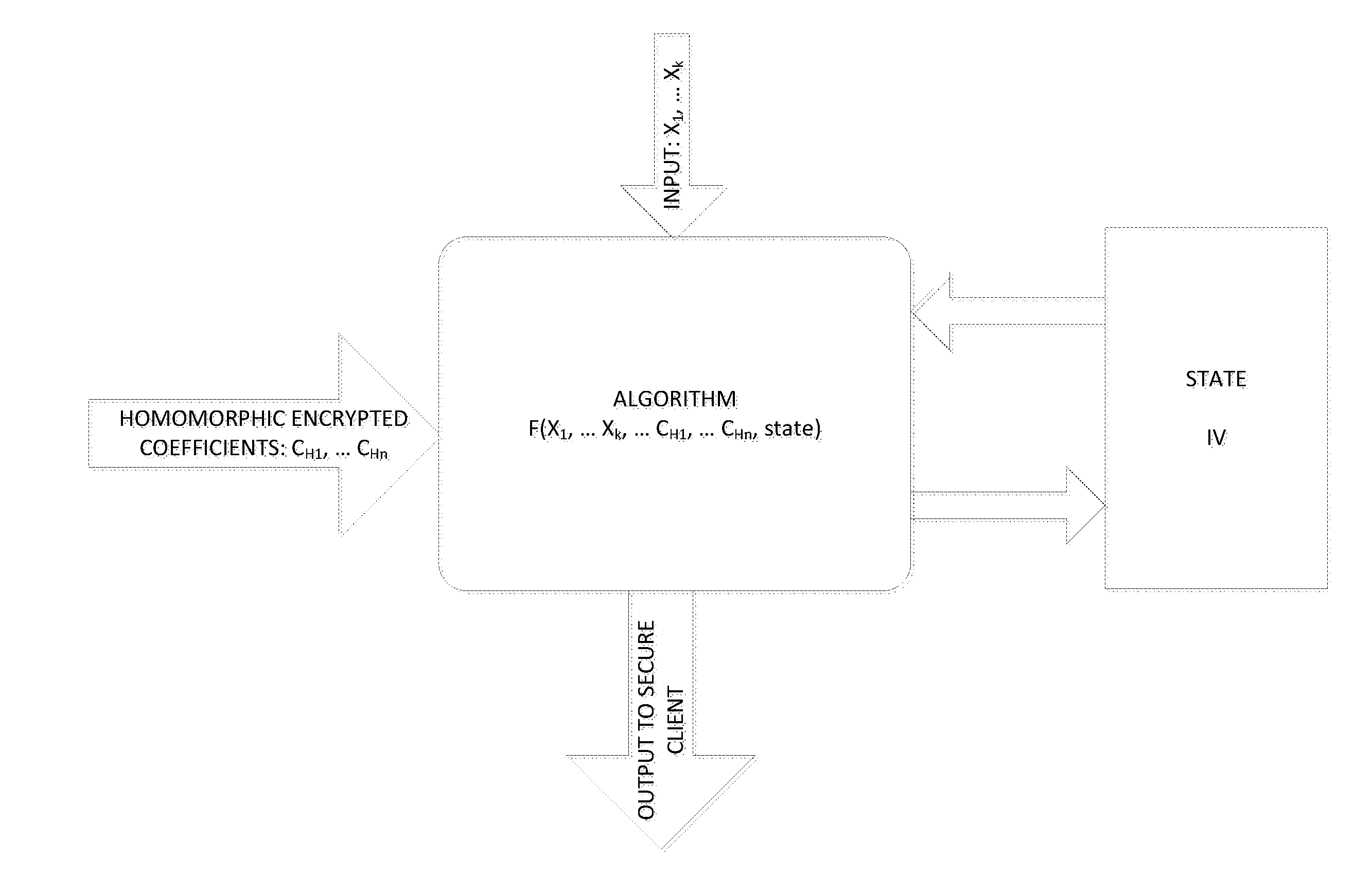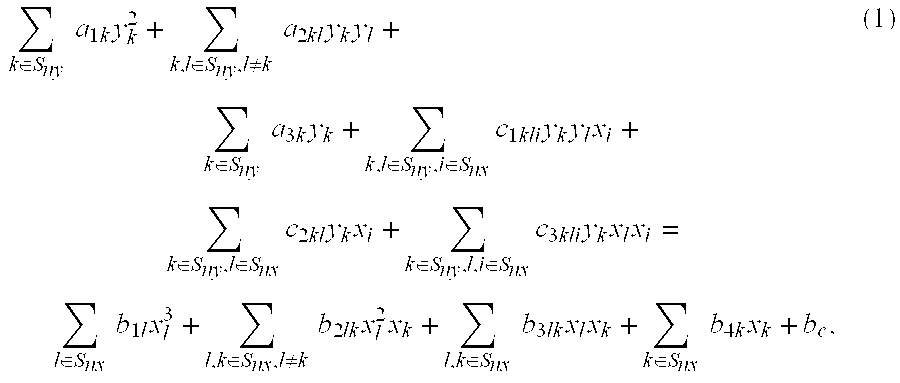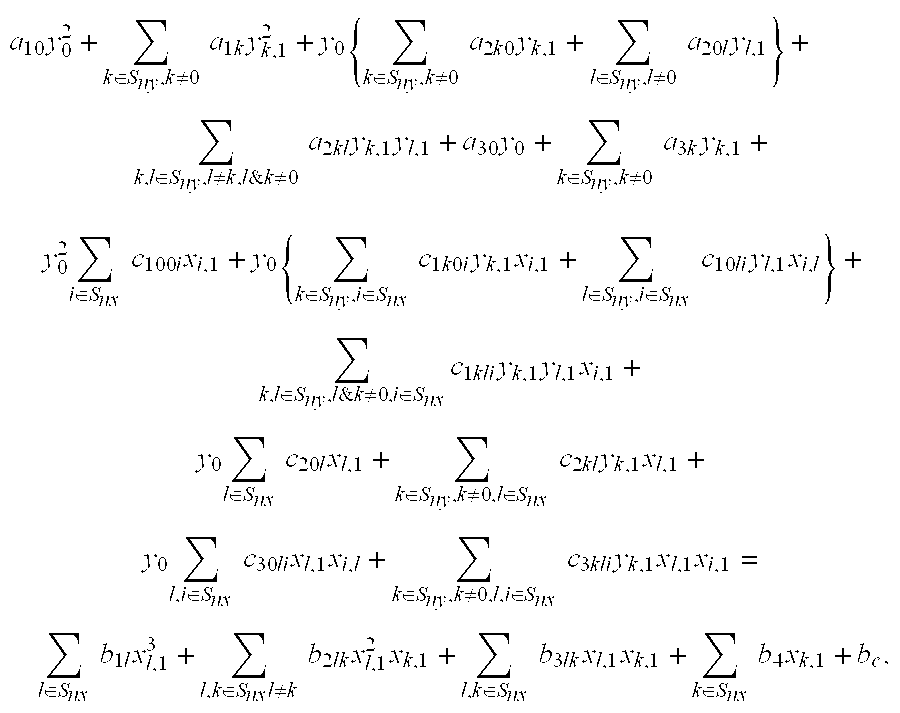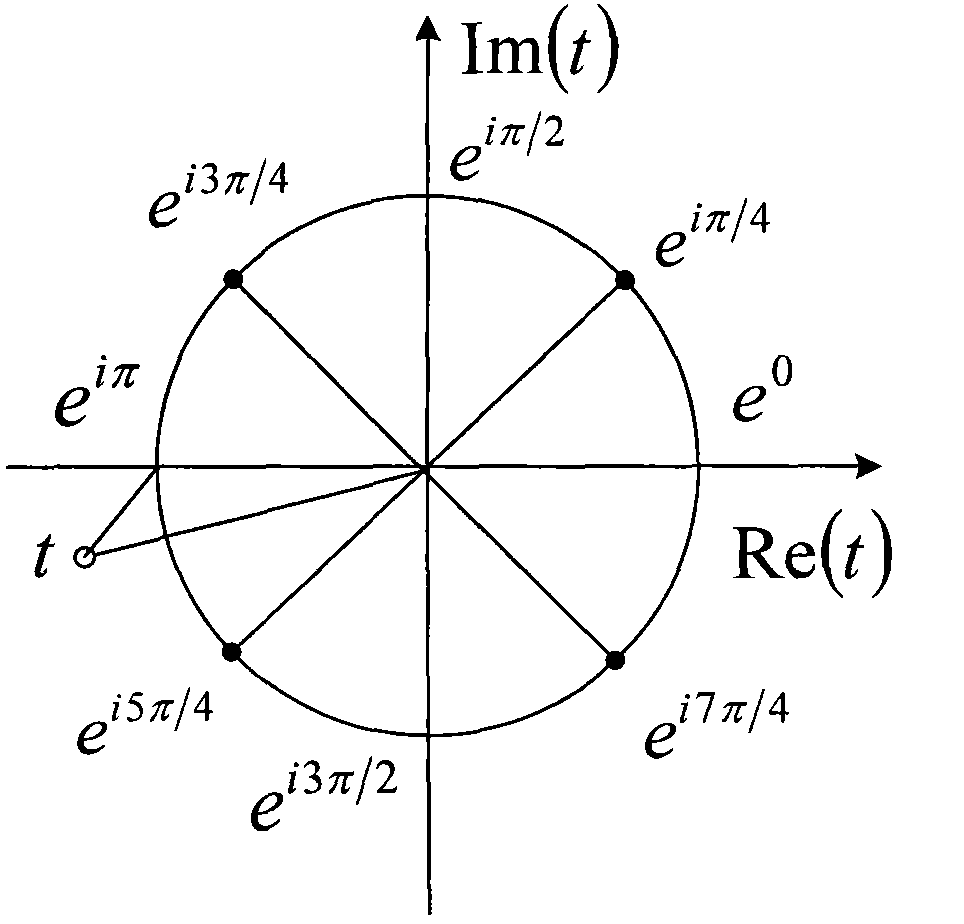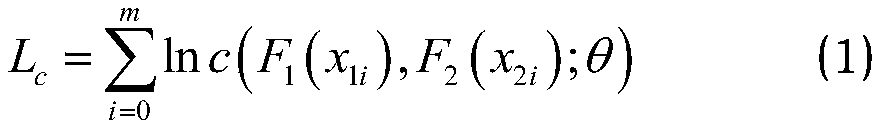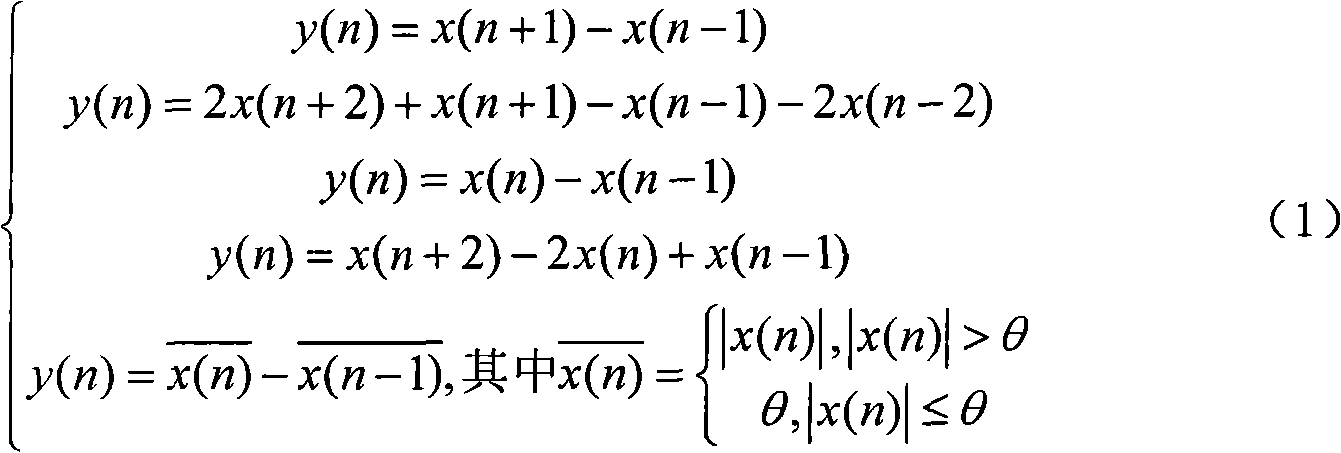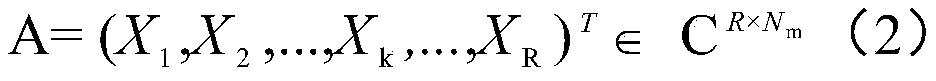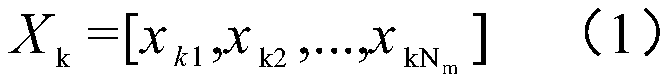Patents
Literature
82 results about "Hermite functions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hermite functions as eigenfunctions of the Fourier transform. The Hermite functions ψ n(x) are a set of eigenfunctions of the continuous Fourier transform. To see this, take the physicist's version of the generating function and multiply by exp(−x 2/2).
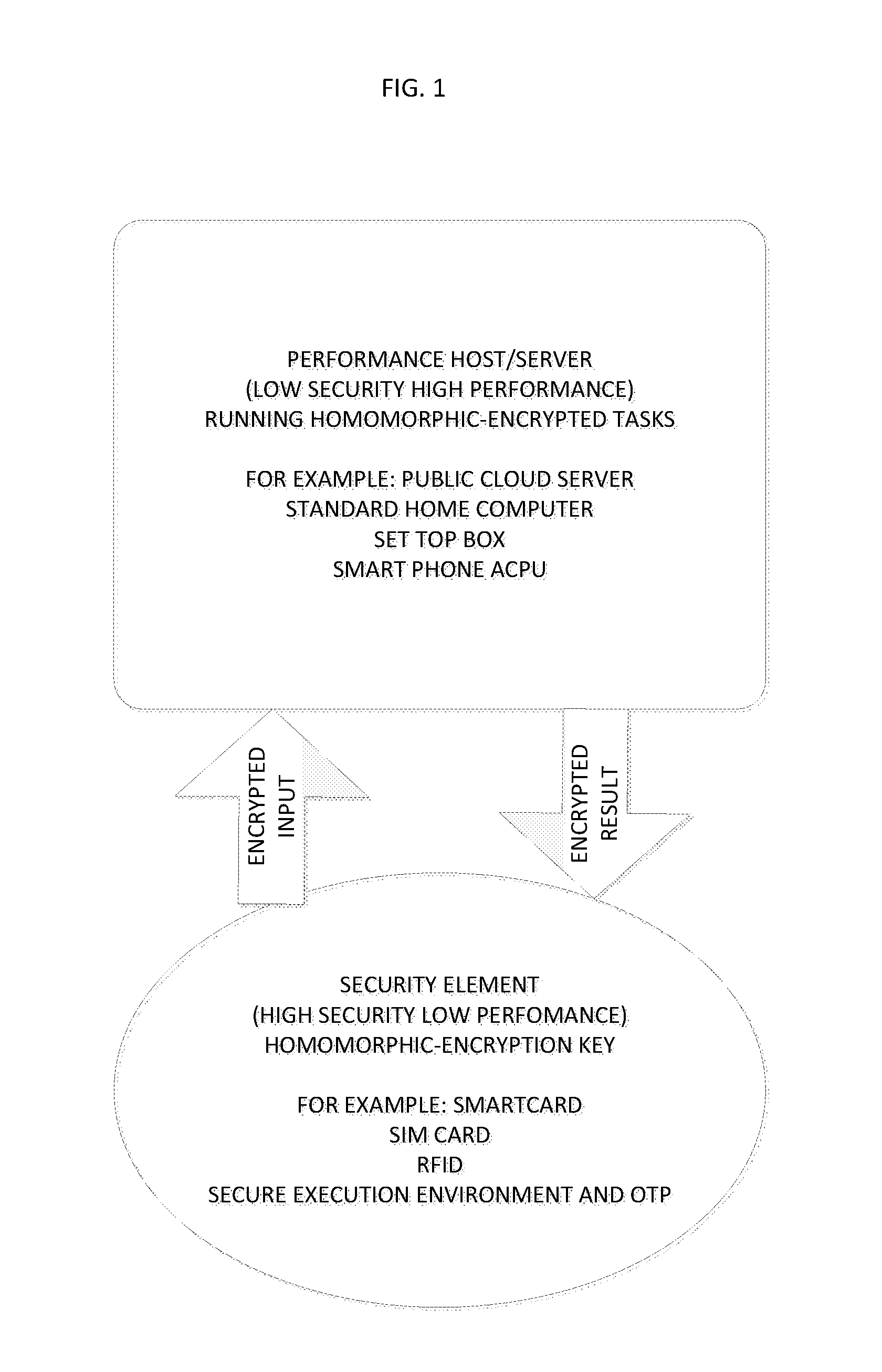
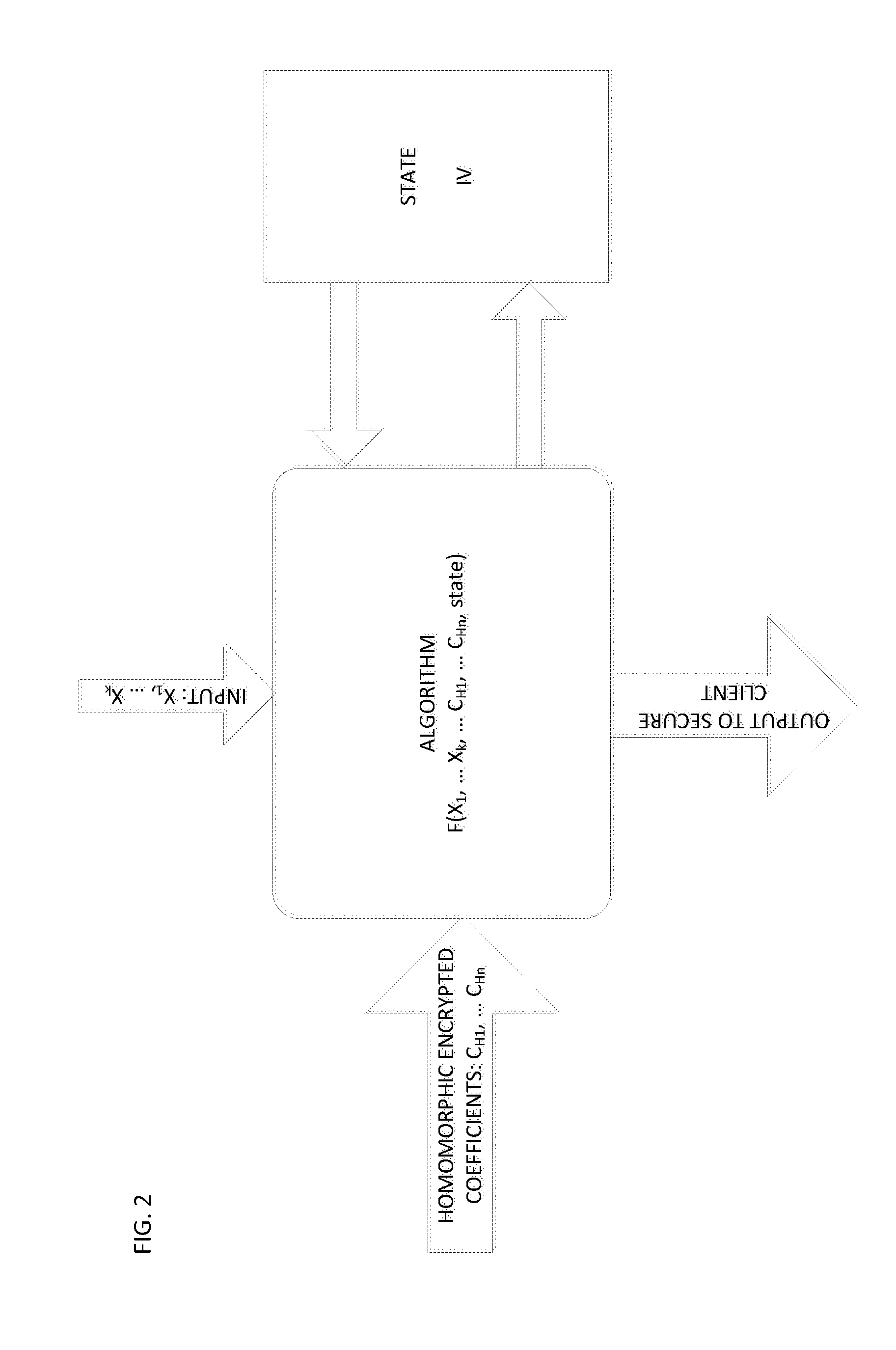
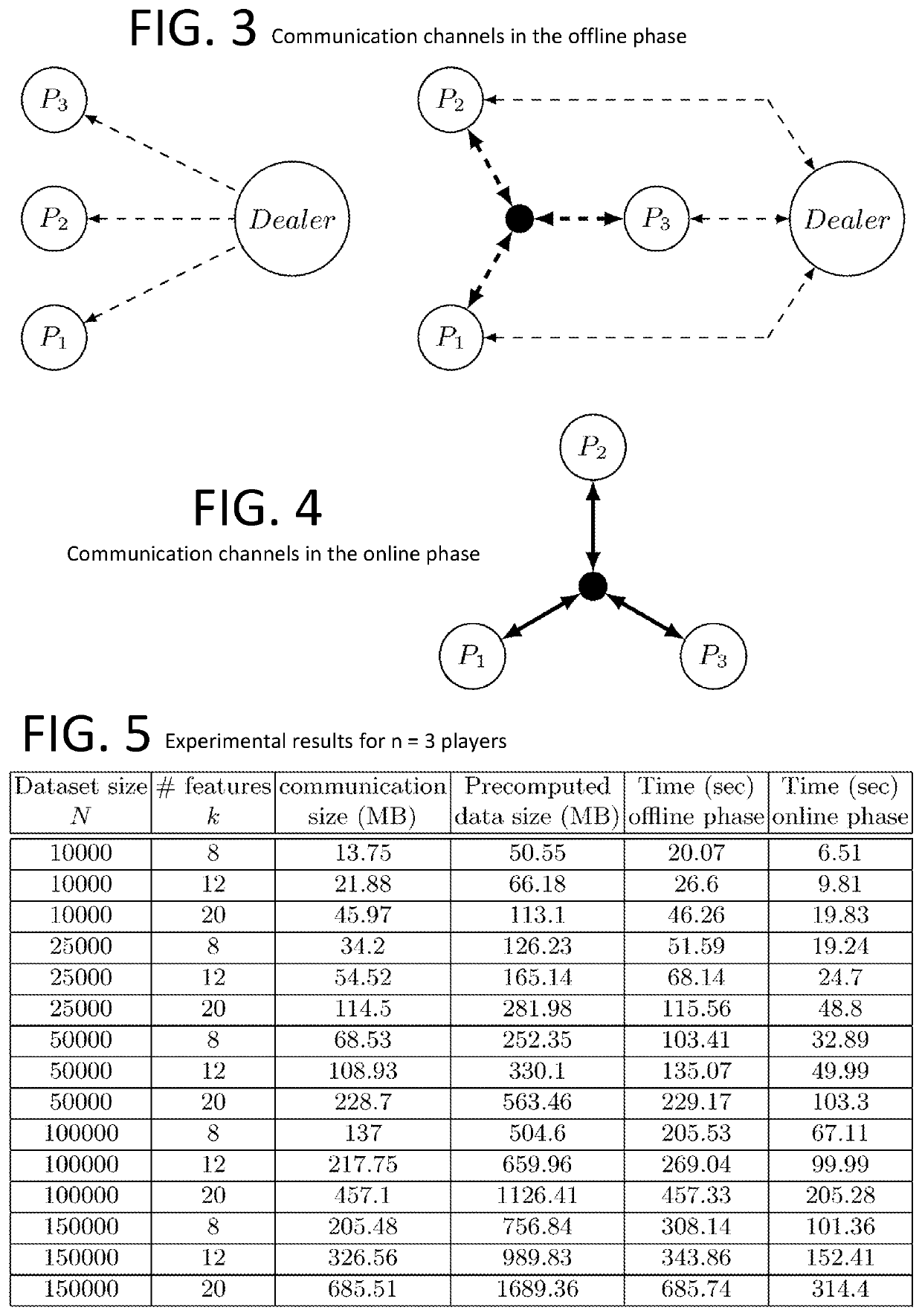
Method and system for homomorphicly randomizing an input
ActiveUS20150215123A1Easy to useEnsure confidentialityKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsThird partyAlgorithm
A fully homomorphic method and system for randomizing an input, wherein all computations are over a commutative ring is described. Equivalent methods for performing the randomization using matrices and polynomials are detailed, as well as ways to mix the matrix and polynomial functions. Addition, multiplication, and division of the matrix and polynomial functions is further described. By performing computations of the functions modulo N over a ring ZN, the functions are usable as encryption functions. The method and system can also be used for verifying that a returned result of a calculation performed by a third party is valid for any of the calculations described herein. Related methods, systems, and apparatus are also described.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
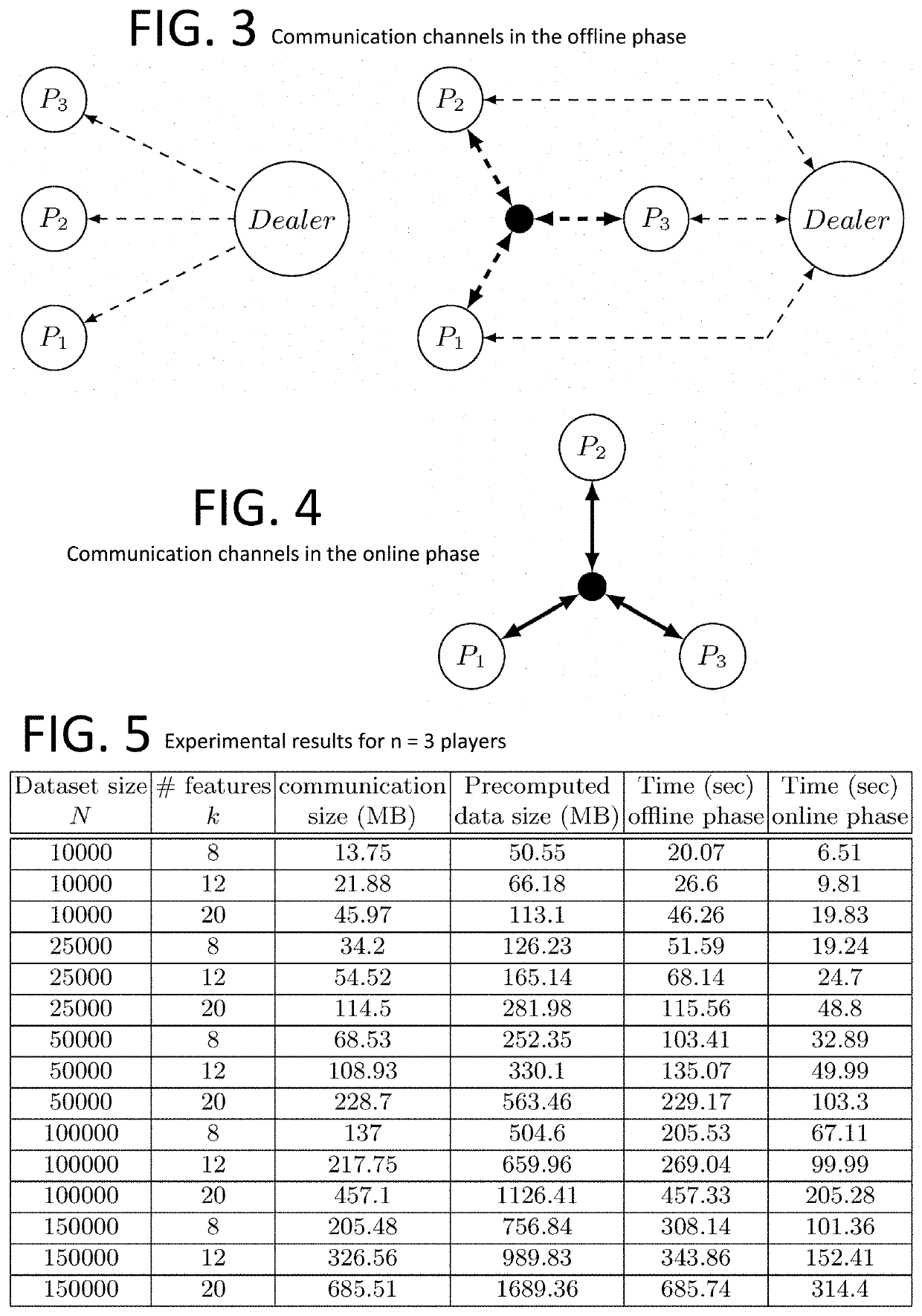
High-Precision Privacy-Preserving Real-Valued Function Evaluation
InactiveUS20200304293A1Reduced memory storage requirementImprove accuracyKey distribution for secure communicationNeural architecturesPlaintextSecret share
A method for performing privacy-preserving or secure multi-party computations enables multiple parties to collaborate to produce a shared result while preserving the privacy of input data contributed by individual parties. The method can produce a result with a specified high degree of precision or accuracy in relation to an exactly accurate plaintext (non-privacy-preserving) computation of the result, without unduly burdensome amounts of inter-party communication. The multi-party computations can include a Fourier series approximation of a continuous function or an approximation of a continuous function using trigonometric polynomials, for example, in training a machine learning classifier using secret shared input data. The multi-party computations can include a secret share reduction that transforms an instance of computed secret shared data stored in floating-point representation into an equivalent, equivalently precise, and equivalently secure instance of computed secret shared data having a reduced memory storage requirement.
Owner:INPHER INC
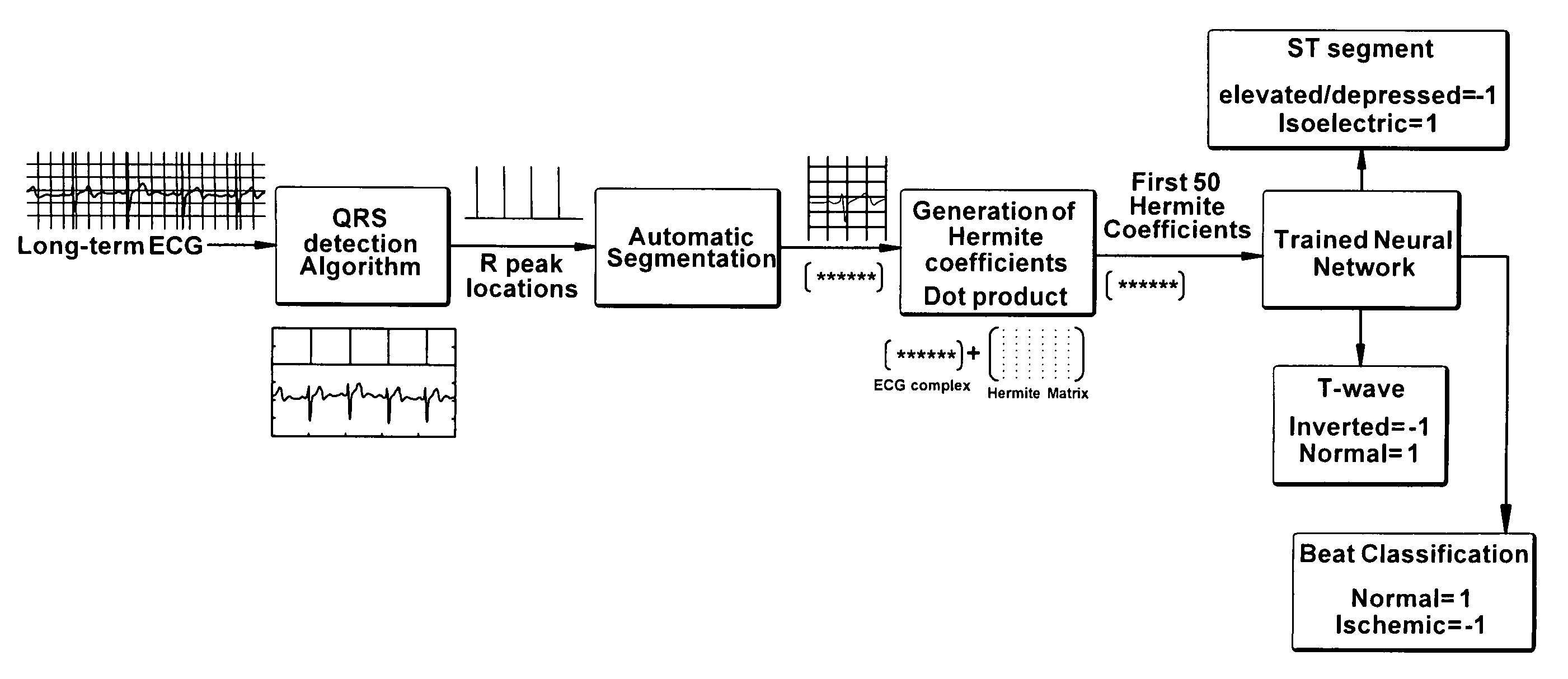
General diagnostic and real-time applications of discrete hermite functions to digital data
InactiveUS8249698B2Accurate modelingData augmentationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDigital dataSignal of interest
General diagnostic and real-time application of digital Hermite functions allows features to be extracted from a measured signal through expansion of the measured signal. Specifically, the digital Hermite functions represent the shape of the measured signal in a set of vectors derived from a symmetrical tridiagonal matrix. This allows for efficient computation of the Hermite expansion coefficients, in real-time, to represent the expanded signal. The signal expansion also allows any artifacts, such as noise, to be isolated and removed, allowing the underlying signal of interest to be revealed.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
General diagnostic and real-time applications of discrete hermite functions to digital data
InactiveUS20080262367A1Accurate modelingData augmentationElectrocardiographySensorsDigital dataComputer science
The present invention relates to general diagnostic and real-time applications of discrete Hermite functions to digital data. More specifically, the invention relates to methods and systems for the application of dilated discrete digital Hermite functions (DDHF) to biomedical data, for example, to extract features from digital signals, including but not limited to, ECGs, EMGs, EOGs, EEGs, and others, by expanding the measured signals using a computationally efficient technique. These digital Hermite functions form the basis for the new discrete Hermite transform, generated on a beat by beat basis, which provides information about the shape of the signals, such as that in the BCG artifact in an EEG or in an ECG interval, or any noise in any other electrical signal. An automated system and method for real-time interpretation of any abnormalities present in a digital biomedical signal is provided.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Cryptographic hash functions using elliptic polynomial cryptography
InactiveUS20100166175A1Readily apparentUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareCryptographic hash function
The cryptographic hash functions using of elliptic polynomial polynomials are based on the elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem, which is well known as a computationally hard problem. The hash functions are based on the elliptic polynomial equation in their generation, where different elliptic polynomials are used for different blocks of the same plain text. Particularly, the hash functions use an elliptic polynomial with more than one independent x-coordinate. More specifically, a set of elliptic polynomial points are used that satisfy an elliptic polynomial equation with more than one independent x-coordinate which is defined over a finite field F.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Automatic correction for continuum background in laser induced breakdown and Raman spectroscopy
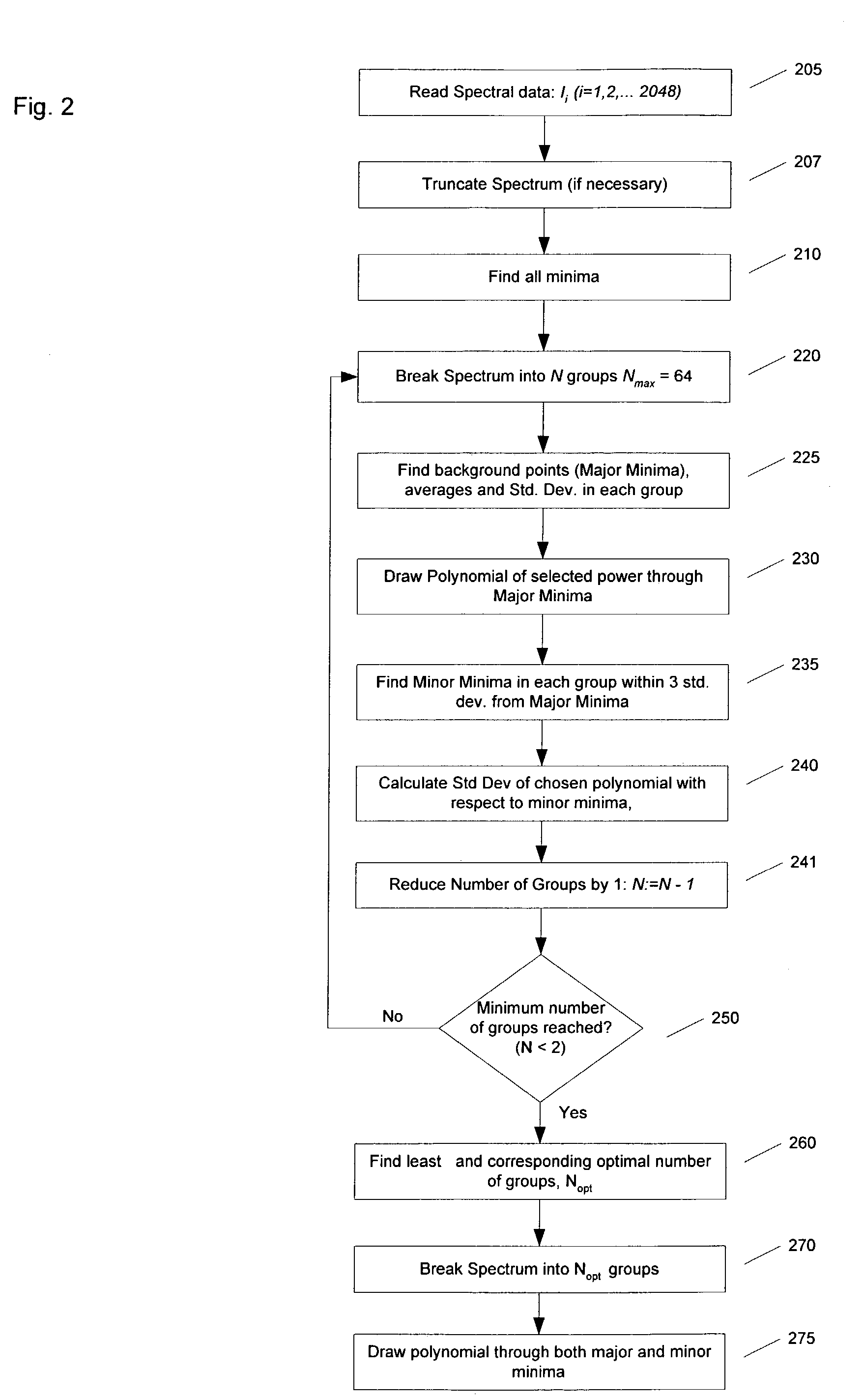
The approximation of a spectral continuum by determining a plurality of minima in the spectral data; splitting the spectral data into a predetermined number of groups N; for each group of spectral data, determining major minima for the group, and calculating an average and a standard deviation for the determined major minima; determining a polynomial function that can be drawn through the major minima of all groups; for each group of spectral data, determining minor minima; calculating an average deviation (ΦN) between this polynomial function and the determined minor minima; reducing the number of groups, and repeating this process for the reduced number of groups until a minimum number of groups is reached. Then, the least ΦN corresponding to an optimal number of groups Nopt is determined. The spectral data is split into Nopt groups; and a polynomial function that can be drawn through both the major minima and minor minima is determined for Nopt groups. This polynomial function approximates the spectral continuum.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA
Unconditional stability FDTD algorithm based on Associated Hermite orthogonal function
InactiveCN103970717AReduce the number of unknowns to solveComputationally efficientComplex mathematical operationsTime domainAlgorithm
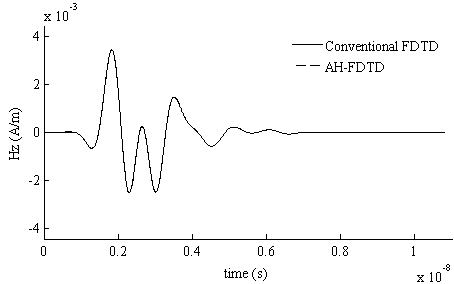
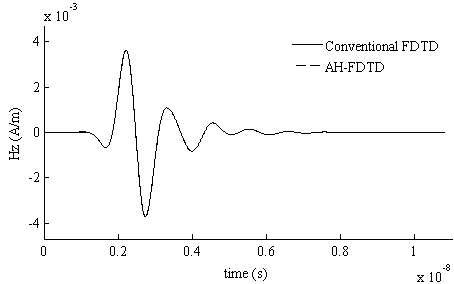
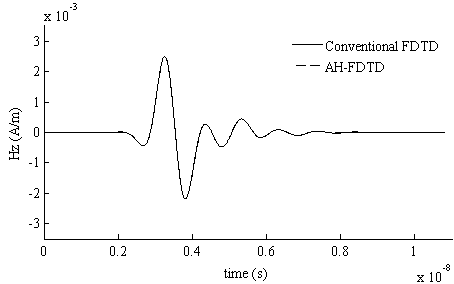
The invention relates to an unconditional stability finite-different time-domain (FDTD) algorithm. The unconditional stability FDTD algorithm expands a differential-form Maxwell equation set through an Associated Hermite (AH) orthogonal function, eliminates a time variable through the Galerkin principle, obtains a finite-dimension AH domain implicit equation for solution, and finally obtains the electromagnetic field time domain result through AH domain inverse transformation. According to the unconditional stability FDTD algorithm based on the AH orthogonal function, through the conversion from the time domain to the AH domain, the solution number of an unknown quantity is largely reduced, and the calculation efficiency is obviously improved. The whole calculation process has nothing to do with the time variable and is not limited by a traditional FDTD stability condition, and the calculation result is unconditionally stable. Through the characteristics, a new resolution method is provided for the problem of efficiently and rapidly calculating a complex electromagnetic field with a multi-scale characteristic.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Generating cryptographic checksums
ActiveCN106688204ASave resourcesError preventionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesChecksumCryptographic nonce
A method (500) of generating a cryptographic checksum for a message M(x) is provided. The method comprises pseudo-randomly selecting (502) at least two irreducible polynomials p i (x). Each irreducible polynomial p i (x) is selected based on a first cryptographic key from the set of irreducible polynomials of degree ni over a Galois Field. The method further comprises calculating (503) a generator polynomial p(x) of degree n = formula (I) as a product of the N irreducible polynomials formula (II), and calculating (505) the cryptographic checksum as a first function g of a division of a second function of M(x), (M(x)), modulo p(x), i.e., g( (M(x)) mod p(x)). By replacing a standard checksum, such as a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC), with a cryptographic checksum, an efficient message authentication is provided. The proposed cryptographic checksum may be used for providing integrity assurance on the message, i.e., for detecting random and intentional message changes, with a known level of security. Further, a corresponding computer program, a corresponding computer program product, and a checksum generator for generating a cryptographic checksum, are provided.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
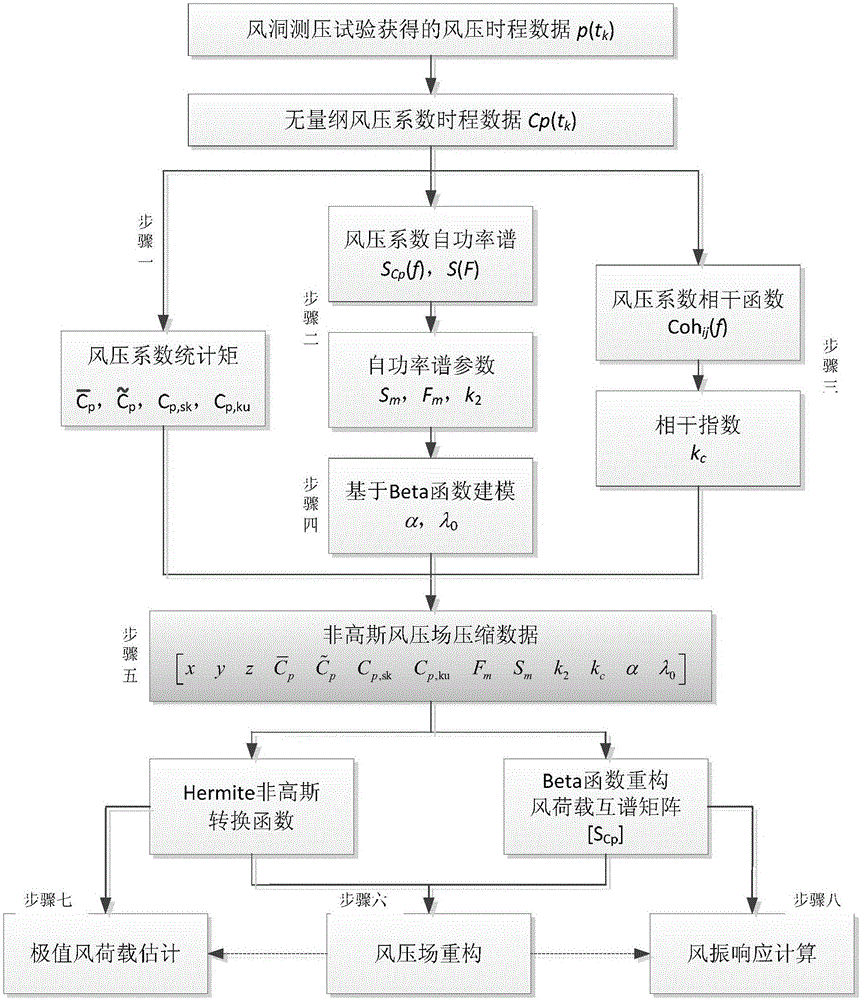
Building wind tunnel pressure measurement test data compression method
ActiveCN106330197AAchieve the purpose of compressionEfficient storageCode conversionData compressionFrequency spectrum
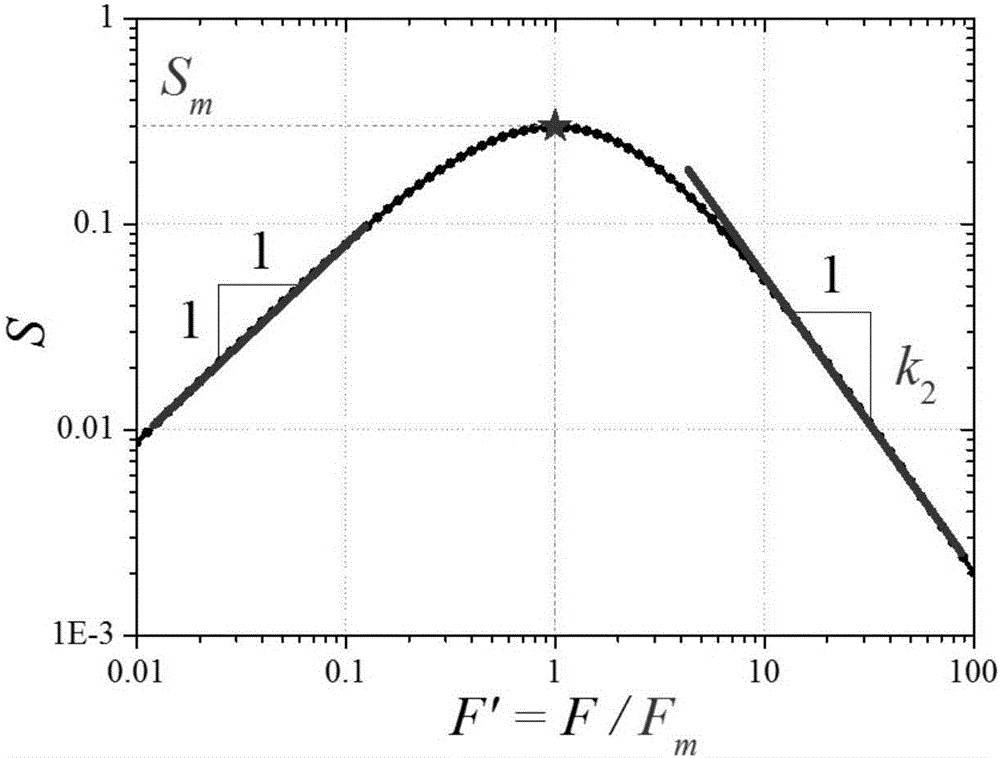
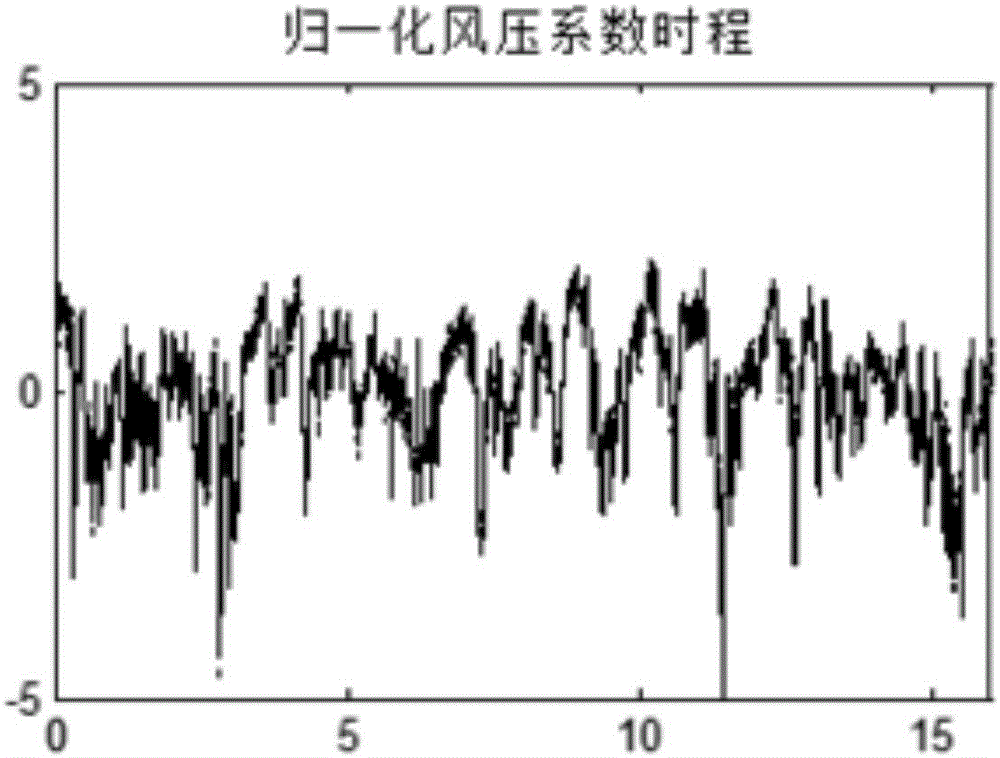
The invention relates to a building wind tunnel pressure measurement test data compression method. The invention aims at solving the problem that the little attention is paid to frequency domain characteristics of wind load and correlation in the prior art, resulting in a data compression error and an actual application error. The statistical information of the data is reconstructed by the Hermite polynomial, and the spectrum information is reconstructed by the Beta function theory, and a compressed wind pressure filed can be reconstructed at last in combination with random simulation technology. By adoption of the building wind tunnel pressure measurement test data compression method provided by the invention, the building wind tunnel pressure measurement data of GB and TB levels can be compressed to the KB and MB levels, and a novel information extracting and modeling method is provided for the high-dimension time-course large data of the wind load changing with time and space so as to achieve the data compression purpose at last. The building wind tunnel pressure measurement test data compression method is applied to the field of building wind tunnel pressure measurement tests.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
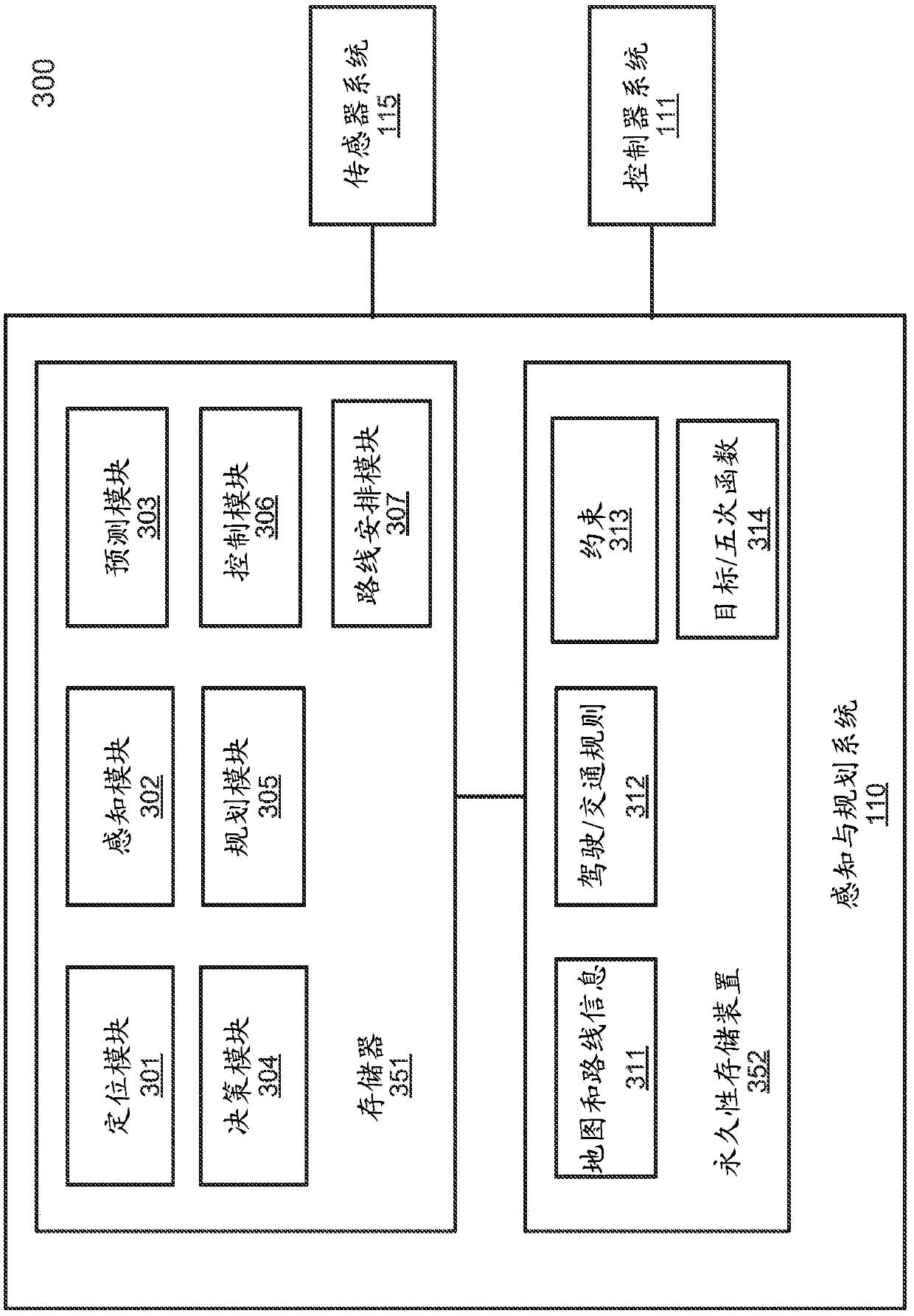
Non-linear reference line optimization method using piecewise quintic polynomial spiral paths for operating autonomous driving vehicles
ActiveCN109955853AAutonomous decision making processRoad vehicles traffic controlSimulationReference line
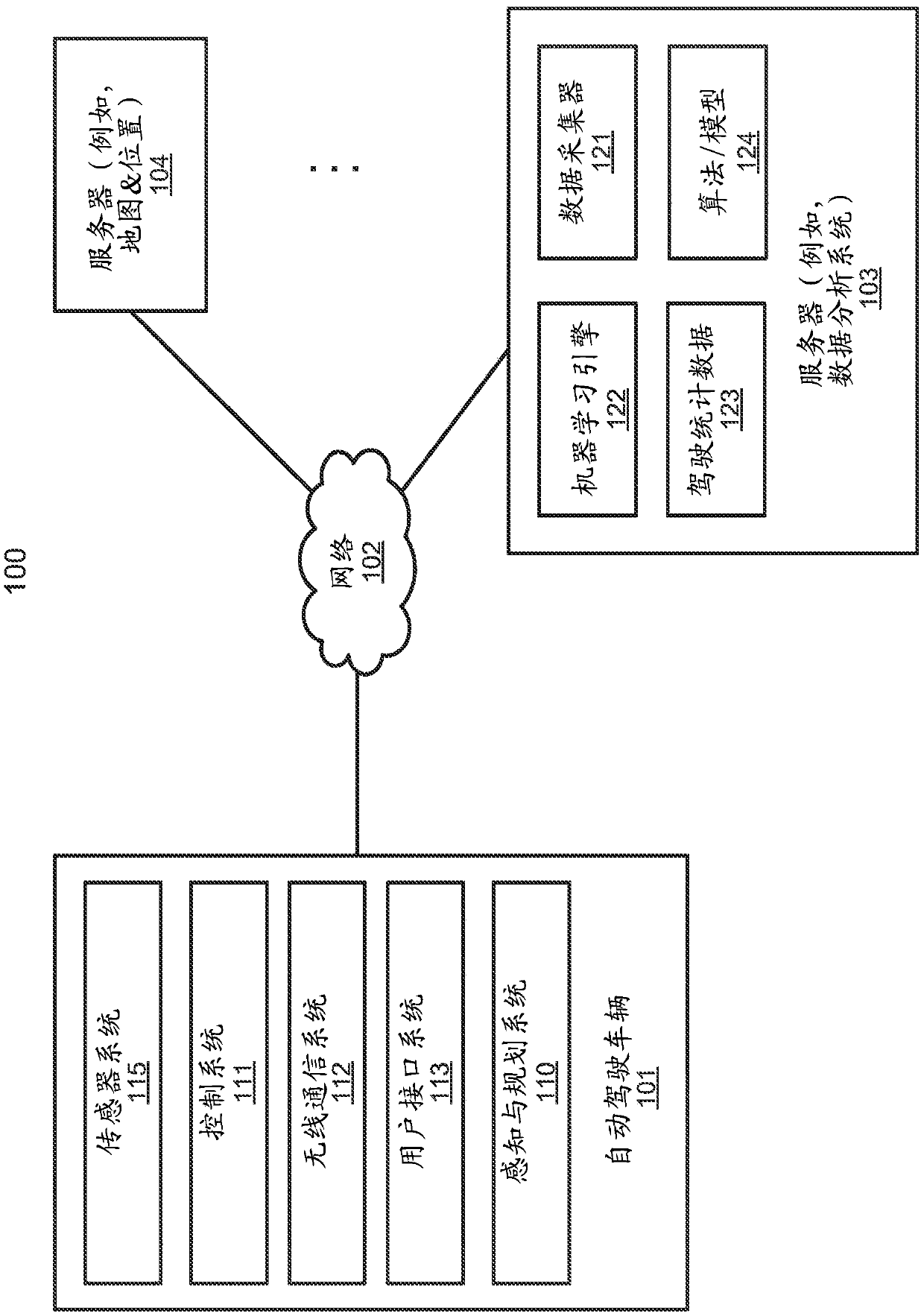
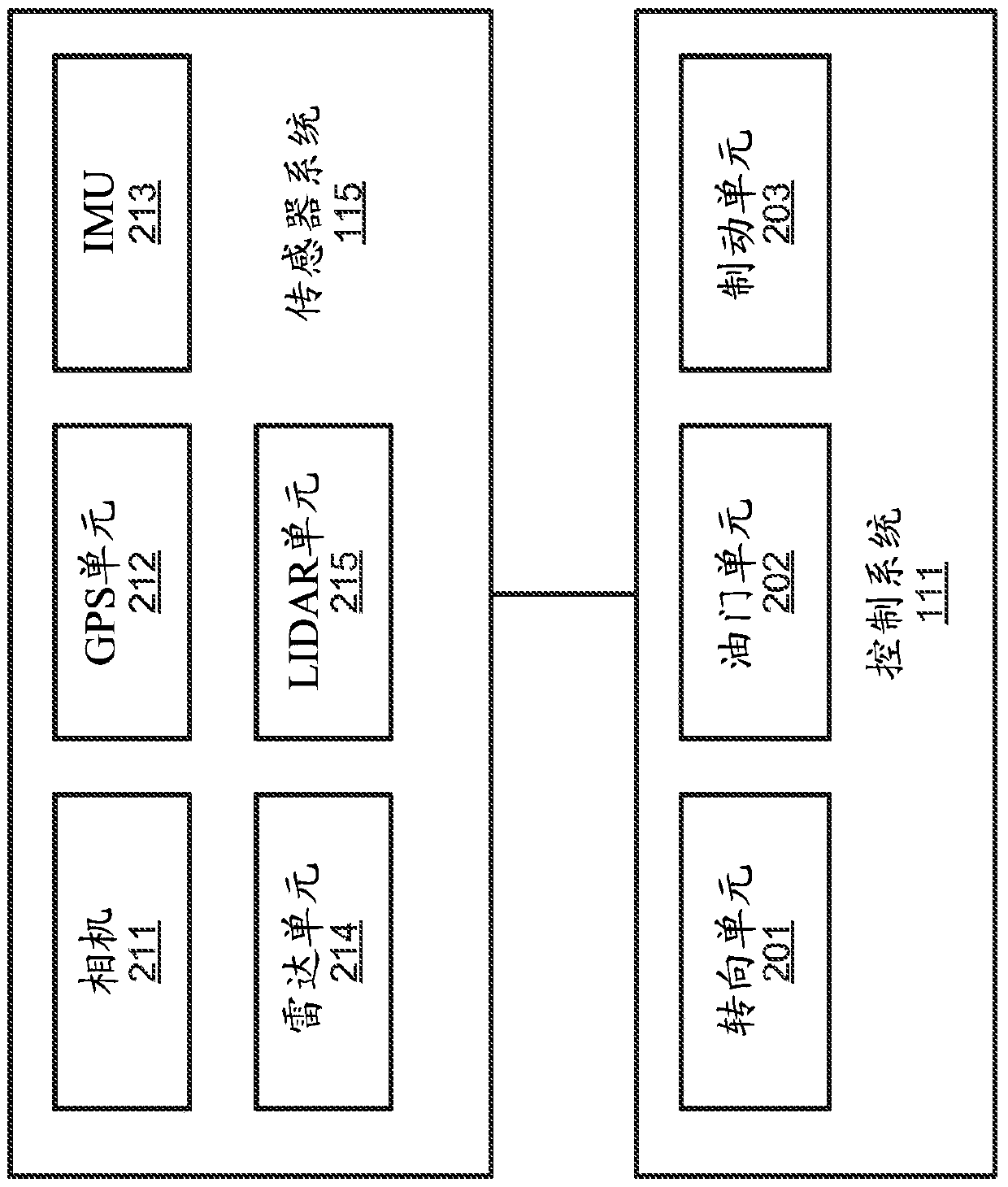
A first reference line representing a trajectory from a first location to a second location associated with an autonomous driving vehicle (ADV) is received. The first reference line is segmented intoa number of reference line segments. For each of the reference line segments, a quintic polynomial function is defined to represent the reference line segment. An objective function is determined based on the quintic polynomial functions of the reference line segments. An optimization is performed on coefficients of the quintic polynomial functions in view of a set of constraints associated with the reference line segments, such that an output of the objective function reaches minimum while the constraints are satisfied. A second reference line is then generated based on the optimized parameters or coefficients of the quintic polynomial functions of the objective function. The second reference line is then utilized to plan and control the ADV.
