Biomarker for evaluating sensitivity of lung cancer patient to proton radiotherapy and application of biomarker
A biomarker and sensitive technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as limited clinical translation potential, and achieve the effects of reducing economic burden, reducing radiation dose, and reducing radiation side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
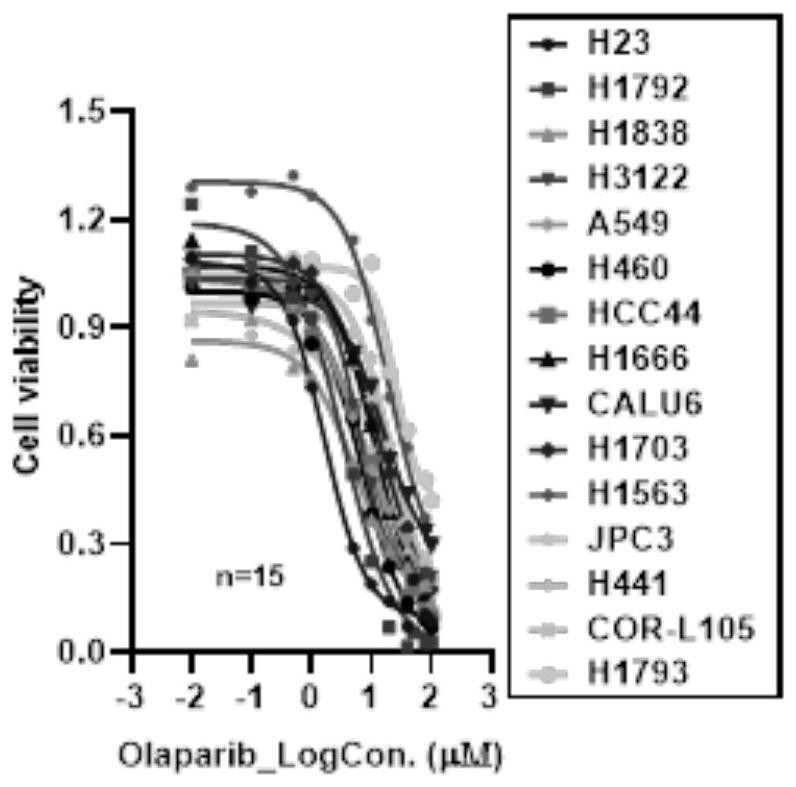
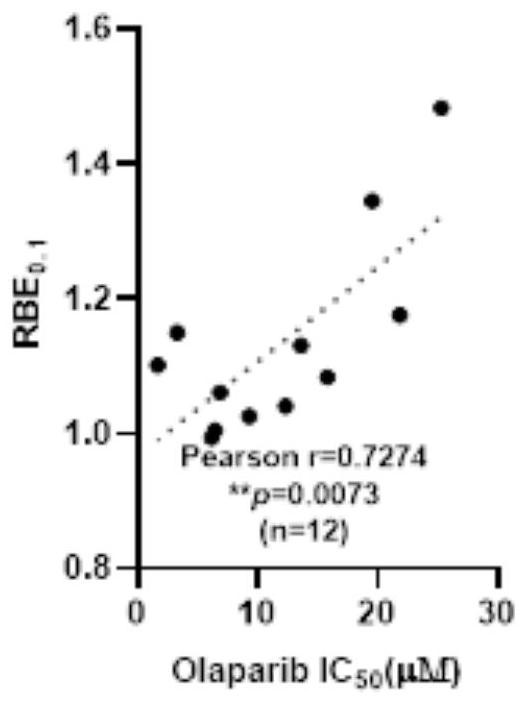
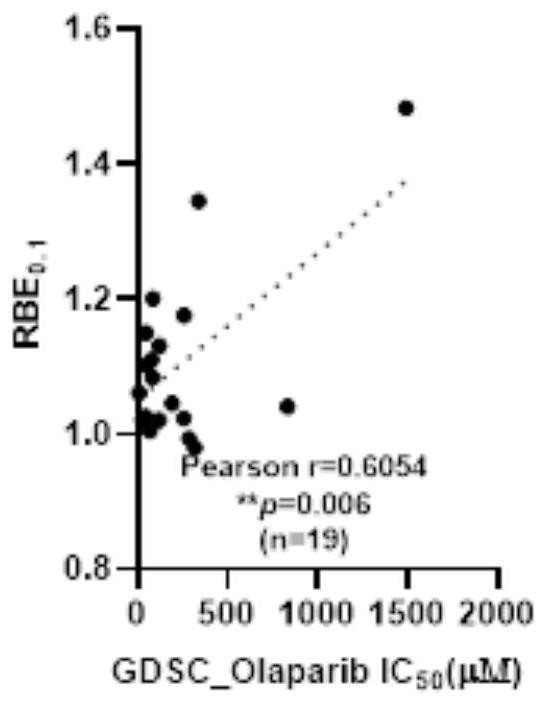
[0168] In the present embodiment, after the Olaparib solution was treated with 15 kinds of NSCLC cells, the half inhibitory concentration IC of NSCLC cells to Olaparib was analyzed. 50 Value of RBE with Proton Radiotherapy 0.1 Correlations between values, including the following:
[0169] 1. The half inhibitory concentration IC of olaparib in 15 kinds of NSCLC cells 50 value
[0170] Experimental cells: 15 kinds of NSCLC cells, including H23 cells, H1792 cells, H1838 cells, H3122 cells, A549, H460 cells, HCC44 cells, H1666 cells, CALU6 cells, H1703 cells, H1563 cells, JPC3 cells, H441 cells, COR-L105 cells cells, H1793 cells.
[0171] Reagent: Olaparib (Olaparib) is dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide and stored at -20°C as a mother solution. Before use, the drug Olaparib is diluted with the complete medium corresponding to cell culture to 12 Olaparib solutions with different concentration gradients. The concentration gradients were 0 μM, 0.01 μM, 0.1 μM, 0.5 μM, 1 μM, 5 μM, 1...
Embodiment 2
[0198] In this embodiment, the half maximal inhibitory concentration IC of NSCLC cells to Olaparib was analyzed. 50 Correlation of values with ARID1A truncating mutations, including the following:
[0199] Somatic mutations in olaparib-sensitive and olaparib-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells (LUAD) were analyzed using the COSMIC database (https: / / cancer.sanger.ac.uk / cell_lines).
