Method for removing multiple heavy metals in underground water by matching modified iron filler with modified zeolite and modified pumice stone
A technology for modifying zeolite and heavy metals, applied in chemical instruments and methods, contaminated groundwater/leachate treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problem of low removal efficiency of heavy metals, and achieve the effect of compact structure and small size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] A method for removing a variety of heavy metals in groundwater in combination with modified iron fillers and modified zeolite and modified pumice, the method specifically includes:
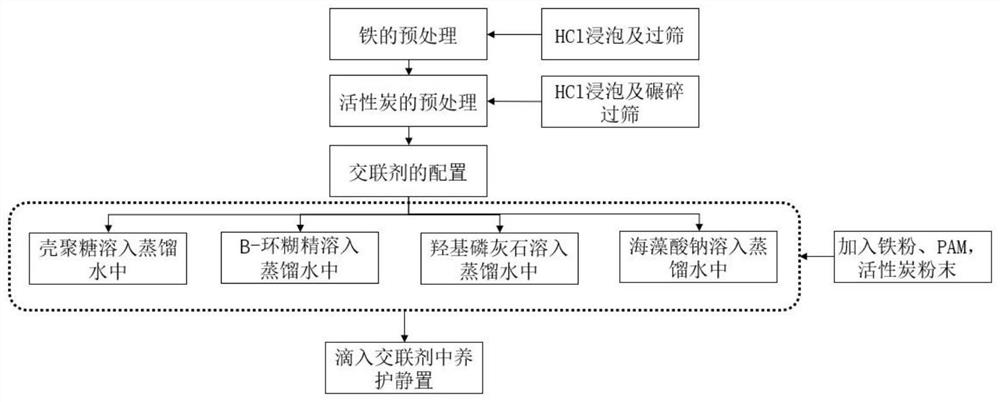
[0044] Step 1: modify the iron powder, the modification steps are as follows figure 1 shown
[0045] (1) Cleaning iron powder with dilute acid can effectively remove the surface oxide film formed during its manufacture, transportation and storage. Prepare a 0.1-1.0mol / L dilute HCl solution, soak and wash the iron powder in the solution for 5-10 minutes, then wash it repeatedly with distilled water, put it in a dry beaker, pass it through a 100-mesh standard sieve after natural air drying; use 5% activated carbon first Soak in hydrochloric acid for 24 hours, then wash with tap water and pure water until the pH is neutral, dry the activated carbon at 60-100°C, crush it to 80-100 mesh, and put it in a desiccator for use;
[0046] (2) prepare 3% calcium chloride solution, add excessive boric ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Preparation of modified iron filler: the steps are as shown above, only the sodium alginate modified material A is prepared, and the three materials B / C / D are not prepared;
