Multicore optical fiber and design method
A multi-core optical fiber and design method technology, applied in multi-core optical fiber, cladding optical fiber, light guide, etc., can solve problems such as ambiguity, and achieve the effects of increasing multiplicity, reducing pulse response width, and expanding transmission capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
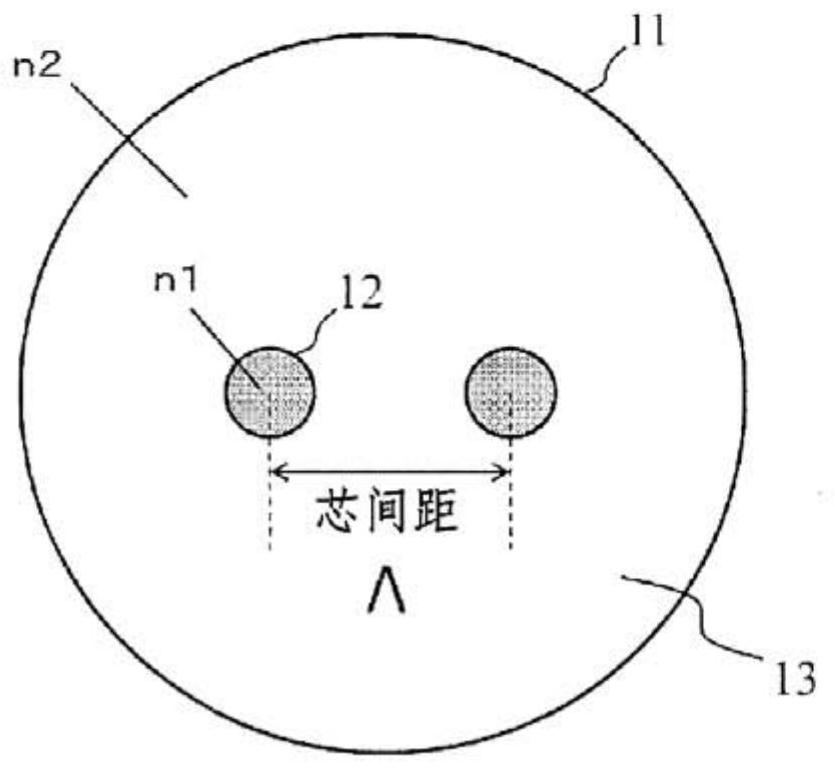
[0061] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view of a multi-core optical fiber 11 having two cores. There is a core region 12 with a refractive index n1 and a cladding region 13 with a refractive index n2, n1>n2.
[0062] exist figure 1 In the structure, the condition of n1>n2 is realized by using pure quartz glass or quartz glass as the material of each region, and the quartz glass is added with germanium (Ge), aluminum (Al), phosphorus (P), etc. to increase the refractive index impurities, or impurities such as fluorine (F) and boron (B) that lower the refractive index. Also, let the core pitch be Λ.
[0063] When designing a coupling-type multi-core fiber, regarding the bending radius, as stipulated in the measurement of the cutoff wavelength in ITU-T, as an alternative to using a cable sample, an optical fiber wire with a bending radius of 140 mm is used, which means that in-line A bend with a bend radius of 140 mm is effectively generated in the cable, and when the optica...
Embodiment approach 2
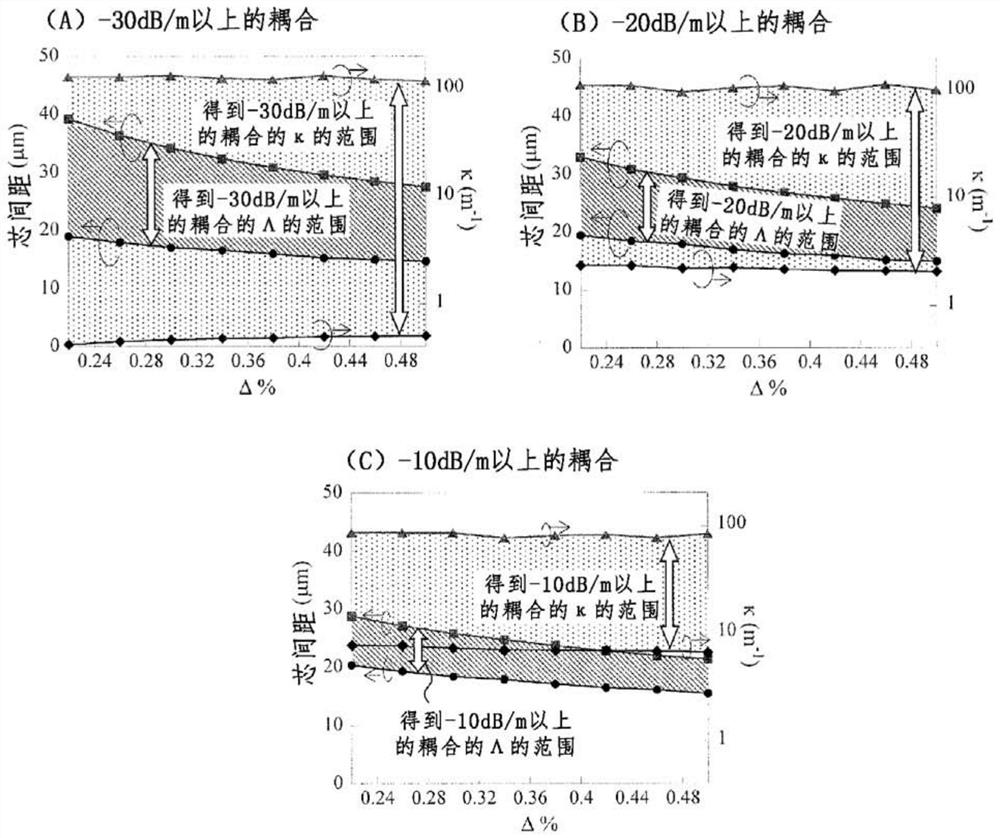
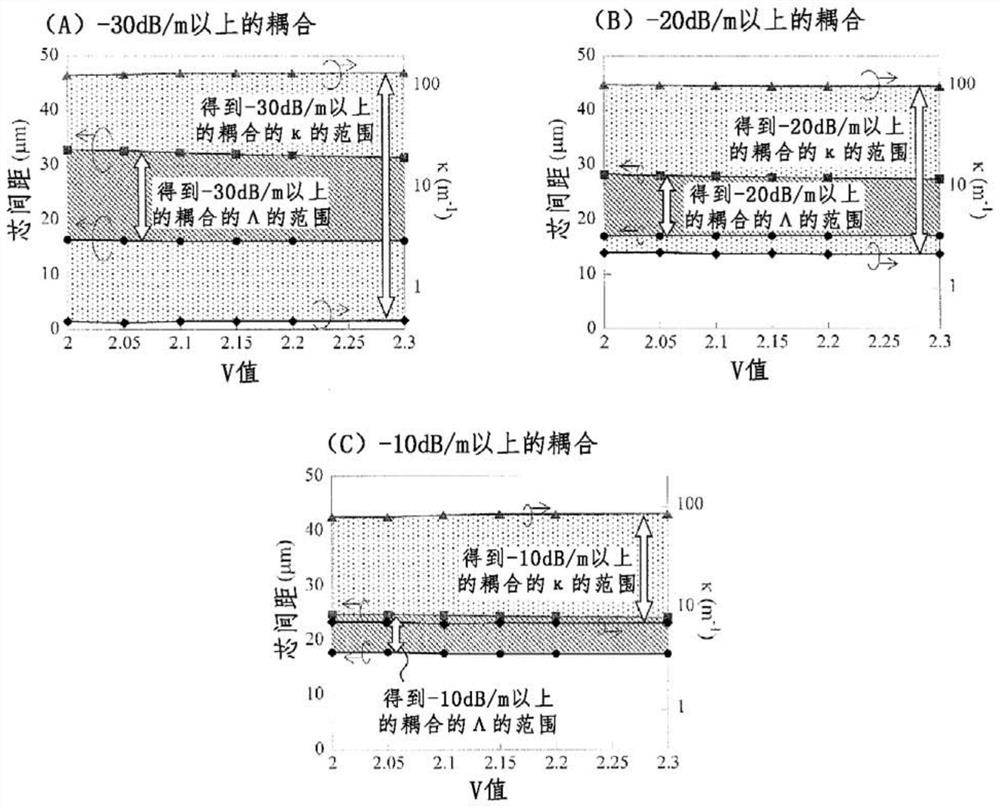
[0103] In Embodiment 1, it was described that the core pitch required to obtain random coupling varies depending on the core structure such as Δ, but the coupling coefficient κ required to obtain random coupling is fixed. Here, according to Non-Patent Document 11 Figure 4 .16, the relationship between aκ / √Δ and Λ / a including the coupling coefficient κ can be expressed as a function of the normalized frequency V, and the constants A and B can be used, by
