A method and system for constructing a microbial gene database
A construction method and database technology, applied in bioinformatics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large number of genes, low accuracy, and many types of annotated microorganisms, and achieve accurate classification information, reliable comparison results, and convenient update and iteration Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] Example 1 Microbial gene database construction system
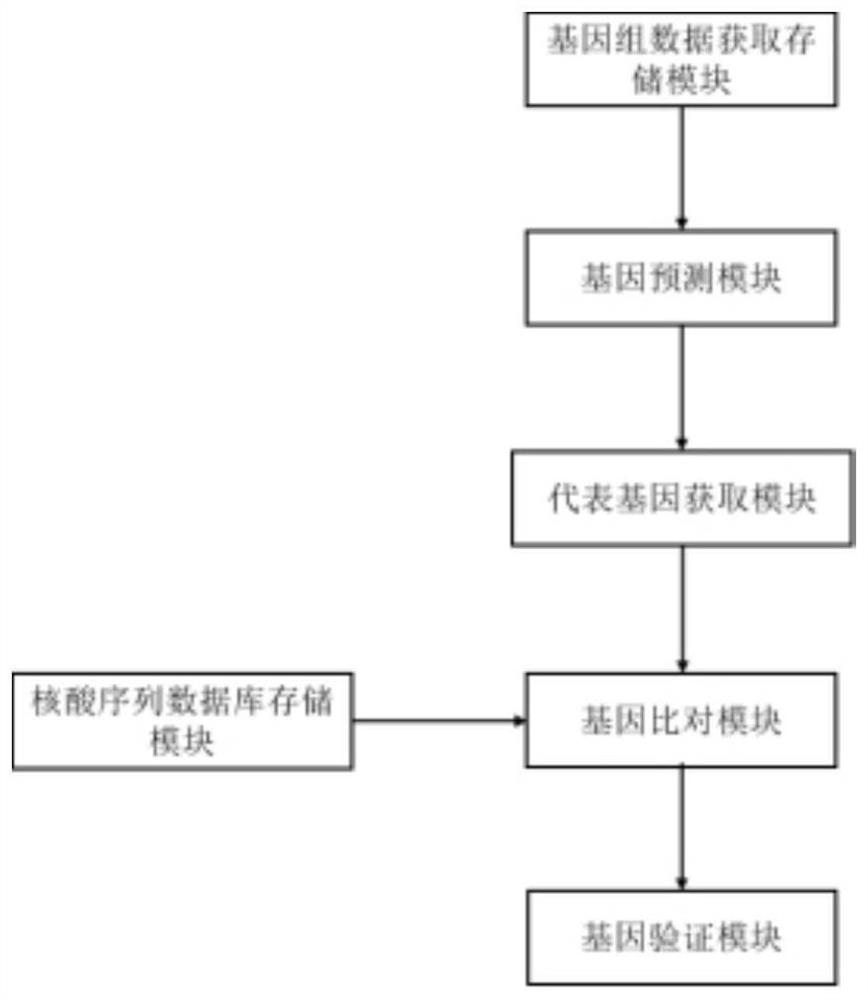
[0079] like figure 1 As shown, the present embodiment provides a construction system for a microbial gene database, that is, construction system #1 includes the following modules:
[0080] The genome data acquisition and storage module is used to acquire and store the genome data of each target microorganism in the target microorganism combination, wherein the target microorganism combination includes N kinds of target microorganisms, and N≥1;
[0081] The gene prediction module is connected with the genomic data acquisition and storage module, and is used to perform gene prediction on the genomic data acquired in the genomic data acquisition module, obtain and output gene annotation files including sequences and annotations;
[0082] a representative gene acquisition module, connected with the gene prediction module, for receiving the gene annotation file output by the gene prediction module, and using the gene ...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Microbial gene database construction system upgraded by embodiment 2
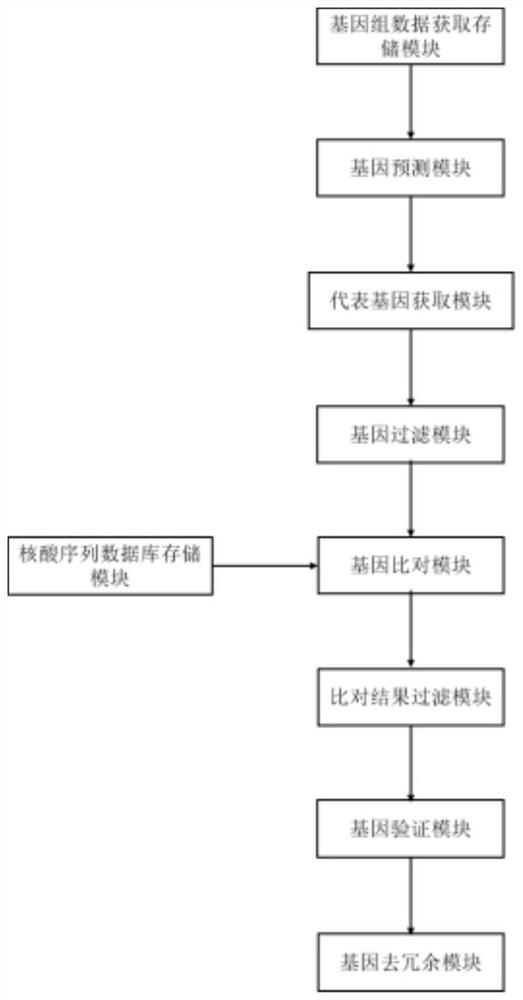
[0087] In this example, the construction system #1 of Example 1 is upgraded to obtain construction system #2. The improvement point is that it further includes a gene de-redundancy module, which is connected to the gene verification module and is used to receive the retained genes output by the gene verification module. , and use gene de-redundancy software to de-redundancy the retained genes, extract single-copy alignment genes, and obtain a non-redundant microbial gene database.
[0088] Wherein, the steps of extracting unit copy comparison genes are as follows:
[0089] For each species, perform de-redundancy separately: filter all the genes of the sequence class with the number of genes greater than 1, and all the remaining genes are the only aligned single-copy genes of the species;
[0090] The de-redundant genes of all species were merged, and all genes of the sequence class with gene number ...
Embodiment 3
[0091] The microbial gene database construction system that embodiment 3 upgrades
[0092] In this example, the construction system #1 of Example 1 or the construction system #2 of Example 2 are respectively upgraded to obtain the construction system #3 and construction system #4. The improvement points are: in the representative genome analysis module and the gene alignment module In between, a gene filtering module is further included, which is respectively connected with the representative gene acquisition module and the gene comparison module, and is used to receive the representative genes output by the representative gene acquisition module and filter: the genes whose sequence length is less than 200 are filtered, and then the filtered Represent gene output to the Gene Alignment module.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com