Free-form surface construction method for laser beam shaping
A construction method and laser beam technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as material overheating, damage, normal vector deviation of data sampling points, etc., and achieve the effect of uniform energy distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
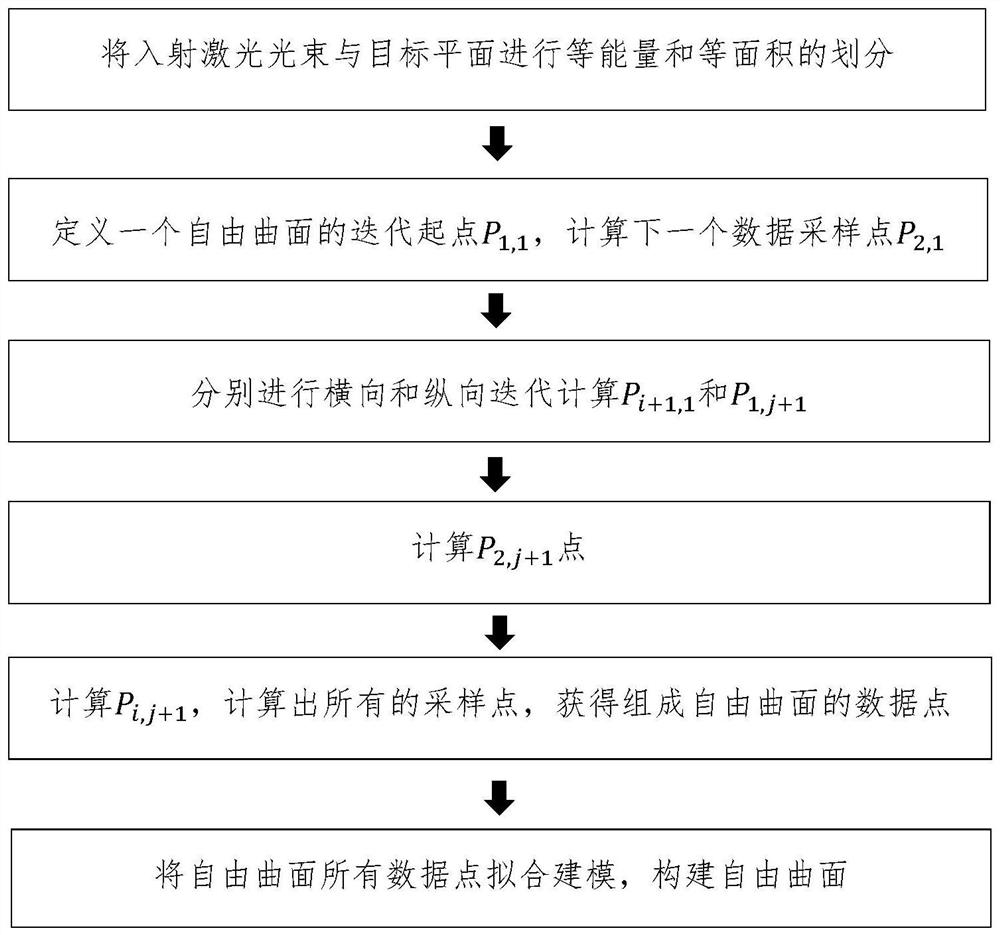
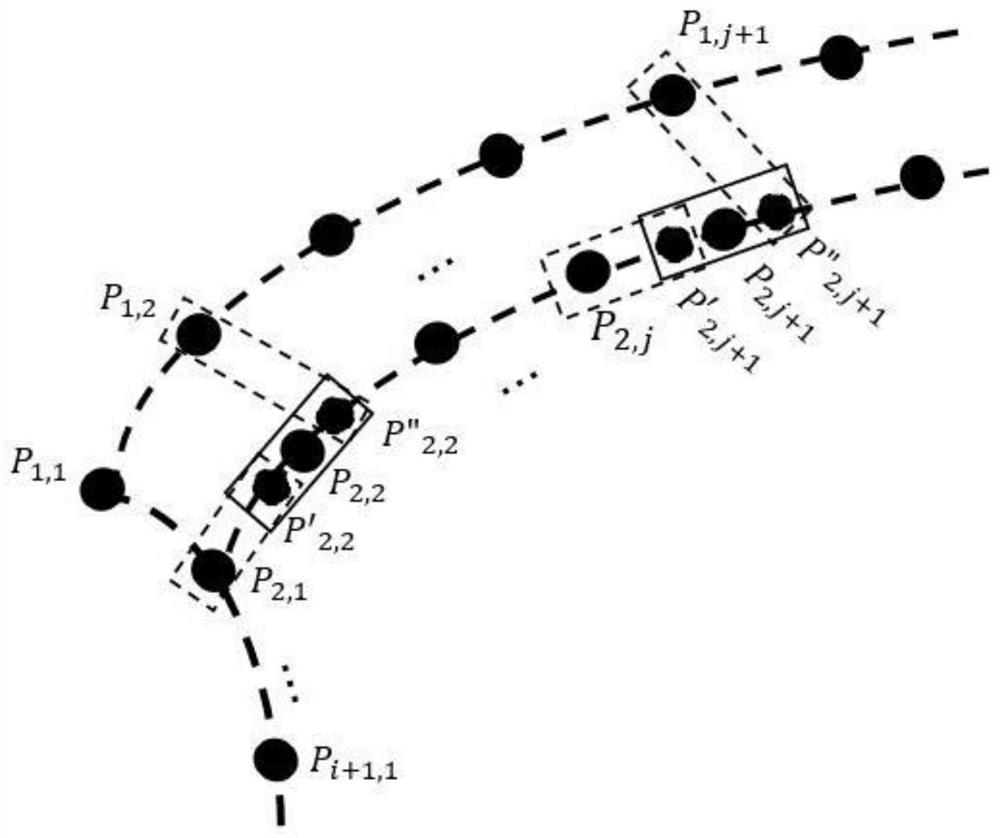
[0071] like figure 1 , a free-form surface construction method for laser beam shaping described in this embodiment, the flow chart is as follows figure 1 shown, including:
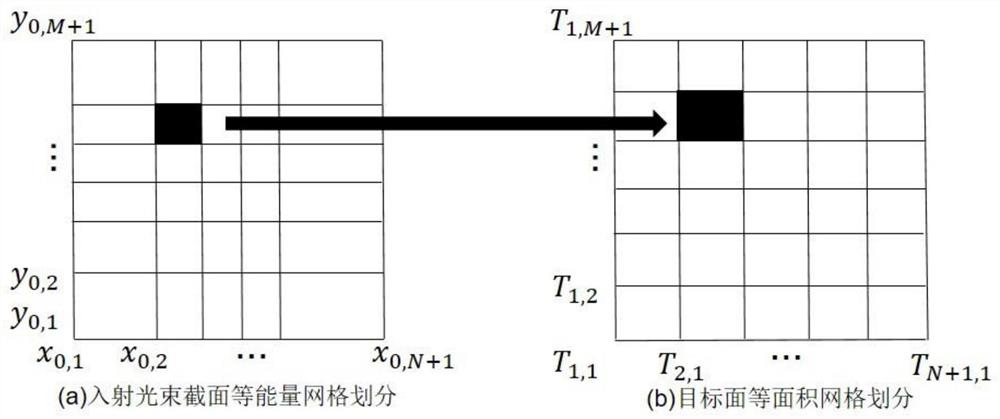
[0072] (1) Divide the collimated laser beam into equal energy divisions on the beam waist section, divide the target plane into equal areas, and construct the corresponding relationship between the collimated laser beam and the target plane according to the marginal ray theory and energy mapping relationship, as shown in figure 2 shown.
[0073] A collimated beam with a rectangular aperture is used, and the equal energy is divided into N×M parts on the beam waist section, and the equal area of the target plane is divided into N×M parts.
[0074] The expression of Gaussian distribution of collimated laser beam irradiance is:
[0075]
[0076] In the formula, r is the distance from the center point of the optical axis, w 0 is the beam waist width of the laser beam, the luminous intensity of the col...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap