Mechanical structure residual life prediction method based on Wiener process and P-EMD
A P-EMD and mechanical structure technology, applied in the testing of machine/structural components, testing of mechanical components, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as dependence on fault interval time data, complicated calculations, and aliasing of equipment failure modes to achieve Avoid the difficulty and inaccuracy of mechanism modeling, good adaptability and prediction accuracy, and the effect of suppressing overshooting phenomenon
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0072] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the implementation manner of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
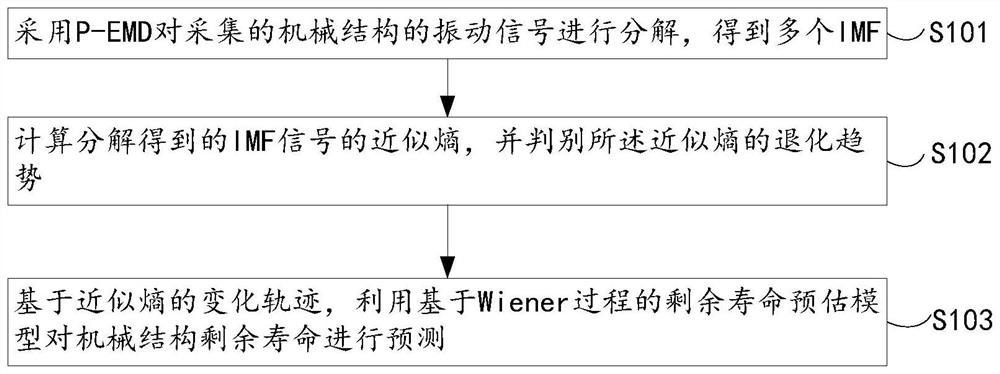
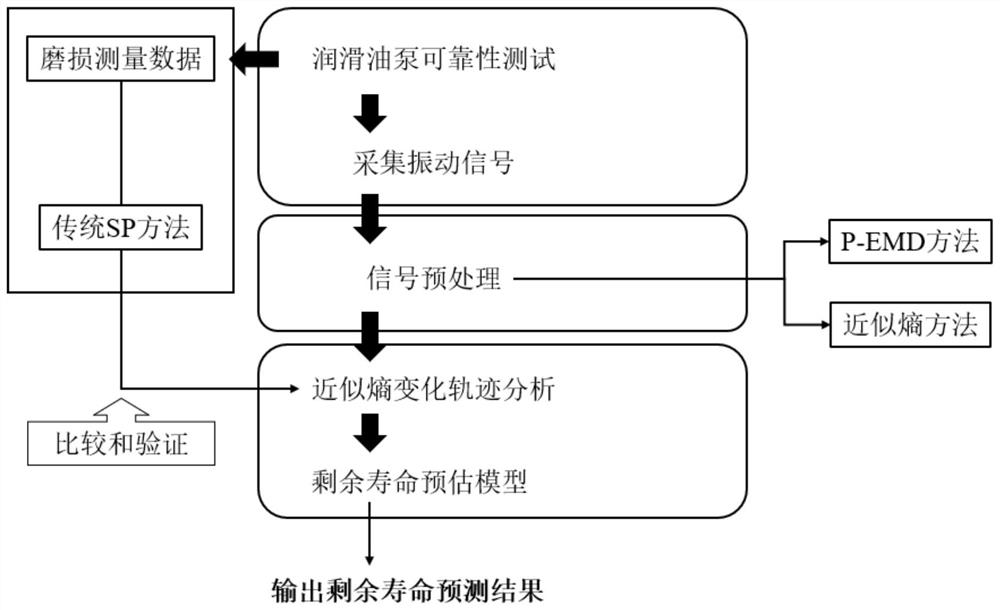
[0073] Such as figure 1 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a method for predicting the remaining life of a mechanical structure based on the Wiener process and P-EMD, including:
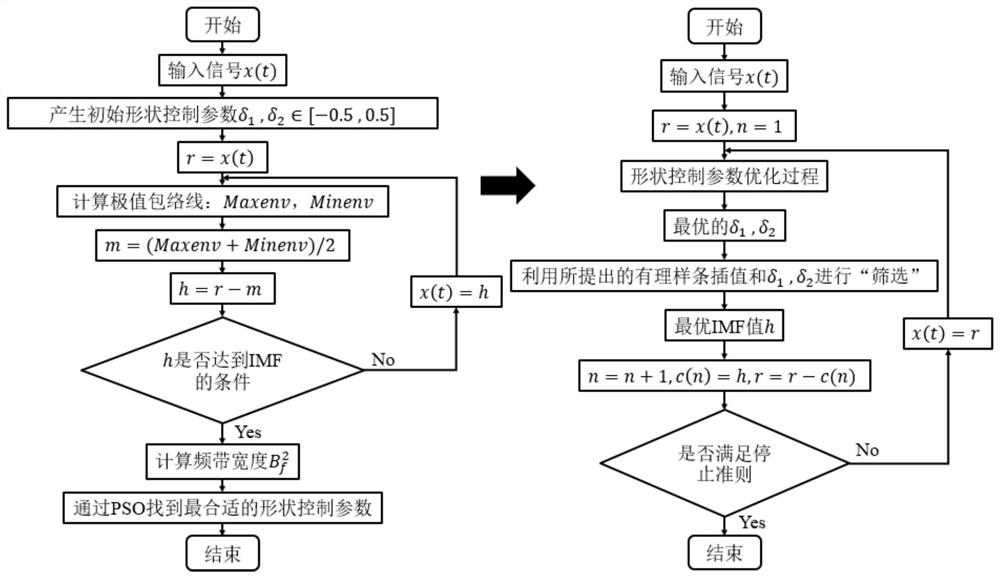
[0074] S101, using P-EMD to decompose the collected vibration signal of the mechanical structure to obtain a plurality of Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMF), where P-EMD means based on particle swarm optimization and Hermite (Hermite) ) Empirical mode decomposition of the interpolation polynomial, such as figure 2 As shown, specifically, the following steps may be included:
[0075] A1, take the collected vibration signal of the mechanical structure as the input signal x(t), and perform initialization processing (setting parameters and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com