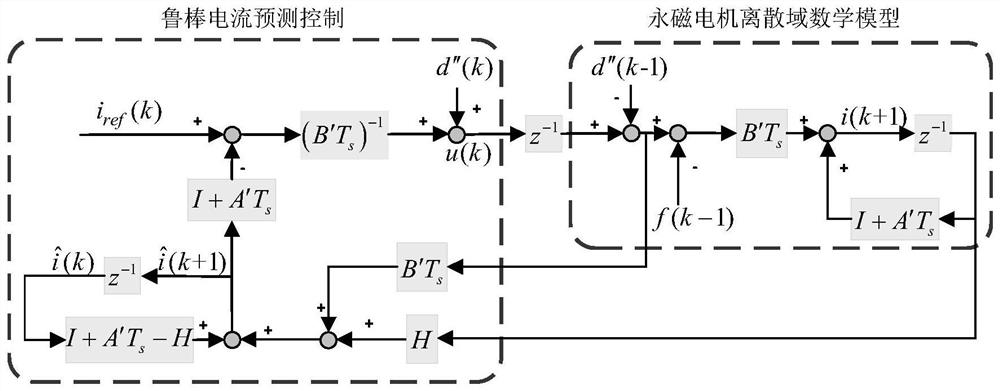
[0076] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 2 in that the deadbeat current prediction equation including the feedback gain matrix is:
[0077]
[0078] where: i, are the actual stator current and the estimated stator current respectively, d″ is the back EMF vector of the adjustable model, A′ and B′ are the state matrix coefficients of the adjustable model, H is the feedback gain matrix;
[0079] The expression of the state matrix coefficient A', B' of the adjustable model is: A'=-a' 1 I+a' 2 J,B'=b 1 I, a' 1 = R s / L, is the estimated value of the rotor electrical angular velocity; the expression of the feedback gain matrix H is: H=h 1 I+h 2 J, h 1 and h 2 is the feedback gain matrix parameter; the estimated stator current The expression is is the estimated stator current in the d-axis coordinate system, is the estimated stator current in the q-axis coordinate system, and the expression of the back EMF vector d″ of the adjustable m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com