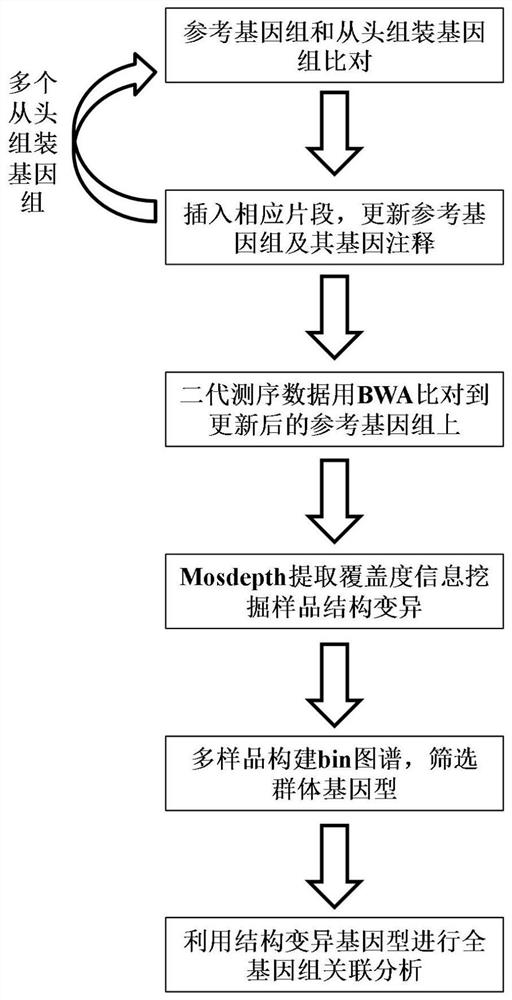
A genome-wide association analysis method based on multiple genome comparisons and next-generation sequencing data
A whole-genome, next-generation sequencing technology, applied in the fields of genomics, sequence analysis, proteomics, etc., can solve the problems that the organizational form of the pan-genome cannot be unified, and the pan-genome is not easy to understand, so as to achieve convenient understanding and subsequent application, accurate Effects of Genome Structural Variation Analysis and Identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1: Rice Reference Genome and Gene Annotation Update
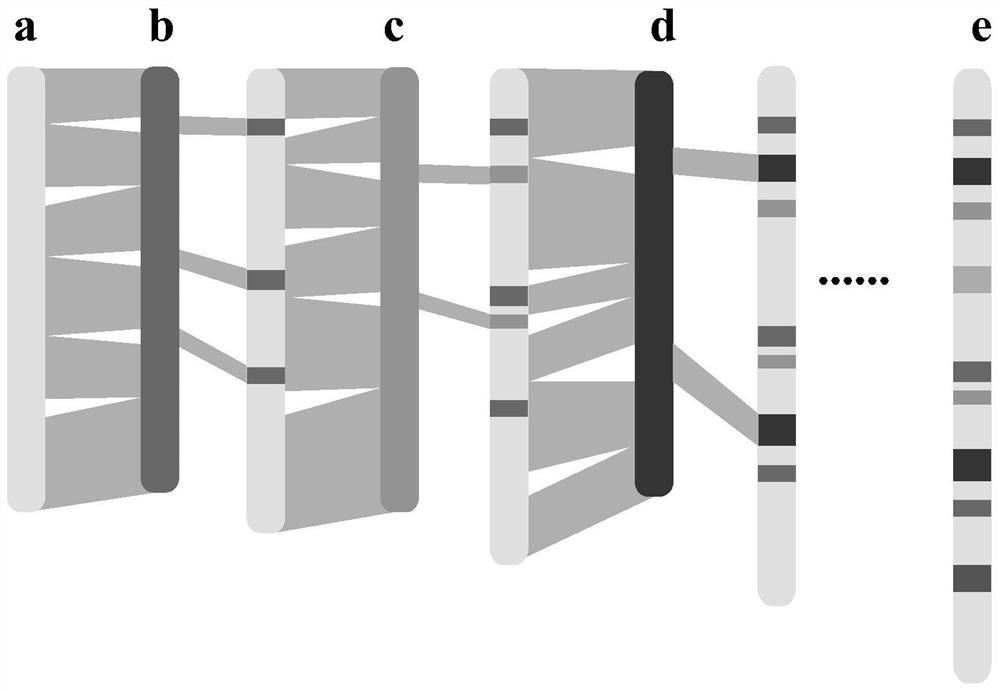
[0053] Using the 33 rice genomes that have been assembled and annotated, and rice Nipponbare MSU as the initial reference genome, DHX2, 02428, Kosh, ZH11, KY131, Lemont, NamRoo, LJ, G46, CN1, FS32, DG, D62, II32 were sequentially compared , R527, S548, 9311, Y58S, J4155, G8, Y3551, IR64, R498, TM, Tumba, G630, YX1, WSSM, FH838, N22, Basmati1, CG14.
[0054] Such as figure 2 As shown, in the first round of alignment, the reference genome (MSU) was compared with the first de novo assembled genome (DHX2) using MUMmer software to obtain the collinearity characteristics between the genomes and generate a delta file;
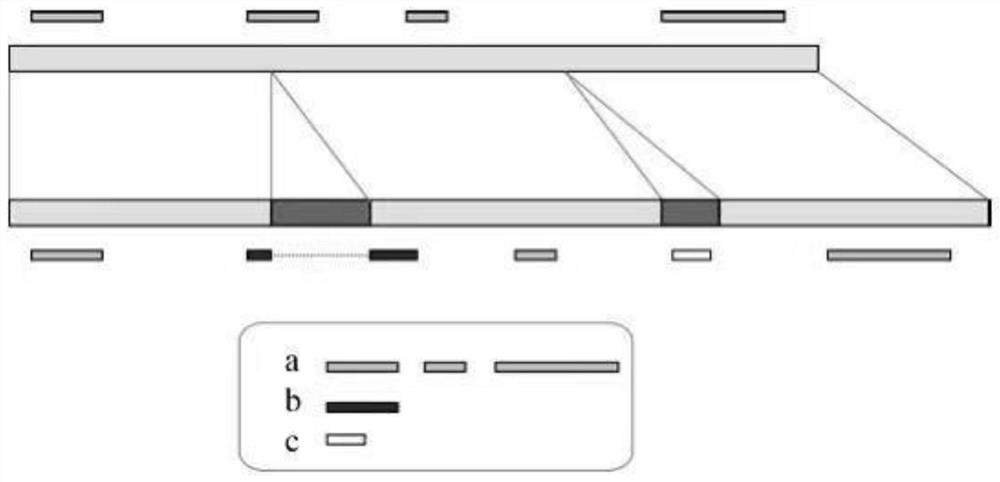
[0055] Use Assemblytics software to extract collinearity features, use python software to organize collinearity feature files to screen insert size (>50bp), and obtain structural variation position information data file (Assemblytics_structural_variants.bed file) based on the reference genome posit...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3: Sequence Structure Variation Mining Based on Next Generation Sequencing Data and Updated Reference Genome
[0075] Such as Figure 4 As shown, use the BWA file to mount the second-generation sequencing data (fq) on the updated reference genome, use the pipeline and SAMtools software to convert the output data into a bam file, use Picad software to sort the bam file, and remove repeated operations to get sorted_add_dedup .bam file, use SAMtools software to remove the sequencing fragments whose comparison quality is less than 20, cannot be mounted on the reference genome, and match to multiple places, and the filtered mapQ20.bam file is obtained.
[0076]Use the self-programmed 2Map_fq_to_Pan.py to mount all the sequencing data in the fqd_dir directory to the reference genome, and generate the bam_dir folder, which contains the mapQ20.bam files of all samples. The sequencing data fq.gz file is placed in the same directory fqd_dir, and the format of the paired-...
Embodiment 4
[0083] Example 4: Genome-wide association analysis
[0084] Genome-wide association analysis was performed using Gapit software.
[0085] Using the initial reference genome and sequencing data, the population SNP genotypes were obtained using BWA and GATK software, and the genome-wide association analysis was performed using Gapit software.
[0086] Such as Figure 6 Comparing the results of genome-wide association analysis between the structural variation genotype and the SNP genotype shown, it can be found that almost all the association sites that can be found using the SNP genotype can be found using the structural variation genotype, and new structural variation genotypes can also be found. associated sites. Since the updated gene annotation also brings in new genes, it makes up for the shortcomings of the limited number of genes annotated in the initial reference genome.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com