Owner:BAIDU USA LLC
Phase shift keying signal blind detection method based on plural discrete full-feedback neural network
InactiveCN102035769AGood signal blind detection effectSolve the optimal solution problem in the field of complex numbersPhase-modulated carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksHopfield networkDecreased energy
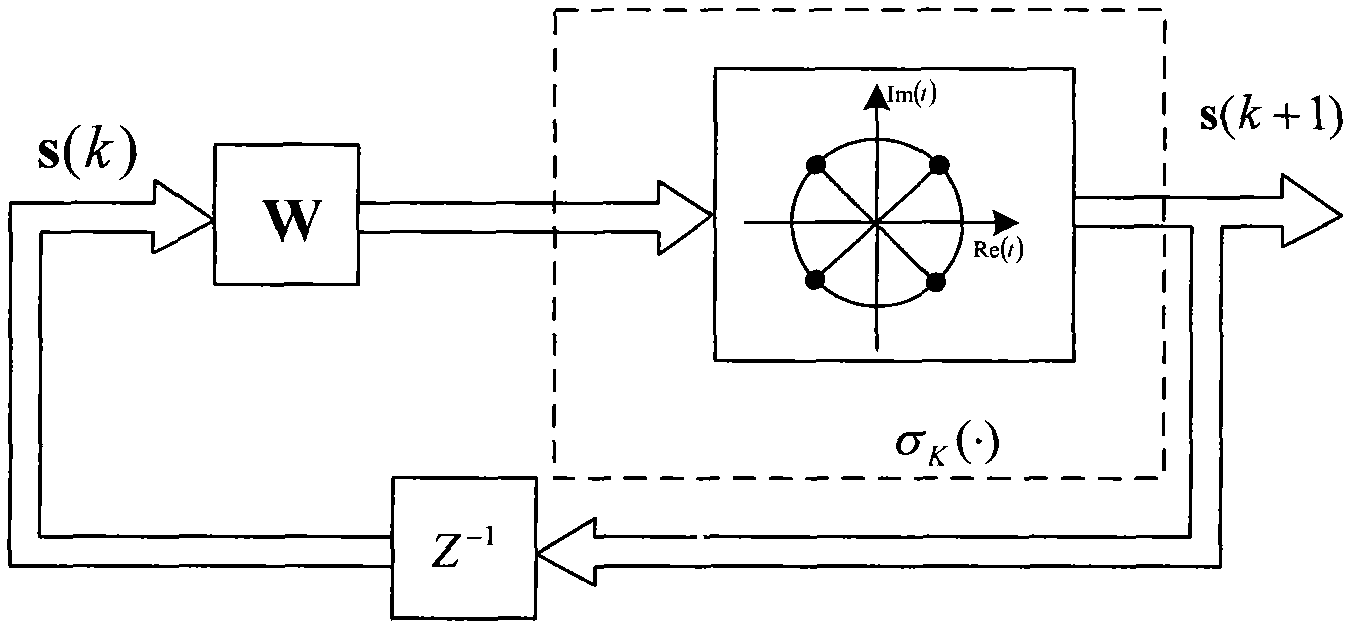
The invention discloses a phase shift keying signal blind detection method based on a plural discrete full-feedback neural network. In the method, according to a principle of decreasing energy function of the plural discrete full-feedback neural network, a Hermitian weight matrix capable of directly detecting phase shift keying signals is constructed, so that each multi-phase shift keying (MPSK) signal centralized constellation signal point is a stable equilibrium point of a Hopfield neural network; therefore, the blind detection of the MPSK signals is realized. The method can realize computing targets by only needing extremely short received data, and can be applied to statistic meaningless occasions. The search space is narrowed, the difficulty is reduced, the search time is obviously superior to that of other blind detection algorithms, and the system performance is correspondingly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
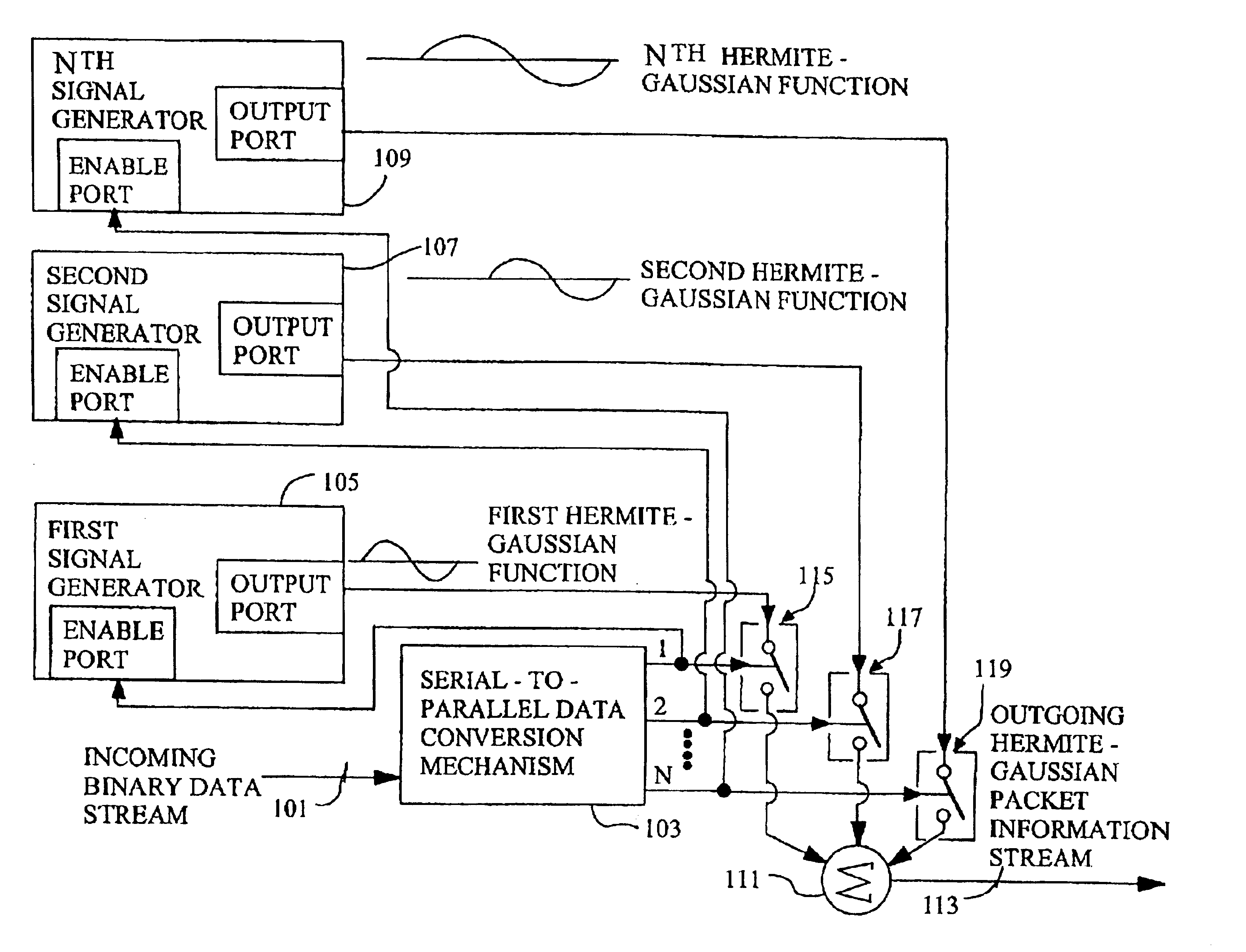
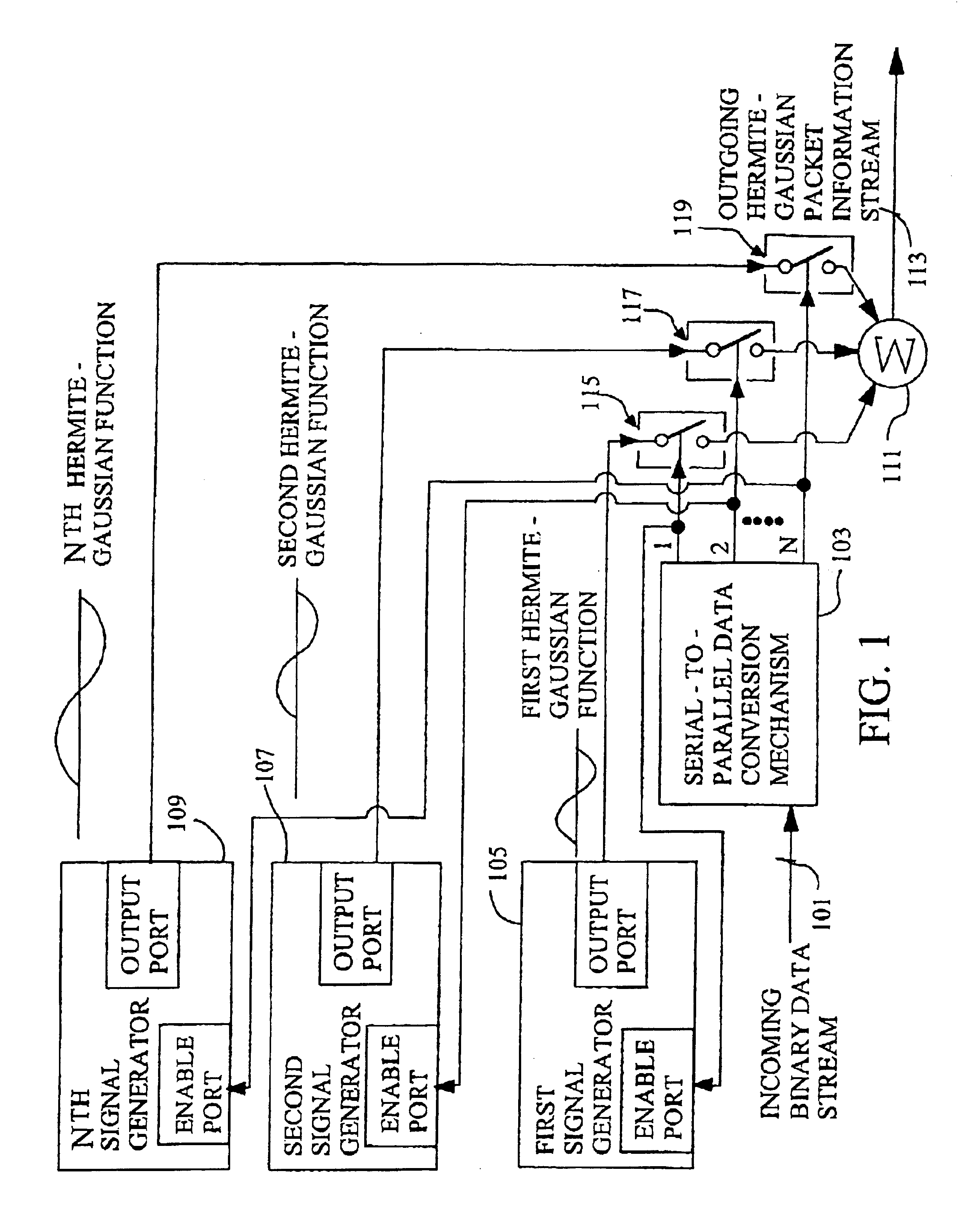
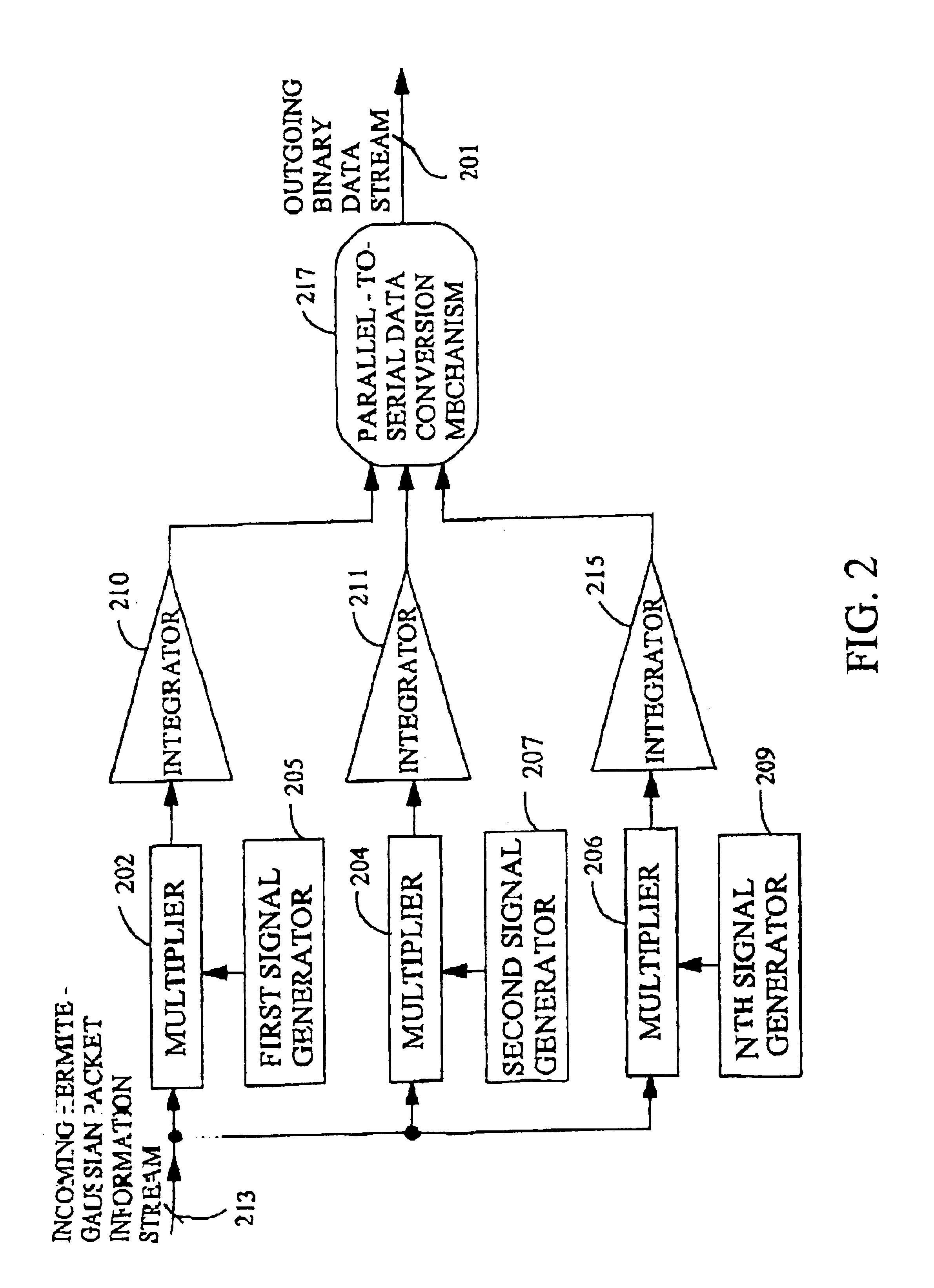
Techniques for communicating information using Hermite-Gaussian basis functions
InactiveUS6898207B2High bit samplingImprove fidelityMultiplex system selection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime domainComputer hardware
Systems and methods for efficiently conveying one or more communication channels over a transmission medium. Communication is effected by transforming an incoming digital bit stream into a Hermite-Gaussian information stream that includes a plurality of Hermite-Gaussian packets. This transformation is accomplished through the use of a plurality of Hermite-Gaussian basis functions. The Hermite-Gaussian information stream is then transmitted over the transmission medium. More particularly, digital bit streams carried on one or more incoming channels may be in the form of binary “on” and “off” bits. These digital bits are converted into a plurality of Hermite-Gaussian waveform components which together comprise a Hermite-Gaussian packet. The conversion process maps each of respective incoming digital bits to a corresponding one of a group of Hermite-Gaussian functions. Optionally, this mapping process could be implemented sequentially, or in parallel form, such that a first bit is mapped to a first Hermite-Gaussian function, a second bit is mapped to a second Hermite-Gaussian function, and so on, until the Nth Hermite-Gaussian function is reached, whereupon the process cycles back to the first Hermite-Gaussian function. In any case, the presence of a “1”, “on”, or “high” bit enables the corresponding Hermite-Gaussian function, whereas the presence of a “0”, “off”, or “low” bit disables the corresponding Hermite-Gaussian function. When enabled, each respective Hermite-Gaussian function specifies the transmission of a corresponding Hermite-Gaussian waveform component. Each waveform component is substantially confined within a range of values in both the frequency and time domains.
