Vacuum carburizing method for obtaining dispersed fine carbides
A dispersion distribution and vacuum carburizing technology, which is applied in the direction of solid-state diffusion coating, coating, heat treatment process control, etc., can solve the problems of harmful product performance, inability to obtain carbides, toughness of difficult materials, etc., to achieve strong practicability, Improving service performance and exerting the effect of toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
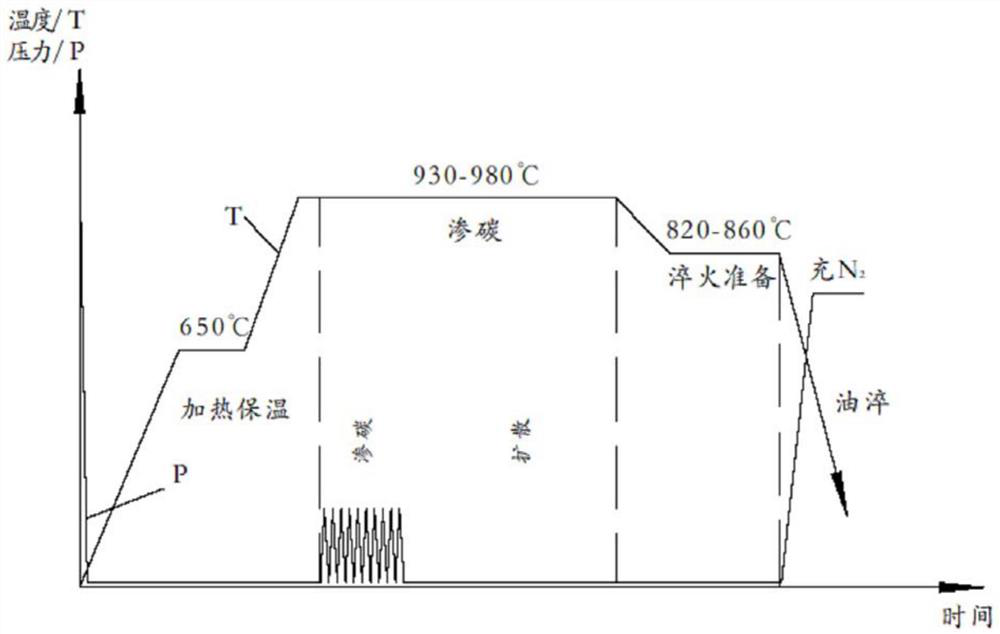
[0045] see figure 2 , in an embodiment of the present invention, a vacuum carburizing method for obtaining dispersed fine carbides, comprising the following stages:
[0046] (1) Heating and heat preservation stage: Determine whether the heating process is segmented according to the material and size of the workpiece, and set the heating temperature, heating time, and holding time of each segment. After the process curve is compiled, the workpiece is placed in a vacuum furnace to evacuate and run for heating. The final carburizing temperature is usually 930-980°C.
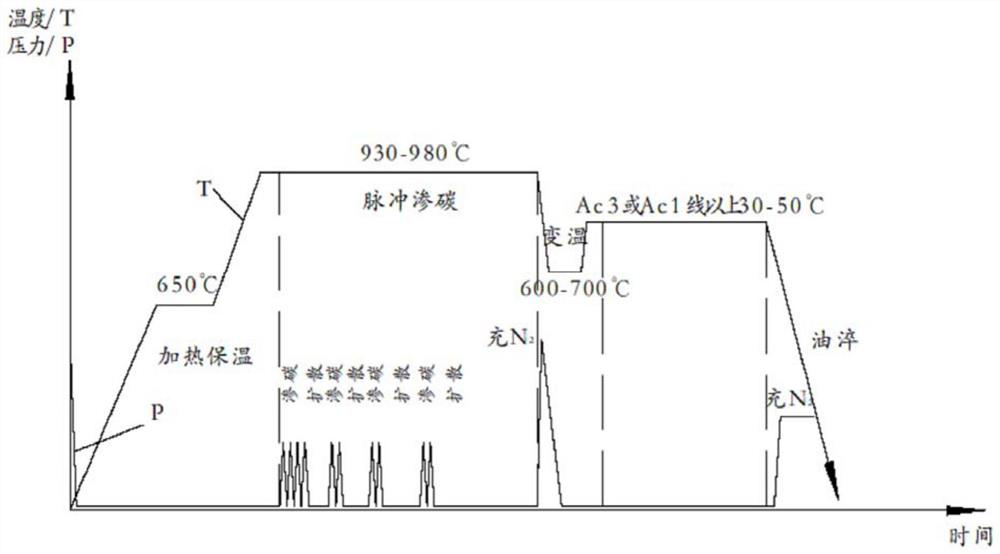
[0047] (2) Pulse carburizing stage: According to the carburizing layer depth of the workpiece or the carbon concentration gradient requirements of the carburizing layer, set the number of carburizing / diffusion alternate operations and the time of each operation, and compile them in the process curve. The carburizing gas is pulsed into the carburizing chamber. The gas type is usually acetylene or propane. The carbu...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Dimensions (mm): shaft diameter φ38, length 150mm
[0053] Material: 18CrNiMo7-6.
