Microwave wireless energy transmission system
A technology of energy transmission and microwave wireless, applied in the direction of electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of high frequency requirements of microwave energy transmission signals, rectification efficiency and capacity of rectification circuits that cannot meet application-level requirements at the same time, and efficiency reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
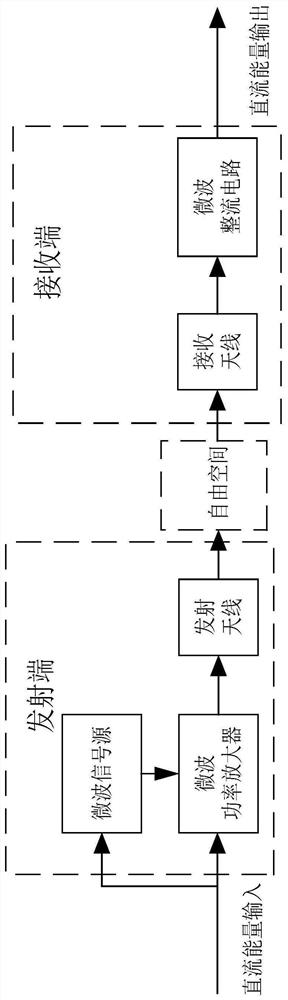
[0028] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a microwave wireless energy transmission system. In the microwave wireless energy transmission system, the function of the receiving end is to receive the microwave energy directionally transmitted to the microstrip antenna in the air, and convert it into DC power and output it to the load. The device used to complete the receiving and conversion functions is called a rectifying antenna. The rectifying antenna is composed of two parts: the receiving antenna and the rectifying circuit. The receiving antenna is used to efficiently receive and transmit the microwave signal transmitted from the air to the rectifying circuit. Then the high-frequency microwave signal is converted into a DC signal and output to the load.
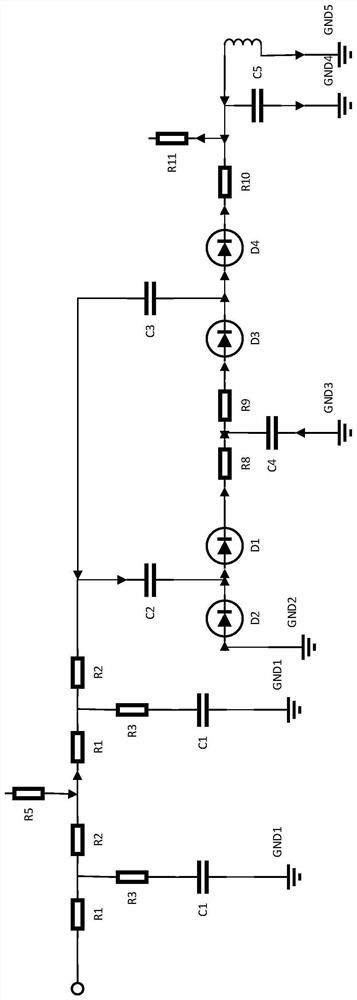
[0029] Such as figure 2 As shown, the rectifier circuit is composed of three parts: input filter, rectifier diode and output filter. The input filter is a low-pass filter, which is used to pass the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com