Method for preparing polydextrose from glucose raffinate
A polydextrose and glucose technology, applied in the field of polydextrose preparation, can solve the problems of high content of polydextrose by-products, high production costs, waste of glucose raffinate resources, etc., to improve the utilization rate of by-products, reduce the generation of by-products, The effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
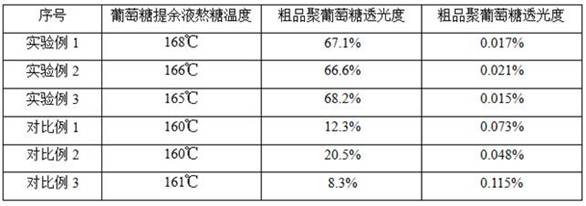
[0026] (1) Using glucose raffinate after chromatographic separation of isomaltose oligosaccharide as raw material, high temperature and high sugar concentration granular activated carbon was used for decolorization. The decolorization temperature was 78°C, the sugar concentration was 50%, and the flow rate was 1.0 BV / h; The remaining liquid is separated, and the separation resin is selected from Na + Type cation and Cl - Type anionic resin, separation temperature 50°C, sugar concentration 50%, flow rate 3 BV / h, after separation, the glucose raffinate was concentrated to sugar concentration 60% by four effects;
[0027] (2) Put the concentrated glucose raffinate into the polymerization reactor, add sorbitol into the reactor, the dry basis ratio of glucose liquid: sorbitol is 89:11, then heat up to 150±5℃ for 90min, and keep the vacuum at -0.07 ~-0.1MPa; add citric acid with 0.53% of the total dry basis of glucose and sorbitol, keep the vacuum at -0.07~-0.1MPa, heat up to 230±5...
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Using glucose raffinate after chromatographic separation of isomaltose oligosaccharide as raw material, high temperature and high sugar concentration granular activated carbon was used for decolorization. The decolorization temperature was 75°C, the sugar concentration was 45%, and the flow rate was 1.2 BV / h; The remaining liquid is separated, and the separation resin is selected from Na + Type cation and Cl — Type anionic resin, separation temperature 50°C, sugar concentration 45%, flow rate 4.5 BV / h, after separation, the glucose raffinate was concentrated to a sugar concentration of 60% by four effects;
[0031] (2) Put the concentrated glucose raffinate into the polymerization reaction kettle, add sorbitol into the reaction kettle, the dry basis ratio of glucose liquid: sorbitol is 89:11, then heat up to 145±5℃ for 120min, and keep the vacuum at -0.07 ~-0.1MPa; add citric acid with 0.53% of the total dry weight of glucose and sorbitol, keep the vacuum at -0.07~...
Embodiment 3
[0034] (1) Using glucose raffinate after chromatographic separation of isomaltose oligosaccharide as raw material, high temperature and high sugar concentration granular activated carbon was used for decolorization. The decolorization temperature was 80°C, the sugar concentration was 55%, and the flow rate was 0.8 BV / h; The remaining liquid is separated, and the separation resin is selected from Na + Type cation and Cl — Type anion resin, separation temperature 55°C, sugar concentration 55%, flow rate 2.5 BV / h, after separation, the glucose raffinate was concentrated to 60% sugar concentration by four effects;
[0035] (2) Put the concentrated glucose raffinate into the polymerization reactor, add sorbitol into the reactor, the dry basis ratio of glucose liquid: sorbitol is 89:11, then raise the temperature to 155±5℃ for 60min, and keep the vacuum at -0.07 ~-0.1MPa; add citric acid with 0.58% of the total dry basis of glucose and sorbitol, keep the vacuum at -0.07~-0.1MPa, he...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com