Method for differentiating macrophages from hiPS
A technology of macrophages and cells, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as production limitations, achieve the effect of increasing the number, avoiding the chance of contamination, and simplifying the differentiation steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
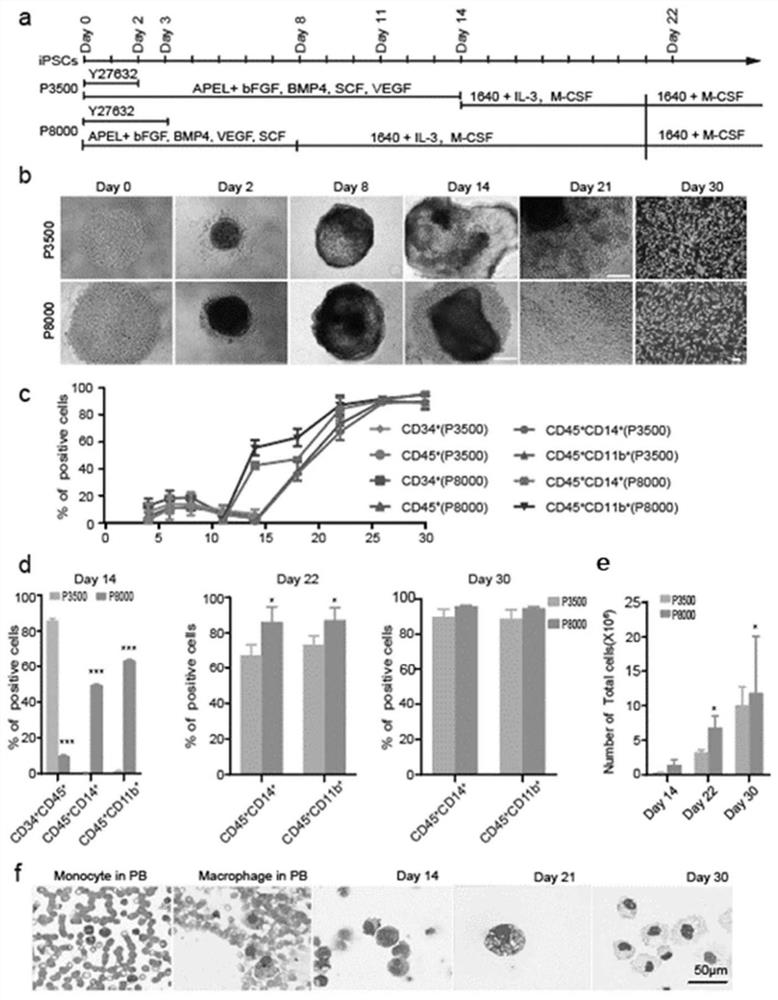
[0024] The solutions of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific examples, but the protection scope of the present invention will not be limited. Embodiment 1 (the scheme of p8000)
[0025] A method for human induced pluripotent stem cells to differentiate macrophages, comprising the steps of:
[0026] 1), culture of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs): no feeder layer, no serum Medium (cellapy, Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Medium) to culture hiPSCs, and passage when the cells reach 70%-80% density. Discard the medium, add 0.5mM EDTA to cover the cells, digest and incubate at 37°C for 4-5 minutes. Suck off the EDTA liquid, add iPS culture medium, pass passage at a ratio of 1:6, and place the plate in an incubator with a temperature of 37°C and 5% carbon dioxide.
[0027] 2), we use the EB-centrifugation protocol for hematopoietic differentiation: when hiPSCs grow to about 70% density, discard the culture medium, add Tryp...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2 (the scheme of p3500)
[0031] 1), culture of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs): no feeder layer, no serum Medium (cellapy, Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Medium) to culture hiPSCs, and passage when the cells reach 70%-80% density. Discard the medium, add 0.5mM EDTA to cover the cells, digest and incubate at 37°C for 4-5 minutes. Suck off the EDTA liquid, add iPS culture medium, pass passage at a ratio of 1:6, and place the plate in an incubator with a temperature of 37°C and 5% carbon dioxide.
[0032] 2), we use the EB-centrifugation protocol for hematopoietic differentiation: but hiPSCs grow to about 70% density, discard the culture medium, add TrypLE Express ((Gbico) digestion solution that can cover hiPSCs, digest at room temperature for 2 minutes. Then discard Remove the digestion solution, resuspend the cells with APEL (STEMCELL Technologies) supplemented with 10mMY27632 (STEMCELL Technologies), 10ng / ml BMP4 (R&D) and 10ng / ml recombinan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com