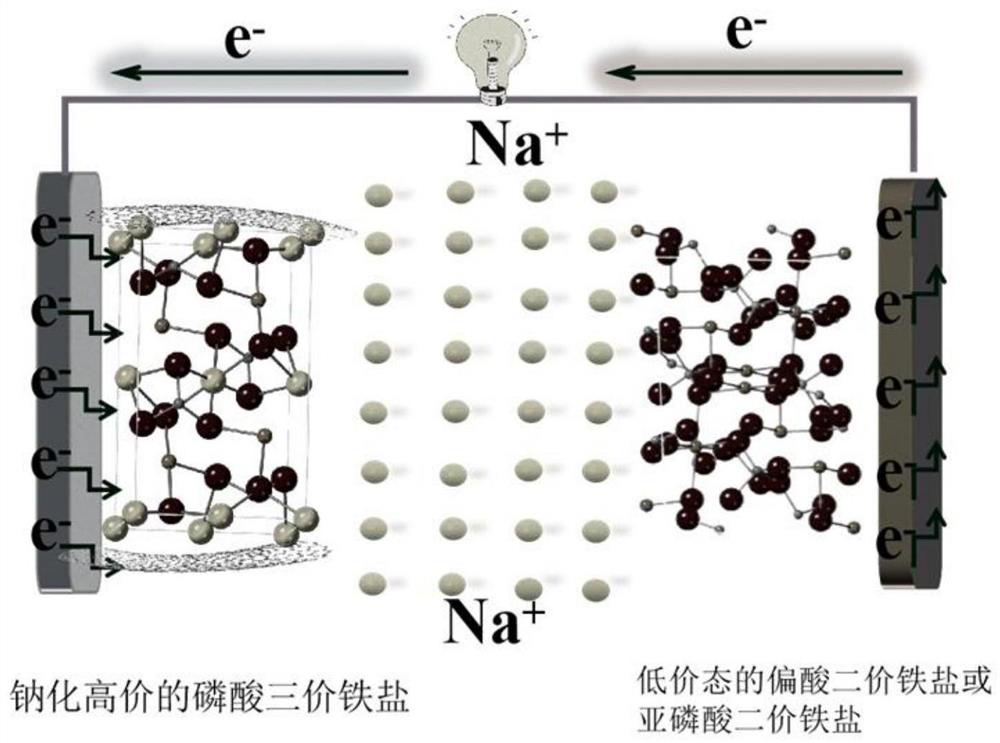
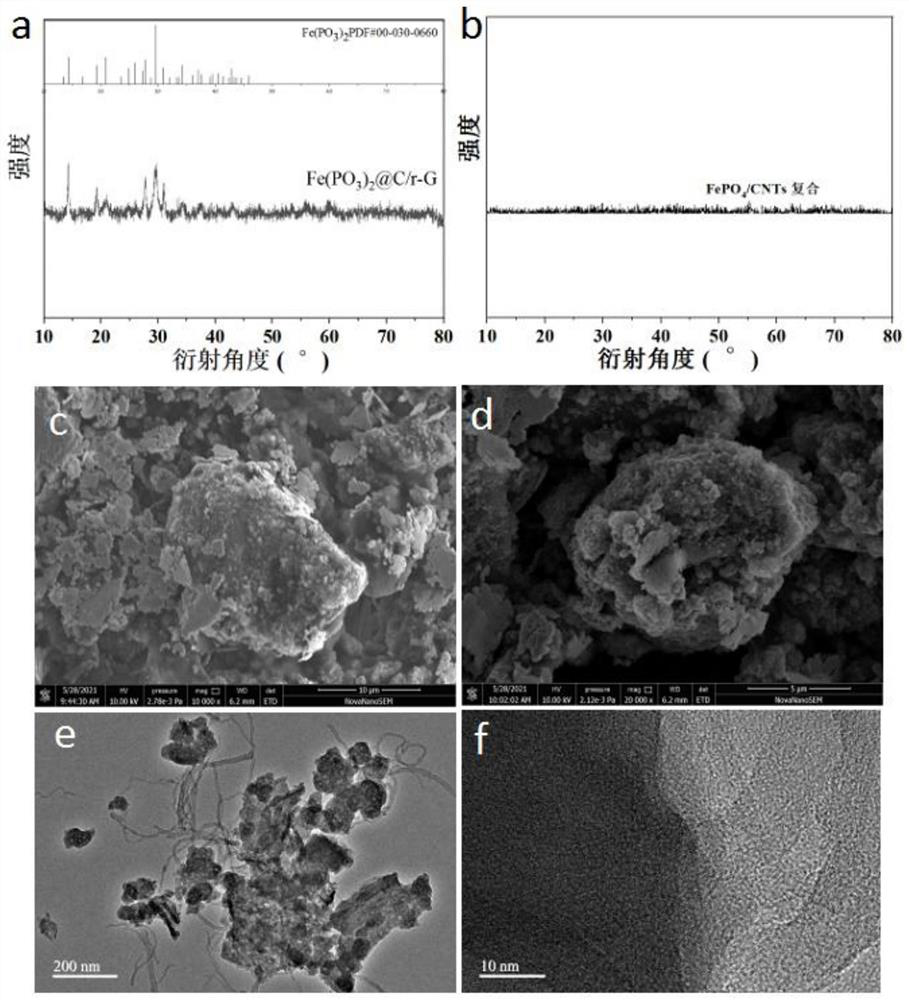
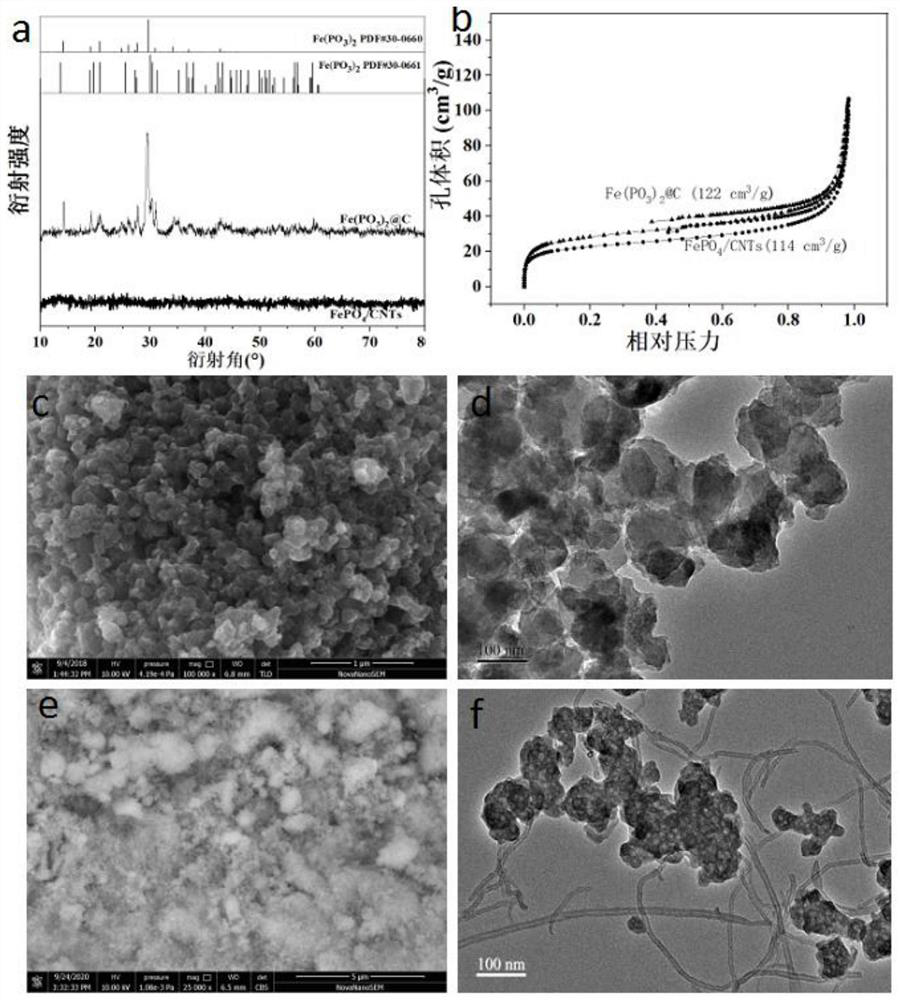
High-safety iron-based phosphate sodium ion total battery and preparation method thereof
An iron-based sodium phosphate, high-safety technology, applied in the field of sodium ion full batteries and their preparation, to achieve the effects of improving stability, eliminating hidden dangers of battery bursting, and excellent high and low temperature performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A high-safety iron-based phosphate sodium-ion full battery. The negative electrode material of the full battery is ferric metaphosphate or ferrous phosphite or a mixture of the two with carbon materials, and the positive electrode material is high-valence Ferric phosphate salt. Its preparation method is as follows:
[0028] Dissolve 0.4 g of P123 in a beaker with 100 ml of deionized water, then ultrasonically stir in an ultrasonic machine until it is completely dissolved, then add 0.5 mM ferric sulfate hydrate (ferric iron salt) into the solution and ultrasonically stir for 10 minutes, A clear and transparent solution was obtained, and the solution A was prepared by stirring continuously in an ice-water bath for 1 h. Take another 47 mg GO powder (1 time of conductive polymer pyrrole) and ultrasonically disperse it in a beaker with 100 ml of deionized water, then take 0.7mM phytic acid and disperse it in the beaker, stir ultrasonically for 10 minutes to form a transpare...
Embodiment 2
[0032] A high-safety iron-based phosphate sodium-ion full battery. The negative electrode material of the full battery is ferric metaphosphate or ferrous phosphite or a mixture of the two with carbon materials, and the positive electrode material is high-valence Ferric phosphate salt. Its preparation method is as follows:
[0033] In 20 mL of deionized water, put 0.2 g of P123, ultrasonically stirred and dissolved to form a clear and transparent solution, then 1 mM ferric sulfate hydrate raw material was added to the above solution, ultrasonically stirred for a period of time, and magnetic stirring was performed to obtain solution A. Dissolve 0.2 g of P123 in 44 ml of deionized water with ultrasonic stirring, add 2.5 mM aniline to dissolve evenly, and then disperse 1 mM phytic acid in it until completely dissolved to obtain solution B. With stirring, solution A was dispersed in the solution of step B, transferred to a 250 ml round bottom flask, and stirred magnetically in an ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] A high-safety iron-based phosphate sodium-ion full battery. The negative electrode material of the full battery is ferric metaphosphate or ferrous phosphite or a mixture of the two with carbon materials, and the positive electrode material is high-valence Ferric phosphate salt. Its preparation method is as follows:
[0038] Weigh out 10 mM FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 15 mM HPO 3 , the two substances were added to 100 mL of water to dissolve them completely; another 1 mM aniline was dissolved in FeSO 4 ·7H 2 In the aqueous solution of O, ultrasonically stir and dissolve evenly; another 0.3 g of ammonium persulfate is dissolved in H 3 PO3 In the aqueous solution, it was dissolved evenly by ultrasonic stirring. Then, under high-speed stirring, the H 3 PO 3 The mixed solution of ammonium persulfate was slowly added dropwise to aniline and FeSO 4 ·7H 2 in a mixed solution of O. A light green precipitate is produced in the container; the solution is filtered, and the precip...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com