[0200] Figure 4 It is the volcano plot of the genetic mutation of lung adenocarcinoma cells (LUAD) and the chemotherapy sensitivity and resistance of Olaparib obtained from the COSMIC cell database in this example. Among them, mut represents a mutation, and the left arrow represents the more leftward, the more sensitive to Olaparib; the right arrow represents the more rightward, the more resistant to Olaparib.
[0201] From Figure 4 It can be seen that compared with wild-type lung adenocarcinoma cells, ARID1A truncated mutant lung adenocarcinoma cells are more resistant to Olaparib (*p=0.034...
Embodiment 3
[0208] In this example, the detection of ARID1A expression in ARID1A wild-type NSCLC cells and ARID1A truncated mutant NSCLC cells, as well as the relationship between ARID1A expression and proton radiotherapy RBE 0.1 Value correlation analysis, including the following:
[0209] Experimental subjects: 8 kinds of NSCLC cells, including ARID1A wild-type NSCLC cells and ARID1A truncated mutant NSCLC cells. Among them, ARID1A wild-type NSCLC cells are: H23, H1792, A549, CALU6 and JPC3; ARID1A truncated mutant NSCLC cells are: H460, H1563 and H1793.
[0210] Using β-actin as an internal reference, the expression of ARID1A in ARID1A wild-type NSCLC cells and ARID1A truncated mutant NSCLC cells was detected by western blotting, and the gray value of the western blot protein bands was analyzed by Image J to calculate the relative expression of ARID1A. At the same time, the cell clone experiment was used to detect the RBE of the proton radiotherapy in each cell 0.1 value.
[0211] 1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Half inhibitory concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Half inhibitory concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Half inhibitory concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com