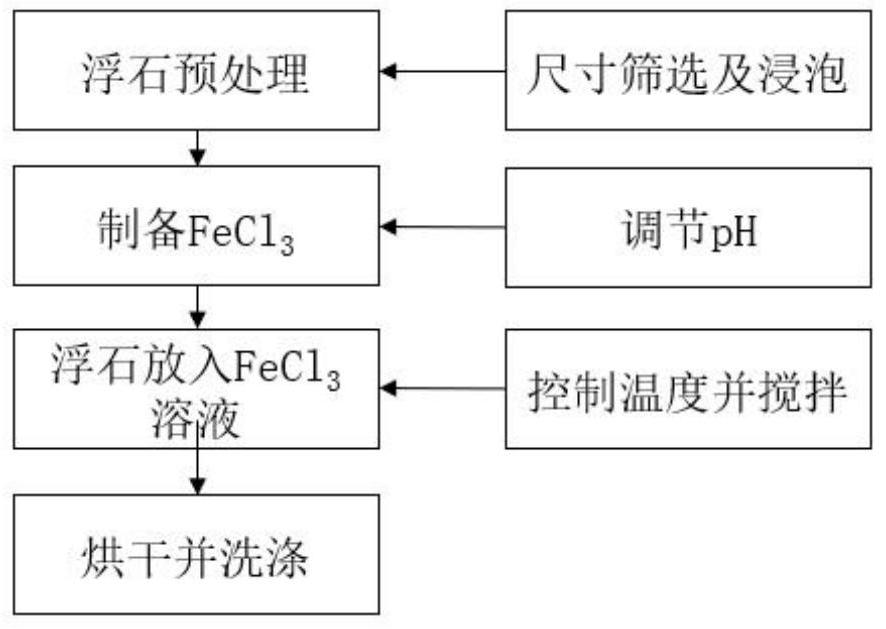
[0065] The preparation of modified pumice: with embodiment 1 step;
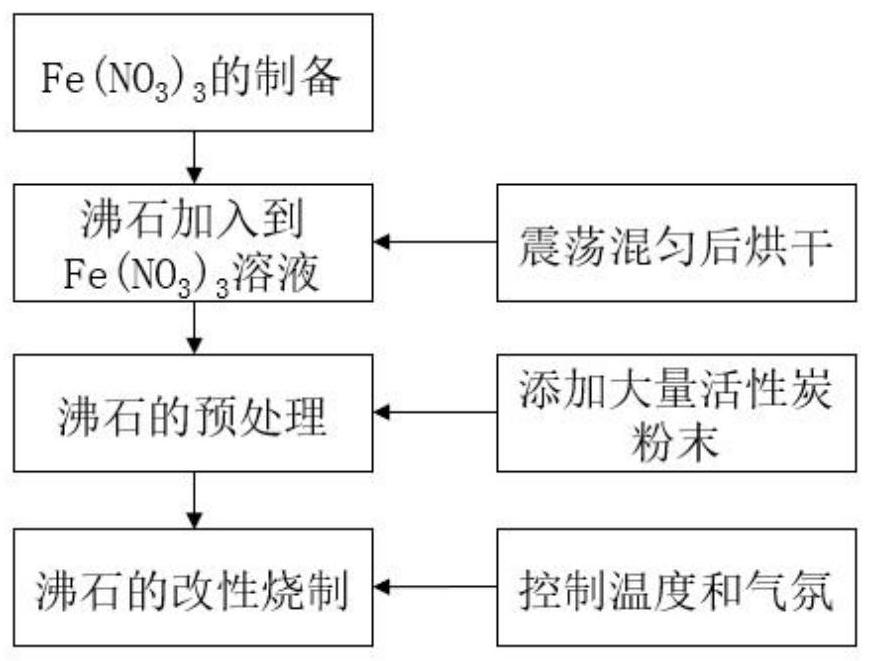
[0066] The preparation of modified zeolite: with embodiment 1 step;
[0067] Combined filling of modified fillers: such as Figure 4 As shown, in the middle filler, put large-size pumice as the skeleton support, and then put A modified iron filler as the main filler for removing heavy metals. The rest are the same as step 1.
[0068] This method can specifically remove Cu(II) in groundwater. A 15mg / L Cu solution was configured and a dynamic experiment was carried out at a flow rate of 2ml / min. The removal efficiency did not decrease significantly after 30 days of operation, and the removal rate was determined to exceed 95% on the 30th day. .
Embodiment 3
[0070] Preparation of modified iron filler: the steps are as above, only chitosan modified material B is prepared;
[0071] The preparation of modified pumice: with embodiment 1 step;
[0072] The preparation of modified zeolite: with embodiment 1 step;
[0073] Combined filling of modified fillers: such as Figure 4 As shown, in the middle filler, put large-size pumice as a skeleton support, and then put B modified iron filler as the main filler for removing heavy metals. The rest are the same as step 1.
[0074] This method can specifically remove Cr(Ⅵ) in groundwater. Configure 2mg / L Cr solution, and conduct dynamic experiments at a flow rate of 2ml / min. The efficiency decline is not obvious between 85-90% in the first 20 days, and the subsequent efficiency gradually decreases, but the removal rate can exceed 70% on the 30th day.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com