Method for treating rifamycin residues in mushroom dregs through ultrasonic-alkali heat combination
A technology of rifamycin and combined treatment, which is applied in biological organic part treatment, preparation of organic fertilizer, organic fertilizer and other directions, achieves the effects of simple method, low damage degree and simple treatment means
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] The influence of embodiment 1 reaction temperature on degradation efficiency
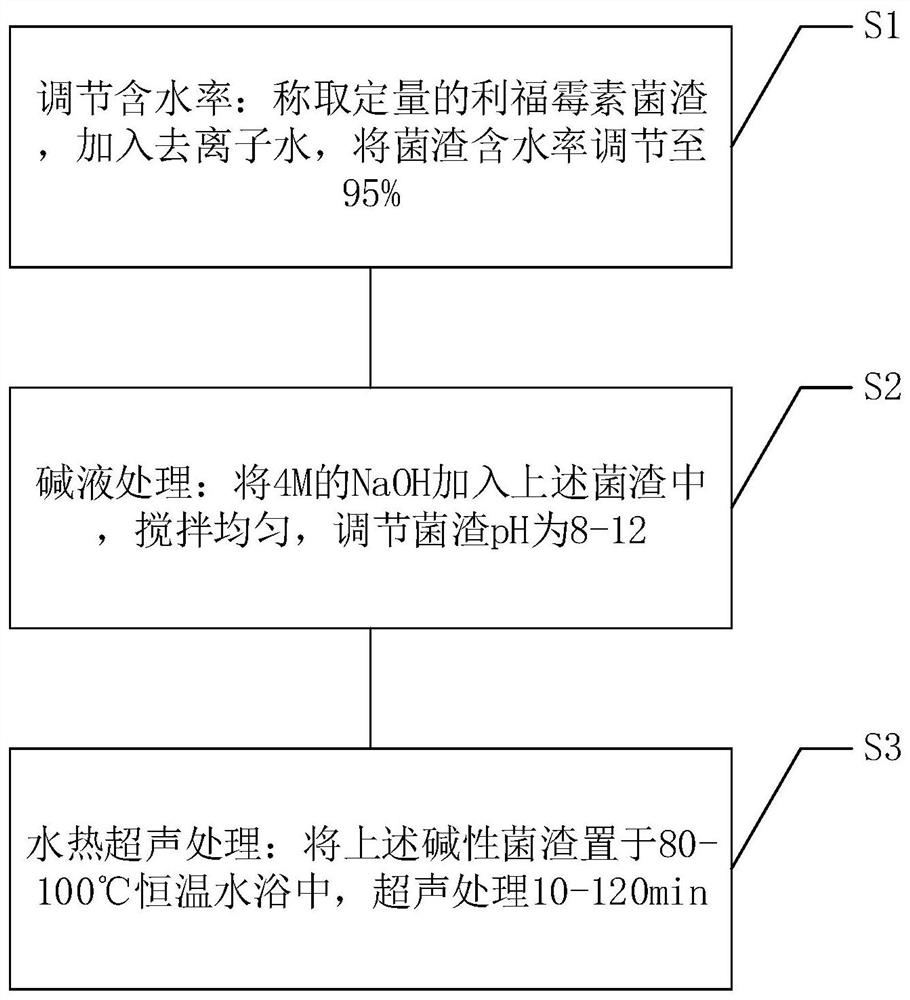
[0042] Weigh a certain amount of fresh rifamycin residue, add deionized water to adjust the moisture content of the residue to 95%, add the prepared 4M NaOH to the residue after adjusting the moisture content, stir evenly, and adjust the pH to 11. Place the bacteria residue with adjusted moisture content at 80, 90, and 100°C respectively, and adjust the ultrasonic intensity to 2.5W / mL in the ultrasonic processor, and start the reaction for 120 minutes.