[0104] [number 5]
[0105]
[0106] express.
[0107] Here, assuming a step core, if the changes of A and B are calculated with respect to the V value, and the values are obtained empirically, then as Figure 12 shown in Table 2. Figure 5 and Figure 6 The results of deriving the relationship between A and B and the V value from Table 2 are shown, respectively. according to Figure 5 and Figure 6 ,
[0108] A=f(V)=-8.7812+5.51V
[0109] B=f(V)=1.0027-1.188V.
[0110] Let κ required for random coupling be κc....
Embodiment approach 3
[0119] Here, it is calculated to what degree the amount of coupling becomes random coupling and the impulse response width can be reduced. Considering that the relay section sandwiched between optical amplifiers is generally more than 40km, the shape of the impulse response when the coupling amount is changed at a transmission distance of 40km is calculated, and the results are shown in Figure 7 . For ease of illustration, the DMD between modes is set to 1 ns / km.
[0120] At -50dB / m, there are pulses showing relatively high intensity at both ends, the width of which is 40ns, and becomes the same value as the cumulative DMD (1ns / km×40km). In the case of -40dB / m, the pulse intensity at both ends is reduced, but the pulse response width is the same as the accumulated DMD.
[0121] On the other hand, at a coupling amount of -30 dB / m or more, the impulse response shape is Gaussian. It can be seen that the shape of the impulse response is Gaussian when the inter-mode coupling is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com