Lead removal method for nickel chloride solution
A nickel chloride and solution technology, applied in the field of lead removal, can solve the problems of high cost, insufficient lead removal depth, low efficiency, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, high lead removal efficiency, and short process flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
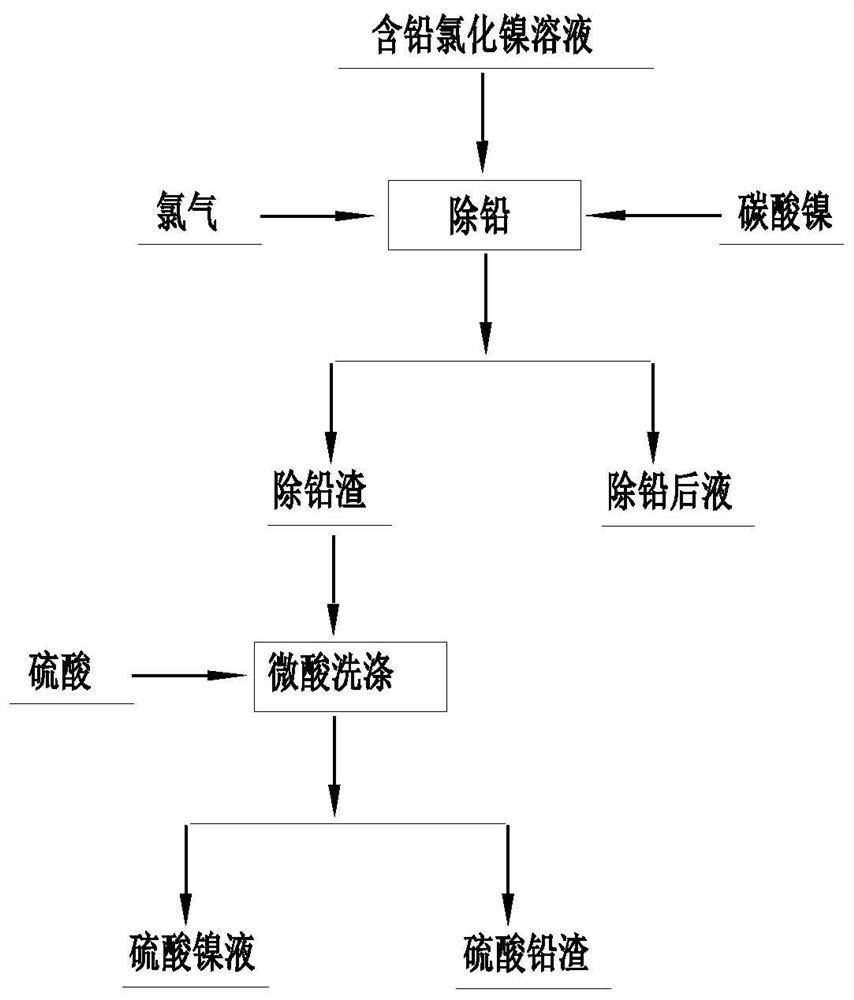
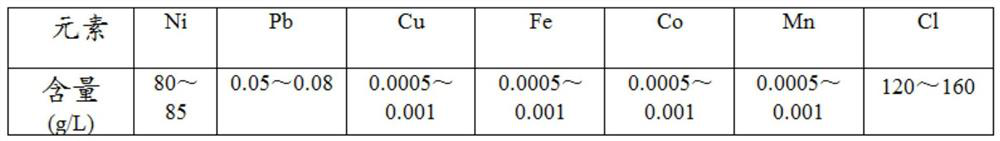
[0022] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for removing lead from a nickel chloride solution. Take 800 mL of lead-containing nickel chloride solution in a four-necked flask, the initial pH of the solution is 4.5, and the initial oxidation-reduction potential is 750 mV. Heating and stirring, when the temperature rises to 65°C and is maintained, introduce chlorine gas, control the flow rate of chlorine gas, and keep the solution potential to rise steadily to 1050mV. At this time, the pH of the solution drops to about 2.5, slowly add nickel carbonate slurry solution, and adjust the pH to 3.9 At this time, the potential correspondingly drops to about 900mV. By adjusting the flow rate of chlorine gas and the amount of nickel carbonate added, the pH of the solution is kept at 3.85-3.9, and the redox potential is 1020-1050mV. React for 4 hours. After the reaction is completed, filter and take a sample for analysis. Table 2. The chlorine gas escaped from the ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for removing lead from nickel chloride solution. Take 800 mL of lead-containing nickel chloride solution in a four-necked flask, the initial pH of the solution is 4.5, and the initial potential is 750 mV. Heating and stirring, when the temperature rises to 60°C and is maintained, introduce chlorine gas, control the flow rate of chlorine gas, and keep the potential of the solution rising steadily to 1020mV. At this time, the pH of the solution drops to about 2.5, slowly add nickel carbonate slurry solution, and adjust the pH to 4.0 At this time, the potential correspondingly drops to about 900mV. By adjusting the flow rate of chlorine gas and the amount of nickel carbonate added, the pH of the solution is kept at 3.9-4.0, the potential is 990-1020mV, and the reaction is performed for 3 hours. After the reaction is completed, filter and take samples for analysis. . The chlorine gas escaped from the reaction is ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Such as figure 1As shown, this embodiment provides a method for removing lead from nickel chloride solution. Take 800 mL of lead-containing nickel chloride solution in a four-necked flask, the initial pH of the solution is 4.5, and the initial potential is 750 mV. Heating and stirring, when the temperature rises to 70°C and is maintained, introduce chlorine gas, control the flow rate of chlorine gas, and keep the solution potential to rise steadily to 1070mV. At this time, the pH of the solution drops to about 2.5, slowly add nickel carbonate slurry solution, and adjust the pH to 3.9 At this time, the potential drops to about 1000mV accordingly. By adjusting the flow rate of chlorine gas and the amount of nickel carbonate added, the pH of the solution is kept at 3.8-3.9, the potential is 1050-1070mV, and the reaction is 2.5h. After the reaction is completed, filter, sample and analyze. 4. The chlorine gas escaped from the reaction is absorbed by liquid caustic soda. S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com