Method for evaluating microplastic pollution level based on plant physiology indexes
A pollution level, microplastic technology, applied in the field of environmental ecology, can solve the problem of difficult to know the impact of microplastics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
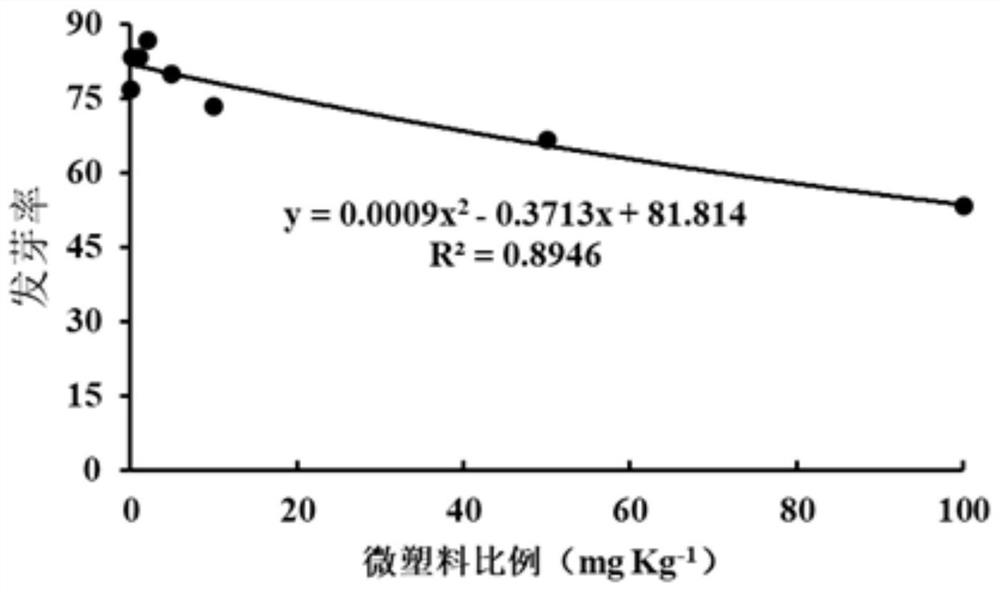
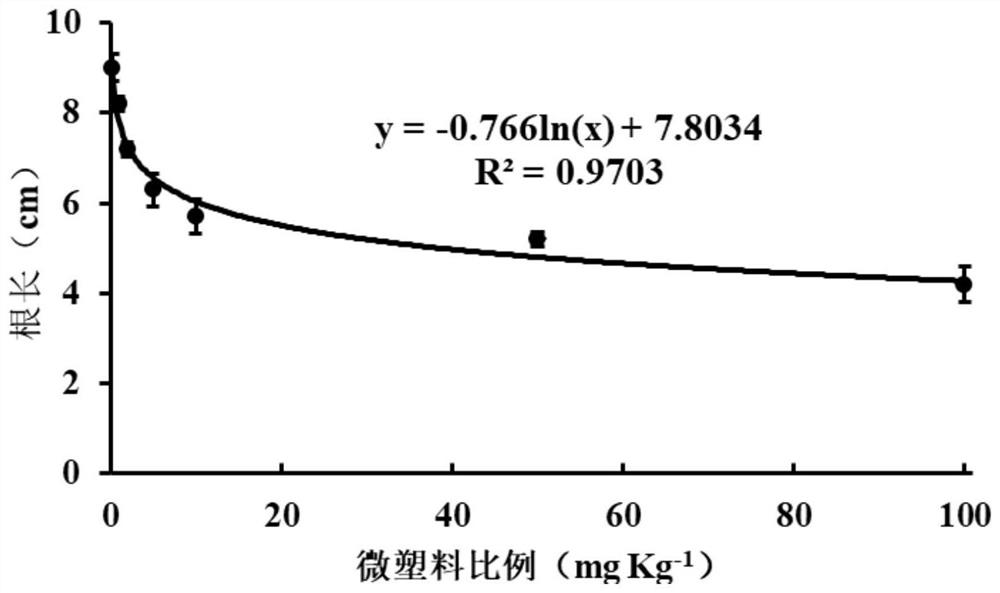
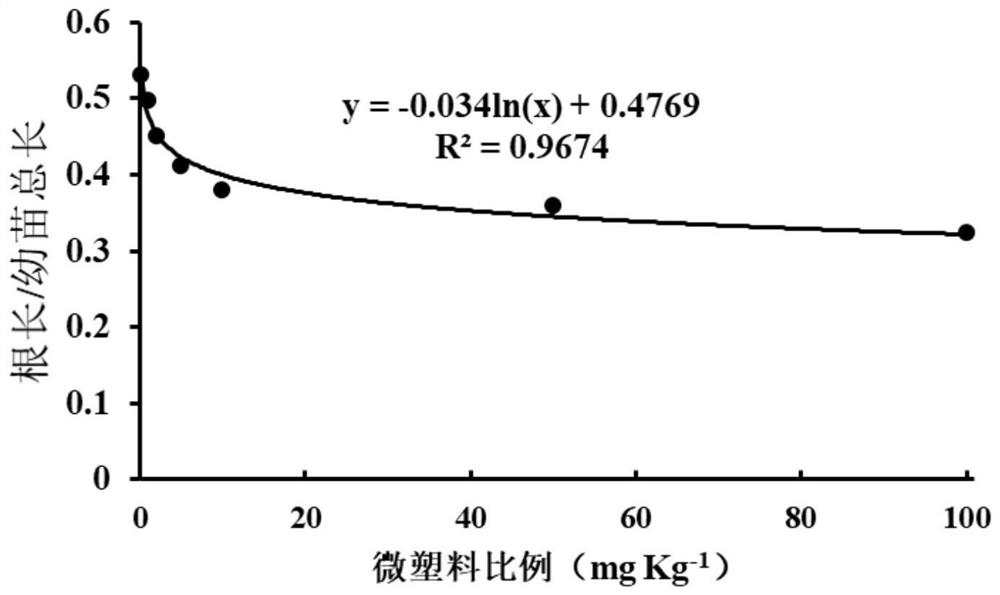
[0030] (1) Seed collection: Collect Spartina alterniflora seeds that are plump and of uniform shape in the wild coastal wetlands.
[0031] (2) Microplastic treatment:
[0032] Collect the masks in the sediment, cut them into pieces, and pass through a 200-mesh sieve through a pulverizer to obtain microplastics, then clean the microplastics with ultrapure water and absolute ethanol, and then add HNO to the microplastics 3 +H 2 o 2 The mixed solution was soaked at room temperature for 1 h, then heated to 250 °C for 2 h, evaporated and concentrated after cooling down, and filtered with a 0.45 μm water phase filter head to obtain the microplastic sample to be used.
[0033] Microplastics of different weights were weighed, and ethanol and purified water (1:1) were added to them, followed by ultrasonication for 1 h to make them evenly distributed, and the concentrations of microplastics were 0, 0.2, 1, 2, 5, 10 , 50, 100 mg / kg suspension.
[0034] (3) Spartina alterniflora seeds...
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) Seed collection: Collect Spartina alterniflora seeds that are plump and of uniform shape in the wild coastal wetlands.
[0038] (2) Microplastic treatment:
[0039] Collect the masks in the sediment, cut them into pieces, and pass through a 200-mesh sieve through a pulverizer to obtain microplastics, then clean the microplastics with ultrapure water and absolute ethanol, and then add HNO to the microplastics 3 +H 2 o 2 The mixed solution was soaked at room temperature for 1 h, then heated to 250 °C for 2 h, evaporated and concentrated after cooling down, and filtered with a 0.45 μm water phase filter head to obtain the microplastic sample to be used.
[0040] Microplastics of different weights were weighed, and ethanol and purified water (1:1) were added to them, followed by ultrasonication for 1 h to make them evenly distributed, and the concentrations of microplastics were 0, 0.2, 1, 2, 5, 10 , 50, 100 mg / kg suspension.
[0041] (3) Add Spartina alterniflora s...
Embodiment 3
[0045]The antioxidant system in plants has a certain response to pollution stress, which is the key factor determining the resistance of plant cells to oxidative stress, that is, under pollution stress, plants will produce oxygen free radicals during their internal metabolism, and excessive oxygen free radicals cause oxidative damage to plants. In this example, the levels of superoxide (POD), superoxide dismutation (SOD), catalase (CAT) and malondialdehyde (MDA) of Spartina alterniflora exposed to different concentrations of microplastic pollution were detected. To further explore the evaluation indicators of microplastic pollution levels.
[0046] The POD activity was determined by the guaiacol method, the SOD activity was determined by the NBT photoreduction method, the CAT activity was determined by the same method, and the MDA content was determined by thiobarbituric acid.
[0047] Plant roots are in direct contact with pollutants in soil / water and are the most sensitive ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com