Owner:BANDWIDTH TECH
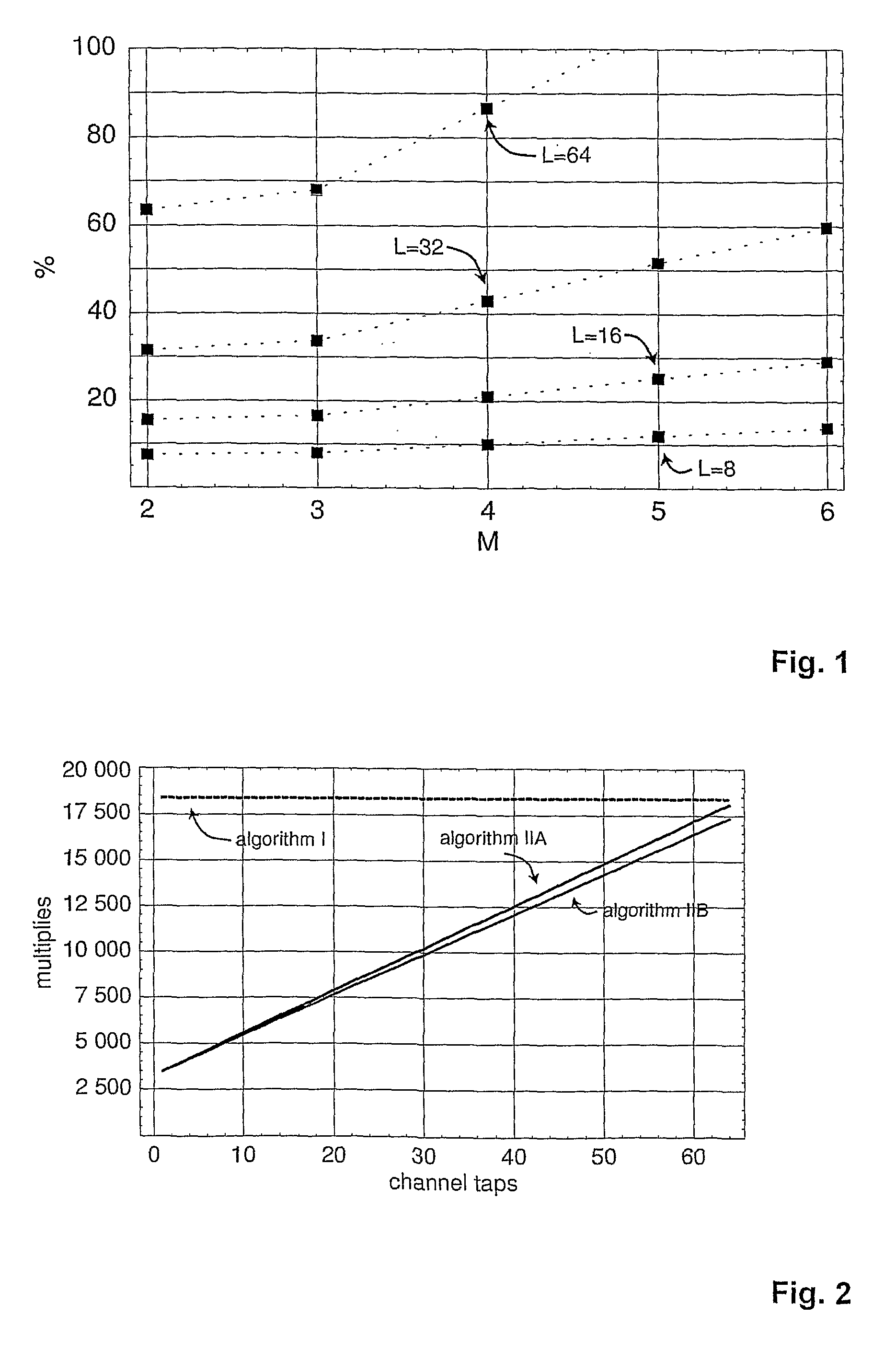
Method for calculating functions of the channel matrices in linear MIMO-OFDM data transmission
InactiveUS7742536B2More computationally efficientPotential for computational savings is particularly largeSecret communicationRadio transmissionAlgorithmEngineering
Owner:ETH ZURICH ETH TRANSTER
High-Precision Privacy-Preserving Real-Valued Function Evaluation
ActiveUS20200358601A1Preserving the privacy of input data contributedImprove accuracyKey distribution for secure communicationNeural architecturesPlaintextAlgorithm
A method for performing privacy-preserving or secure multi-party computations enables multiple parties to collaborate to produce a shared result while preserving the privacy of input data contributed by individual parties. The method can produce a result with a specified high degree of precision or accuracy in relation to an exactly accurate plaintext (non-privacy-preserving) computation of the result, without unduly burdensome amounts of inter-party communication. The multi-party computations can include a Fourier series approximation of a continuous function or an approximation of a continuous function using trigonometric polynomials, for example, in training a machine learning classifier using secret shared input data. The multi-party computations can include a secret share reduction that transforms an instance of computed secret shared data stored in floating-point representation into an equivalent, equivalently precise, and equivalently secure instance of computed secret shared data having a reduced memory storage requirement.
Owner:INPHER INC
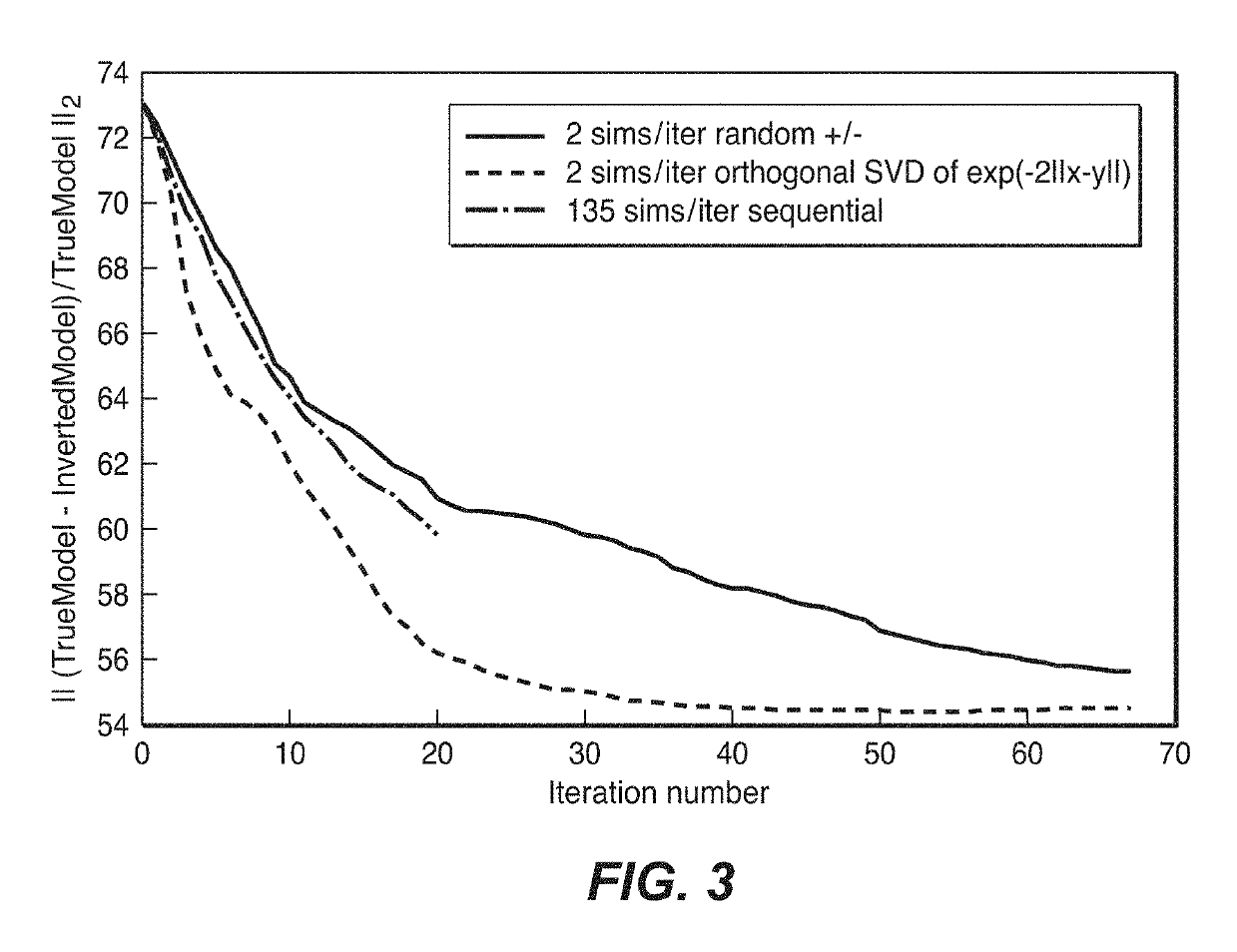
Harmonic encoding for fwi
ActiveUS20160033661A1Computation using non-denominational number representationSeismic signal processingFeature vectorAlgorithm
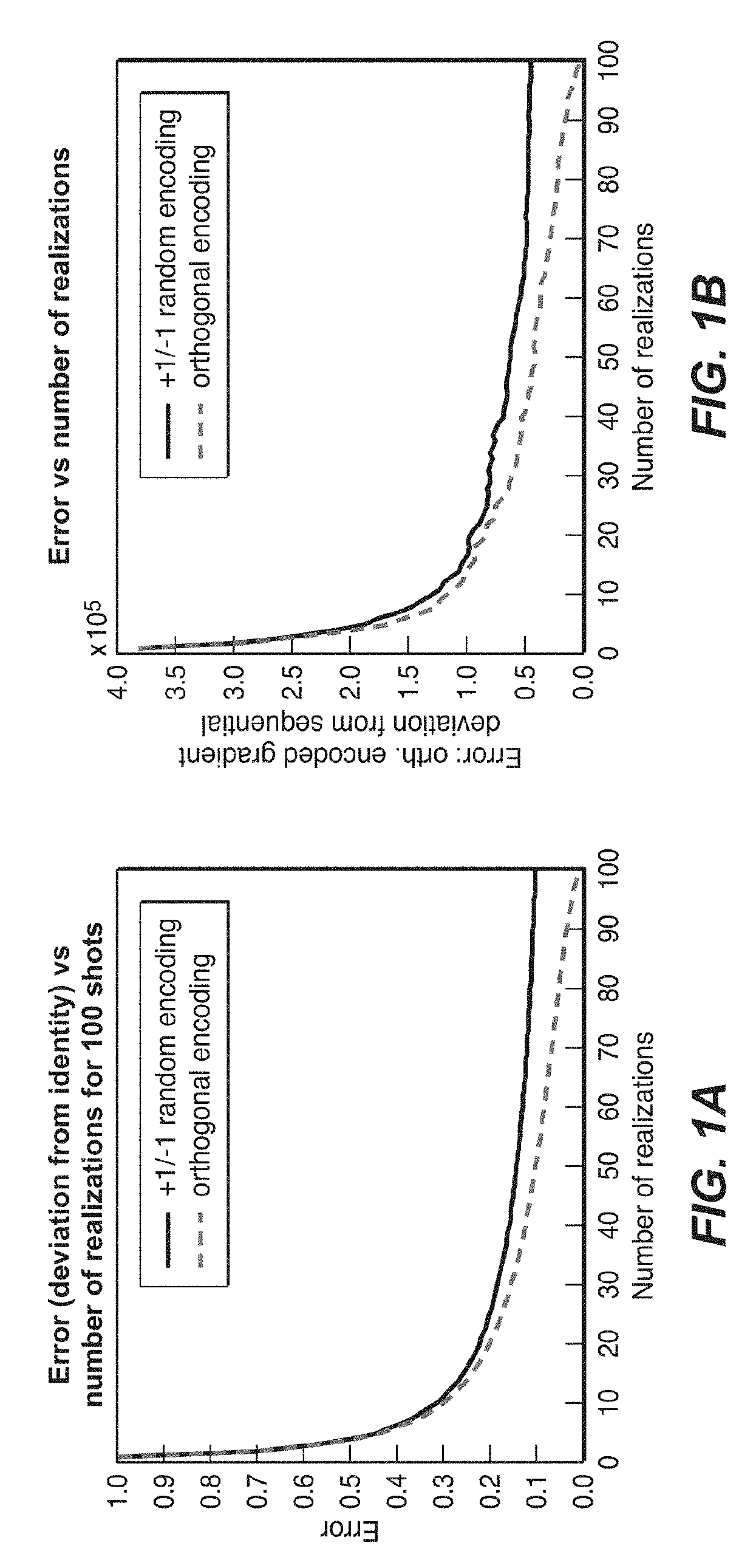
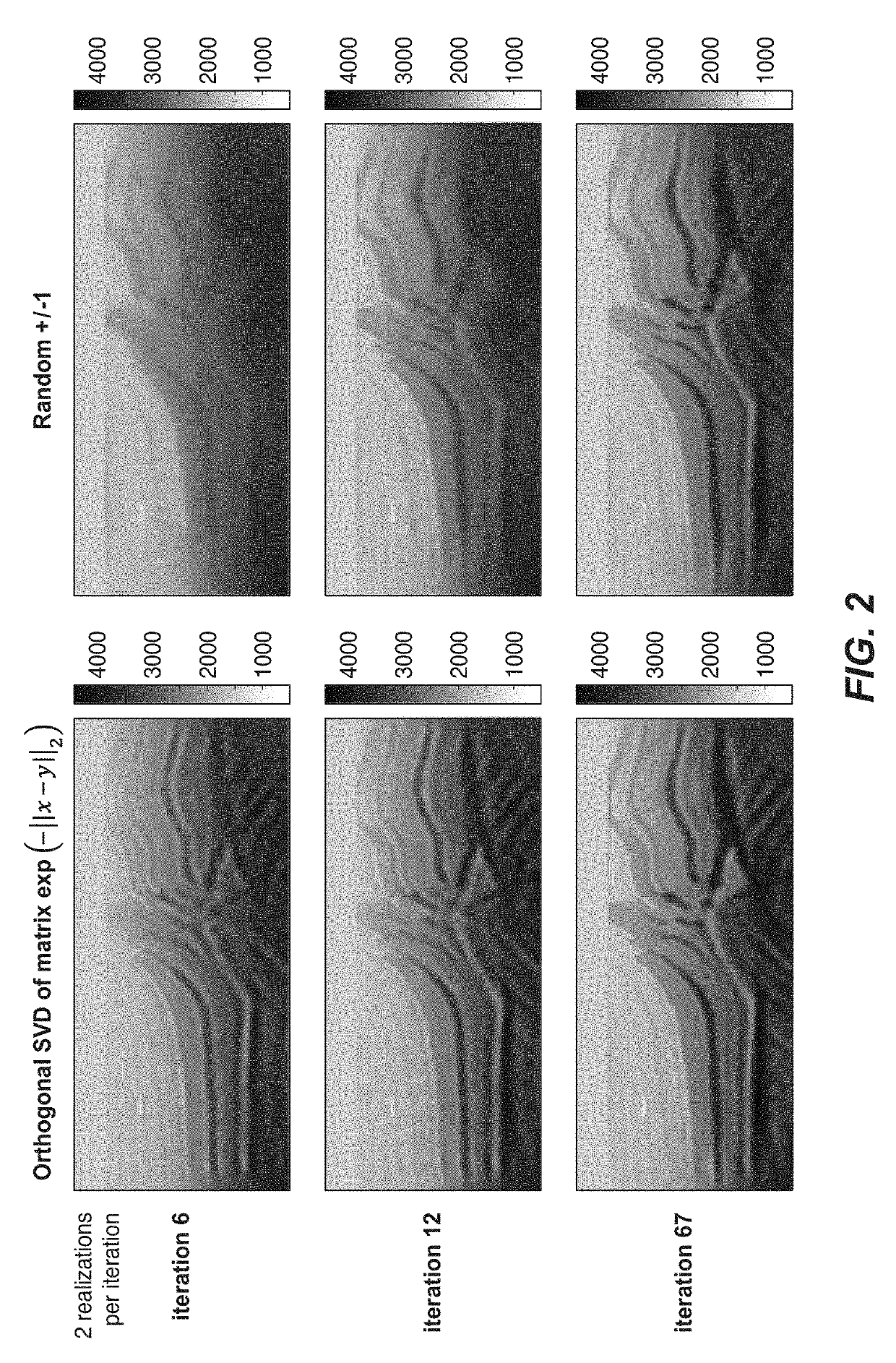
A deterministic method for selecting a set of encoding weights for simultaneous encoded-source inversion of seismic data that will cause the iterative inversion to converge faster than randomly chosen weights. The encoded individual source gathers are summed (83), forming a composite gather, and simulated in a single simulation operation. The invention creates multiple realizations of the simulation (84), each with its own encoding vector (82) whose components are the weights for the shots in the composite gather. The encoding vectors of the invention are required to be orthogonal (82), which condition cannot be satisfied by random weights, and in various embodiments of the invention are related to eigenvectors of a Laplacian matrix, sine or cosine functions, or Chebyshev nodes as given by the roots of Chebyshev polynomials. For non-fixed receiver geometry, an encoded mask (61) may be used to approximately account for non-listening receivers.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