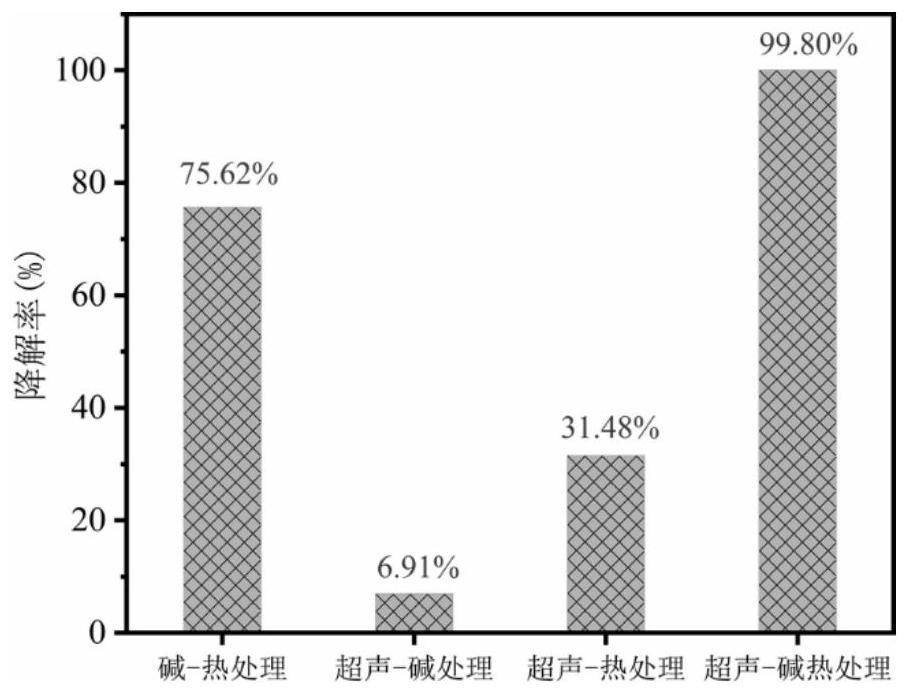
[0043] The experimental results show that the reaction temperature has a great influence on the ultrasonic-alkali-thermal combined treatment of rifamycin slag, as shown in Table 1. When the pH value is 11, the ultrasonic intensity is 2.5W / mL, and the selected reaction temperature is 90°C, the degradation rate of rifamycin in the bacteria residue is 99.80%.
[0044] The influence of table 1 reaction temperature on the degradation efficiency o...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The influence of embodiment 2 pH on degradation efficiency
[0047] Weigh a certain amount of fresh rifamycin residue, add deionized water to adjust the moisture content of the residue to 95%, add the prepared 4M NaOH to the residue after adjusting the moisture content, stir evenly, and adjust the pH to 8, 10, 11, 12, place the bacteria residues with adjusted moisture content at 90°C respectively, adjust the ultrasonic intensity to 2.5W / mL in the ultrasonic processor, and start the reaction for 120 minutes. The experimental results show that the pH value has a great influence on the ultrasonic-alkali-thermal combined treatment of rifamycin slag, as shown in Table 2. When the reaction temperature is 90°C, the ultrasonic intensity is 2.5W / mL, and the pH value is 11, the degradation rate of rifamycin in the bacterial residue is 99.80%, which is obviously better than that of pH 8 and 10.
[0048] Table 2 Effect of pH value on the degradation efficiency of rifamycin in bact...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3 Ultrasonic intensity is to the influence of degradation efficiency
[0051] Weigh a certain amount of fresh rifamycin residue, add deionized water to adjust the moisture content of the residue to 95%, add the prepared 4M NaOH to the residue after adjusting the moisture content, stir evenly, and adjust the pH to 11. Place the bacteria residues with adjusted moisture content at 90°C, and adjust the ultrasonic intensity in the ultrasonic processor to 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0 W / mL, and start the reaction for 120 minutes. The experimental results show that the pH value has a great influence on the ultrasonic-alkali-thermal combined treatment of rifamycin slag, as shown in Table 3. When the reaction temperature was 90°C, the ultrasonic intensity was 2.5W / mL, and the pH value was 11, the degradation rate of rifamycin in the bacteria residue was 99.80%.
[0052] Table 3 The effect of ultrasonic intensity on the degradation efficiency of rifamycin in the bacterial residu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com