[0054] Heat treatment technical requirements: standard JB / T6141.3-1992 vacuum carburized carburized layer carbide ≤ 2 grades, surface martensite and retained austenite ≤ 2 grades, carburized layer 0.9 ~ 1.2mm, surface hardness above HRC62 .
[0055] Carburizing process: The traditional process of vacuum low-pressure carburizing is compared with the vacuum carburizing process of obtaining dispersed fine carbides.
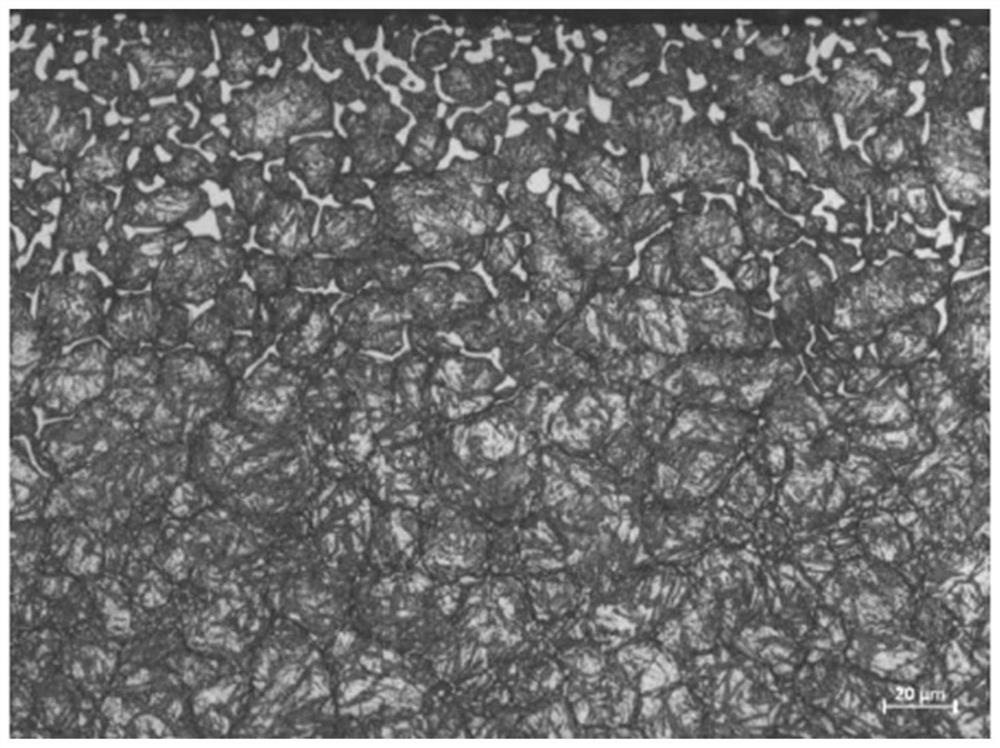
[0056] Using the traditional vacuum low-pressure carburizing process, the surface hardness of the test piece is HRC58.5, the surface carbon content is 1.5%, and the effective hardened layer depth is 1.1mm. Carbide grade 4, in the form of a network, such as image 3 shown.
[0057] Using the traditional vacuum low-pressure carburizing process, once the carbon content of the carburized layer is increased, the harmful structure of network carbide often forms on the surface, an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Shaft diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com