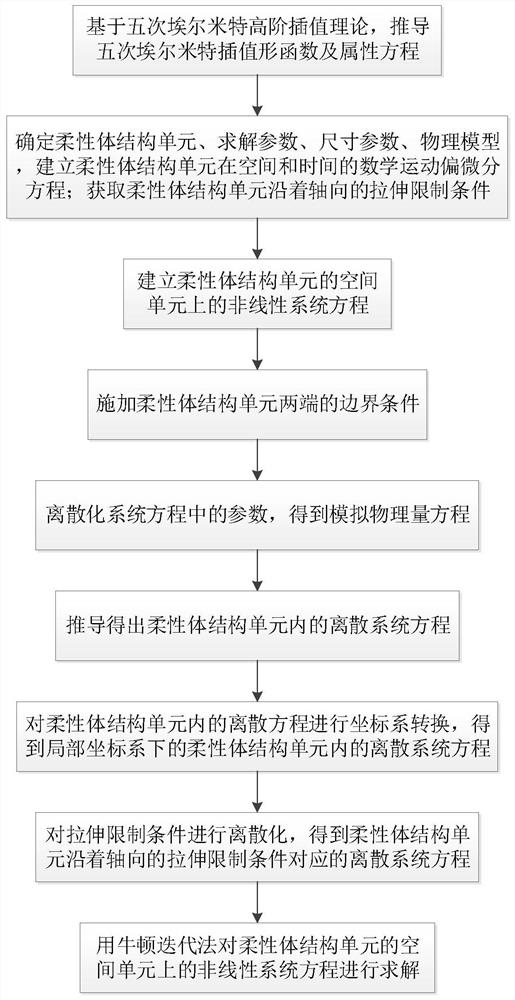
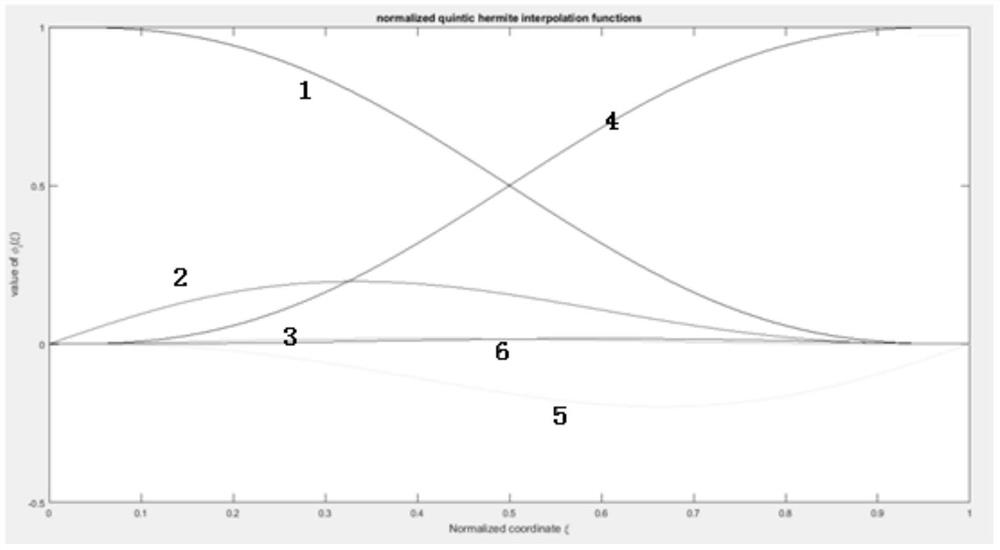
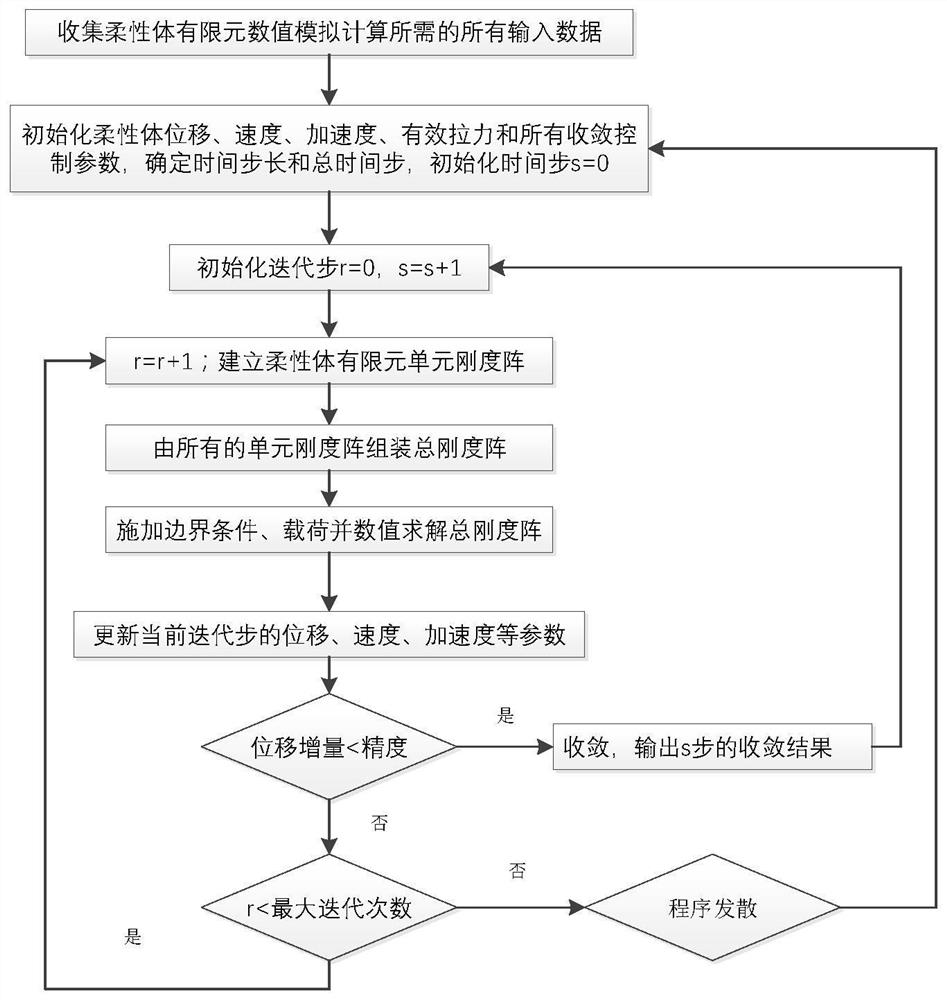
Flexible body structure high-order nonlinear finite element numerical simulation method based on quintic Hermite shape function
ActiveCN113076677AGuaranteed continuityReduce computing costSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelPartial differential equation
The invention discloses a novel flexible body structure high-order nonlinear finite element numerical simulation method based on a quintic Hermite shape function, and the method comprises the steps: deducing a quintic Hermite interpolation shape function and an attribute equation based on a quintic Hermite high-order interpolation theory; determining a flexible body structure unit and parameters, a physical model and a simplified hypothesis which need to be solved by the flexible body structure unit; establishing a mathematical motion partial differential equation of the flexible body structure unit in space and time and axial stretching limiting conditions, namely solving a mathematical model in a domain; and establishing a system equation of the flexible body structure unit, and adopting a Newton iteration method to carry out iterative solution on the parameters. The beneficial effects are that simulation precision of space deformation, rotation angle and curvature of the slender flexible body structure is improved; the continuity of the curvature at finite element nodes is ensured; rapid convergence is achieved, and particularly the prediction precision of the high-order vibration frequency of the flexible body is higher; and when the problems of transverse large gradient load and large bending of the flexible body are solved, higher precision guarantee is provided.
Owner:朱礼云
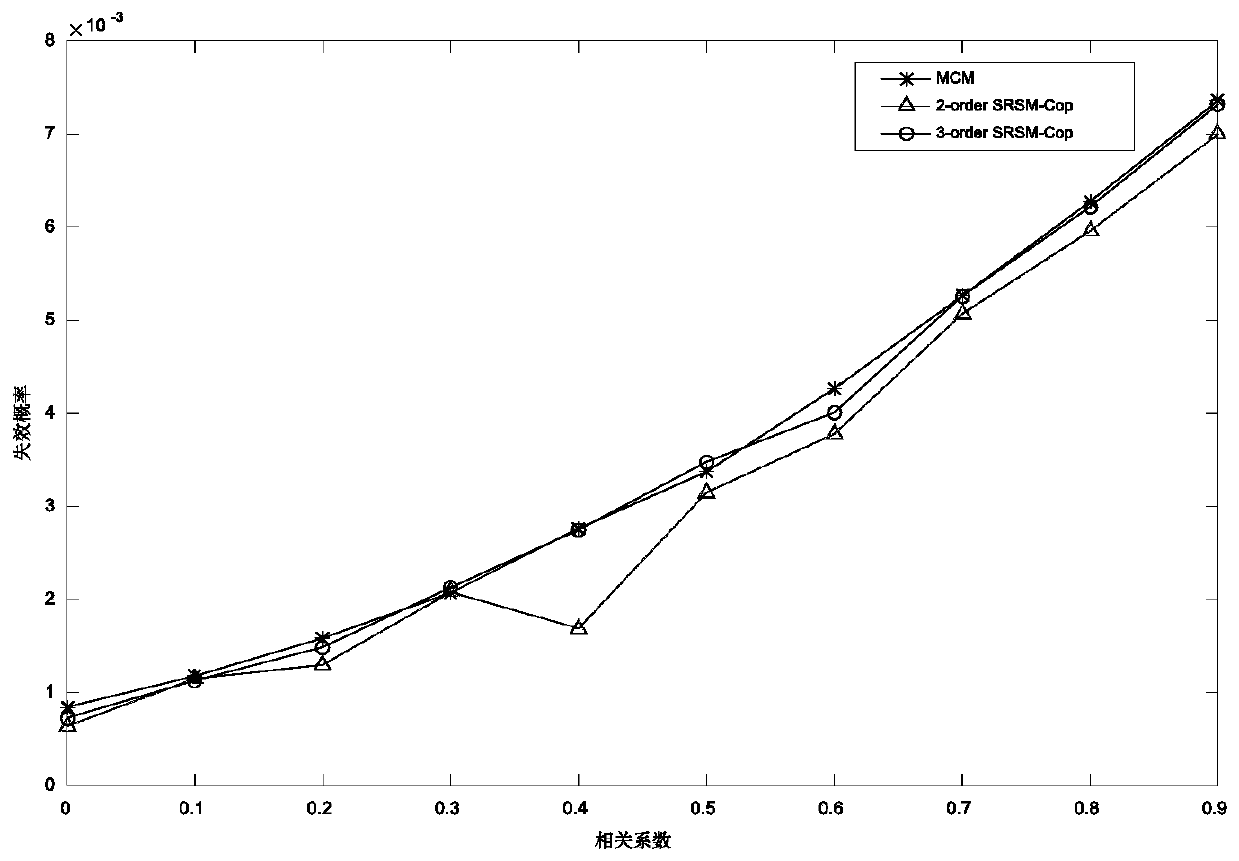
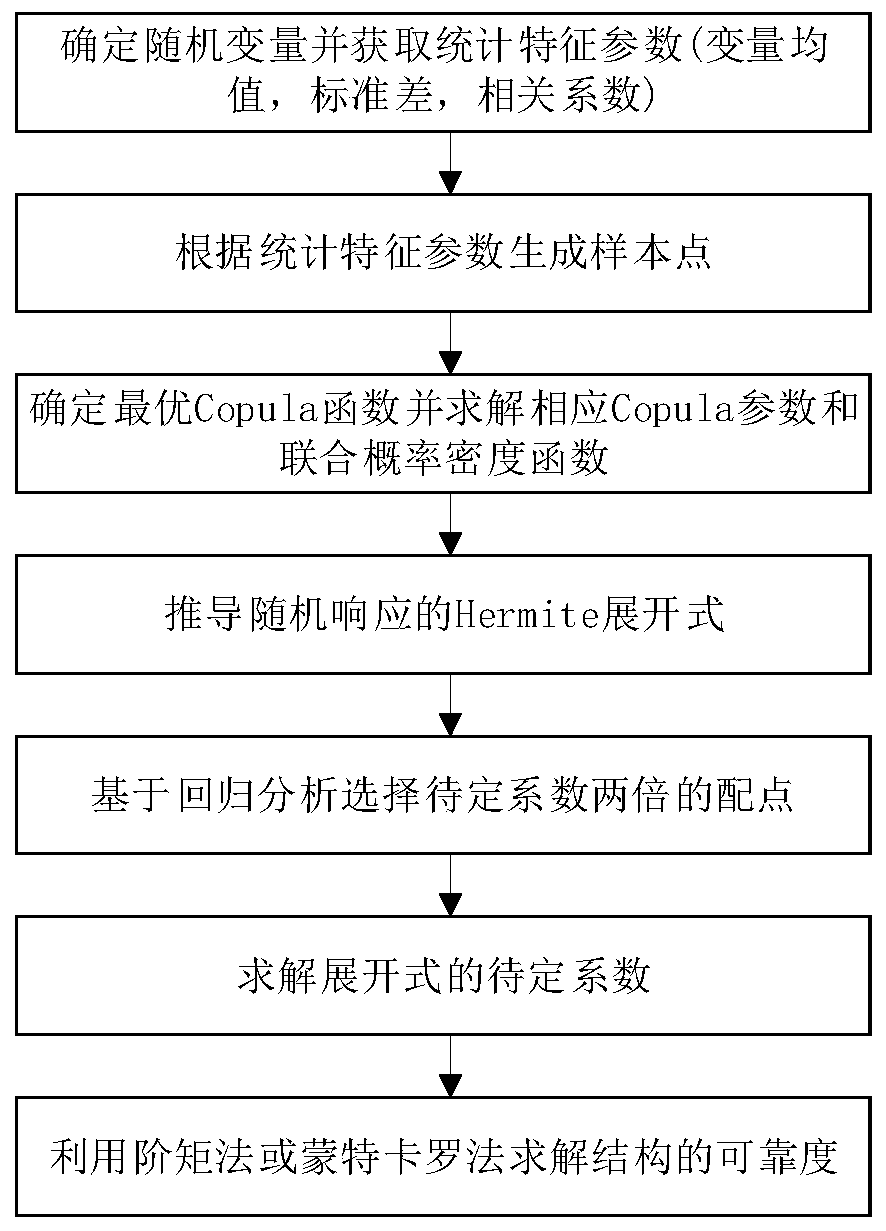
Structural parameter correlation processing and reliability calculation method
ActiveCN111191365AEffectively handle variable correlation problemsWide range of practical engineering problemsMathematical modelsDesign optimisation/simulationNormal densityAlgorithm
