Production process for inhibiting degradation of recombinant human collagen by supplementing competitive protein
A human-derived collagen and production process technology, which is applied in the field of production technology for inhibiting the degradation of recombinant human-derived collagen, can solve the problems that recombinant collagen expression is technically difficult, the stability of recombinant collagen is not as good as that of natural collagen, and the product is easy to degrade, etc. Reduced degradation, improved stability, improved yield and purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-6
[0021] After the induction of recombinant Pichia pastoris was completed, DO>20%, and the methanol feeding was stable, the sterilized competitive protein was added at a time of 15g / L, and then normal methanol feeding was induced. After the fermentation, the temperature was raised to 65° C. for 30 minutes. After the end of the temperature rise, the temperature was rapidly lowered to 25° C. Detect the yield of recombinant human collagen (including degraded protein), and detect the yield of the full sequence target collagen. Thus, the stability of the recombinant human collagen was determined.
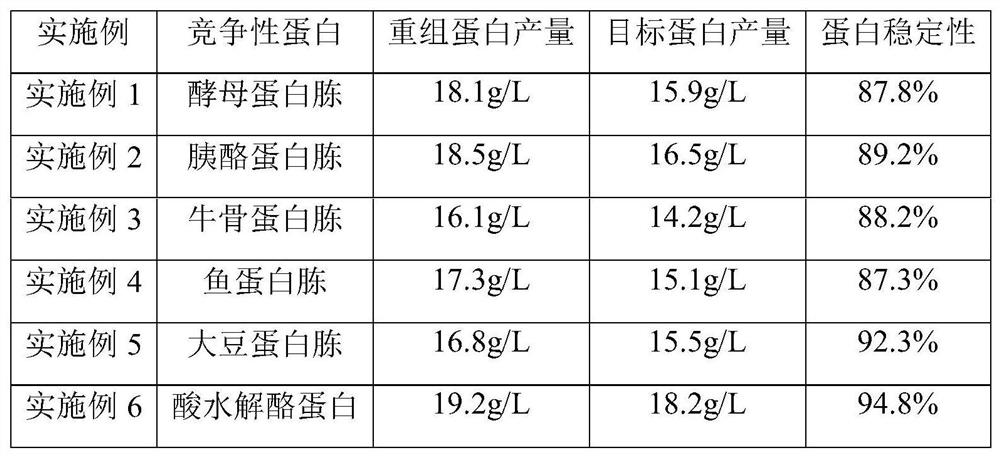
[0022] In Examples 1-6, several competitive proteins such as yeast peptone, tryptone, bovine peptone, fish peptone, soybean peptone, and acid hydrolyzed casein were selected, and the results are shown in the appendix figure 1 .
Embodiment 7
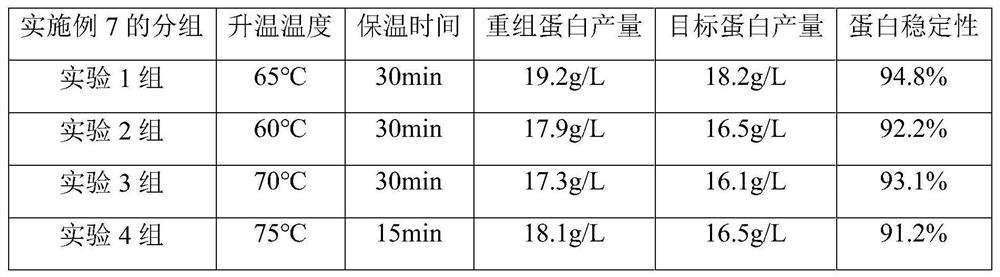
[0024] In this example, acid hydrolyzed casein was used as a competitive protein to conduct a comparative study of different parameters.
[0025] Select Example 6 to add acid hydrolyzed casein for further research, the target protein yield and protein stability at different heating temperatures and holding times. Group experiments were carried out according to the combination of different heating temperature and holding time.
[0026] After the induction of recombinant Pichia pastoris was completed, DO>20%, and the methanol feeding was stable, sterilized acid hydrolyzed casein was added at one time at an amount of 15g / L, and then normal methanol feeding was induced. After the fermentation is finished, the temperature is raised, and the temperature of the warming is selected to be 60-75° C., and the holding time is selected to be 10-30 minutes. After the heating is completed, the temperature is rapidly dropped to 25° C. Detect the yield of recombinant human collagen (including...
Embodiment 8
[0027] Example 8 Comparative Example
[0028] This example provides a set of comparative experiments, specifically comparing the conventional fermentation production process in the prior art with the method in Example 6, and performing electrophoresis experiments on the proteins obtained by the two methods.
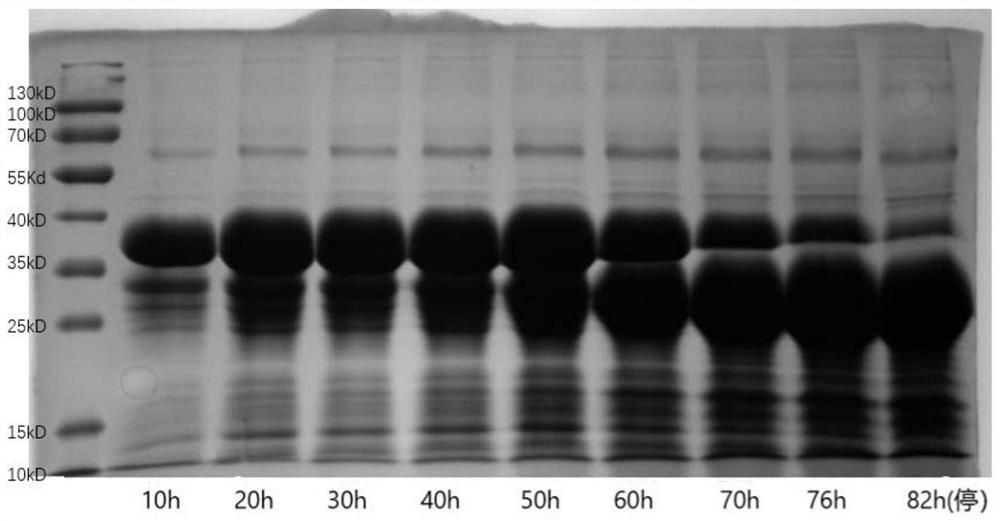
[0029] In the conventional fermentation of the production process in the prior art, after the induction of recombinant Pichia pastoris is completed, DO>20%, normal methanol feed induction is carried out. After the fermentation, the extraction process was carried out normally, and the yield of recombinant human collagen (including degraded protein) reached 17.2g / L, of which the amount of full-sequence target collagen was 2.8g / L. The stability of recombinant human collagen is 16.2%, see the attached electrophoresis image 3 and 4 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com