The invention provides a structural parameter correlation processing and reliability calculation method based on independent transformation and regression analysis. The method comprises the followingsteps: 1, determining random variables of a structure and sample points thereof or statistical characteristic parameters and correlation parameters; 2, in the step 1, if the sample points cannot be obtained, the sample points need to be generated according to the random variable distribution types and the corresponding statistical characteristic parameters; 3, selecting an optimal Copula functionaccording to the sample points and calculating Copula parameters and a joint probability density function between variables; 4, deducing a Hermite expansion formula of the structural response based ona random response surface method; 5, selecting a probability distribution point of which the undetermined coefficient is twice; 6, converting the collocation points by using Rosenblatt transform anda joint probability density function, and solving an undetermined coefficient based on a least square method; 7, solving the reliability of the structure by using a moment method or a Monte Carlo method. The method is scientific and good in manufacturability and has wide application and popularization value.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Self-adaptive point adding strategy uncertainty optimization method and system based on chaotic polynomial
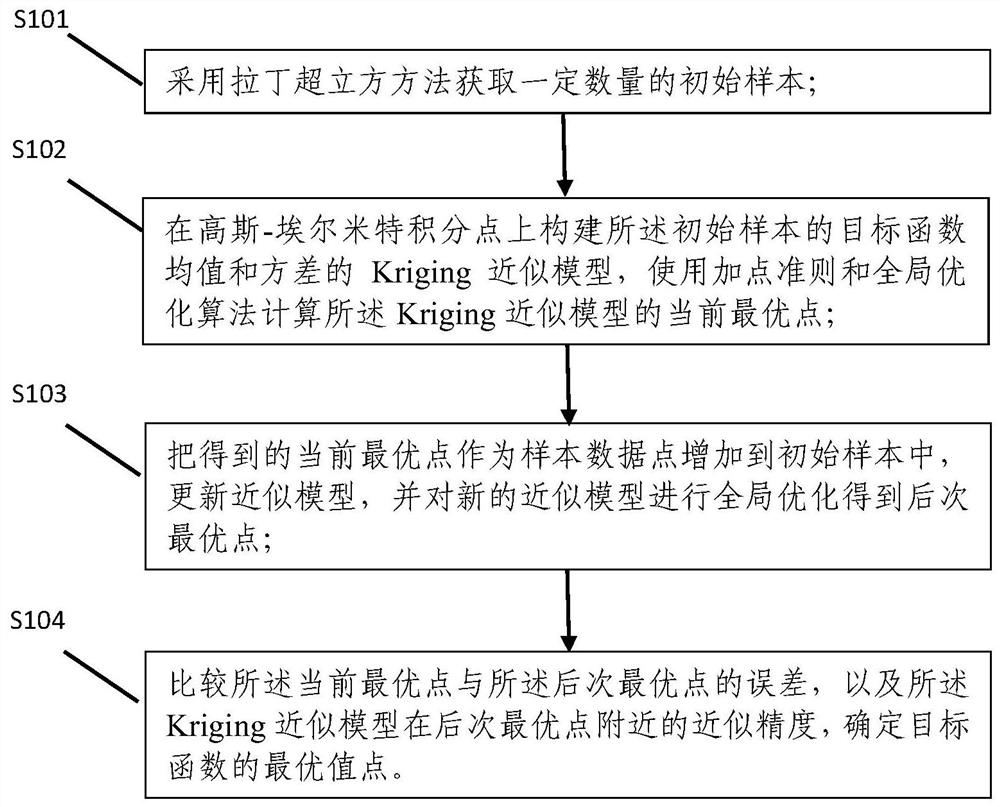
PendingCN112749519AImprove optimization efficiencyImproving the Efficiency of Uncertainty OptimizationGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationInitial sampleHermite functions
The invention discloses a self-adaptive point adding strategy uncertainty optimization method and system based on a chaos polynomial. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a certain number of initial samples by adopting a Latin hypercube method; constructing a Kriging approximation model of an objective function mean value and a variance of the initial sample on a Gaussian-Hermite integral point, and calculating a current optimal point of the Kriging approximation model by using a point adding criterion and a global optimization algorithm; adding the obtained current optimal point to the initial sample as a sample data point, updating the approximate model, and carrying out global optimization on the new approximate model to obtain a next optimal point; and comparing the error between the current optimal point and the next optimal point with the approximation precision of the Kriging approximation model near the next optimal point, and determining the optimal value point of the target function. According to the method, the efficiency of uncertainty problem analysis can be improved, the number of sample points for constructing the proxy model is reduced, and the efficiency of target function uncertainty optimization is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ELECTRONICS SYST ENG
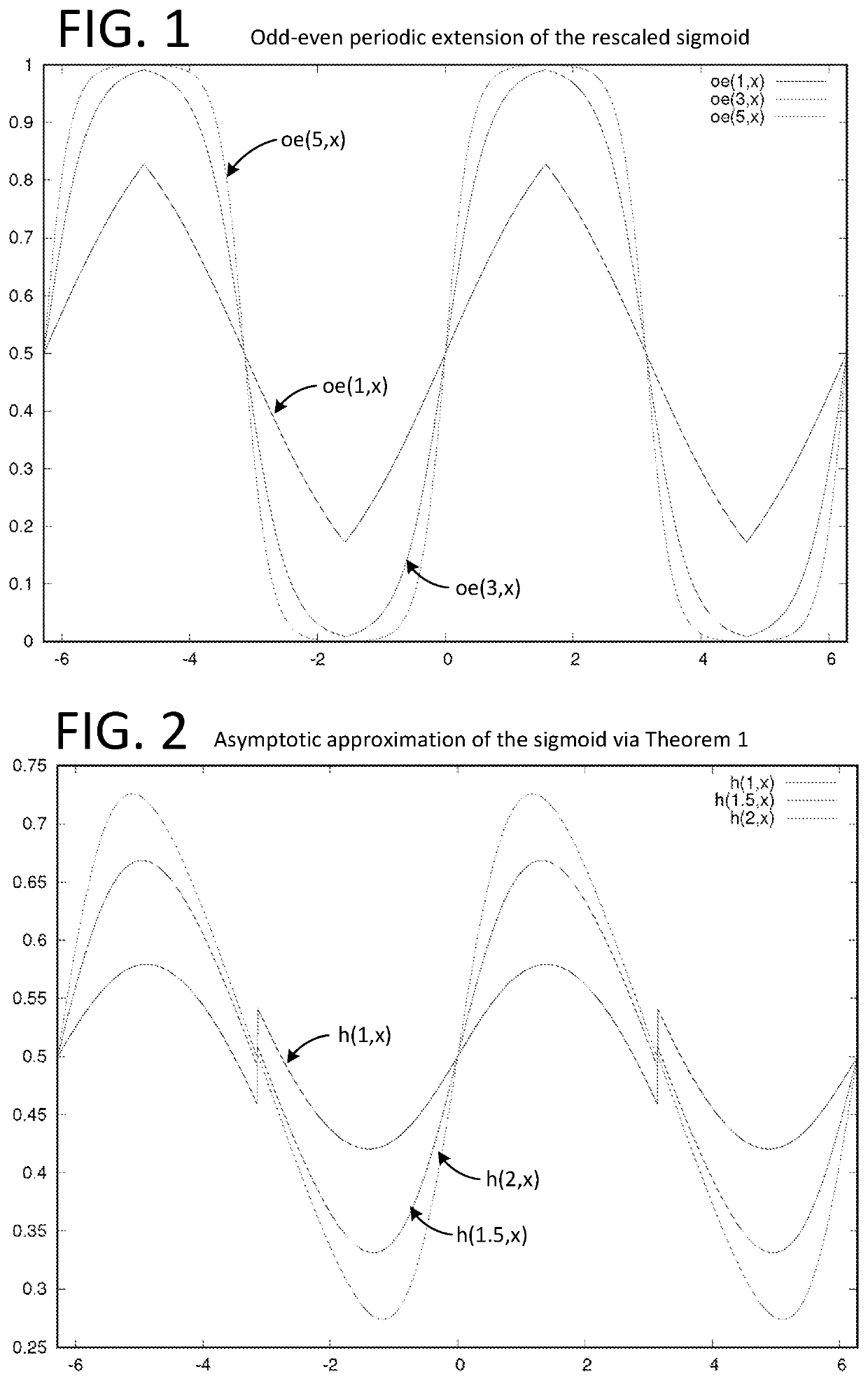
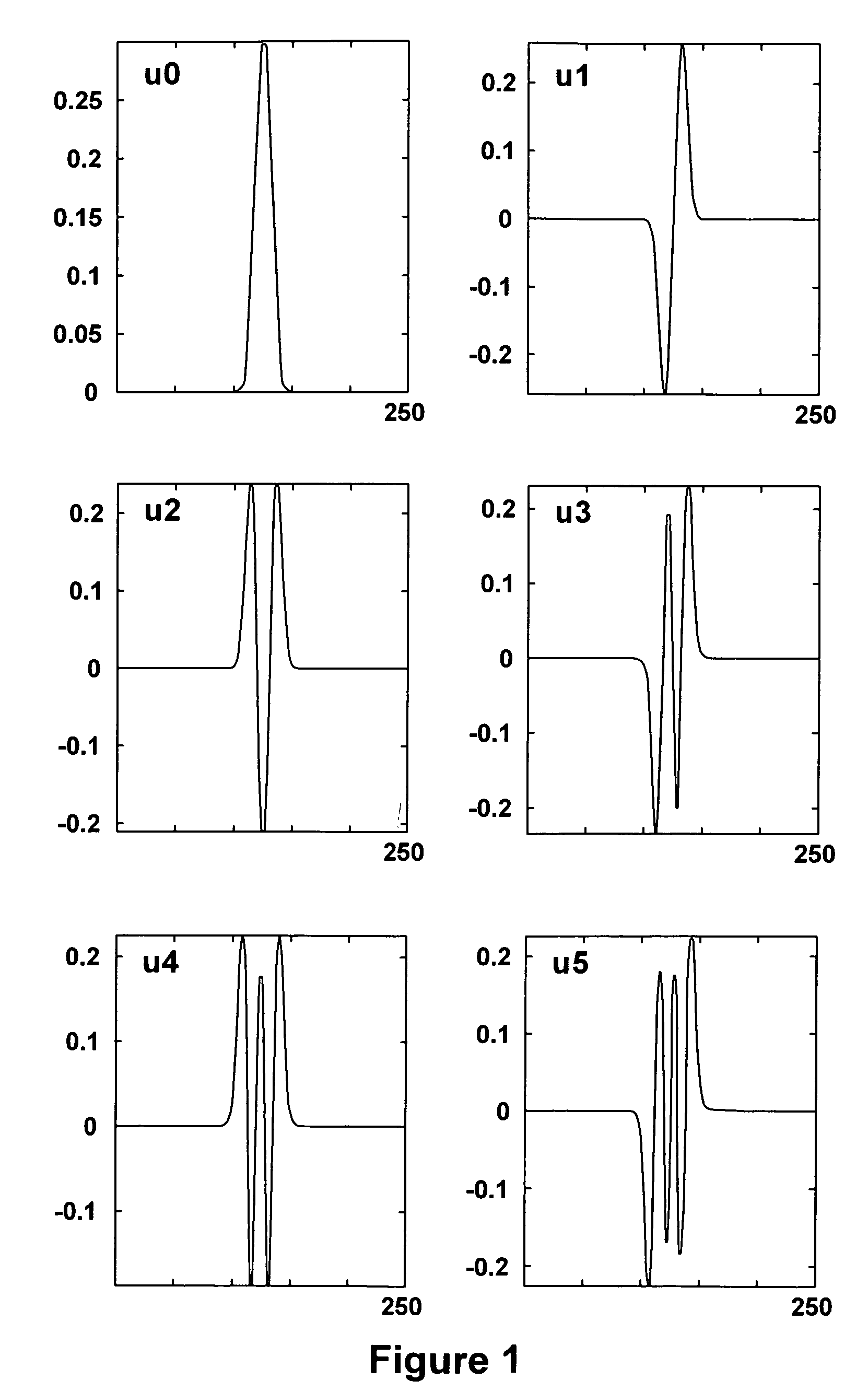
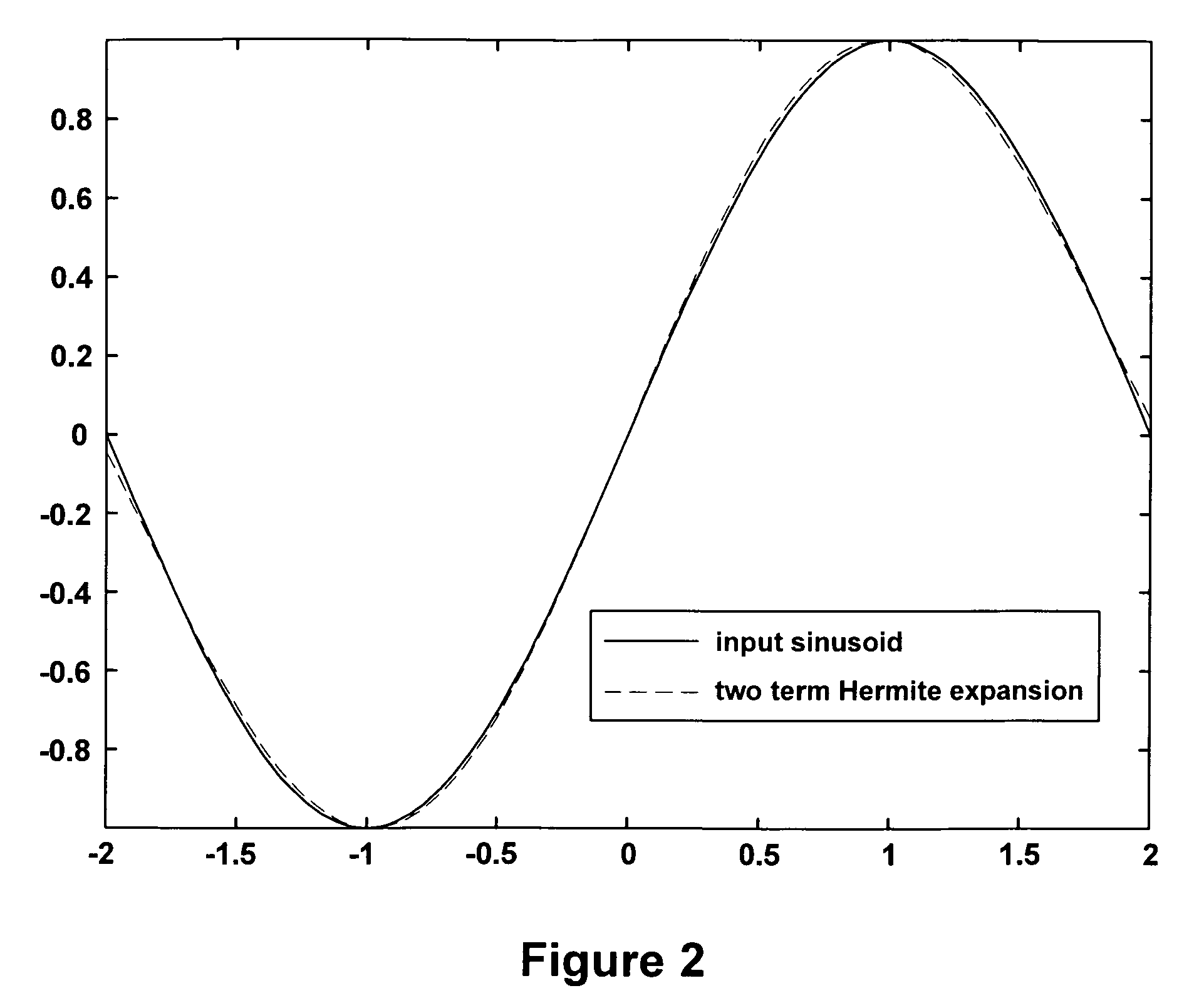
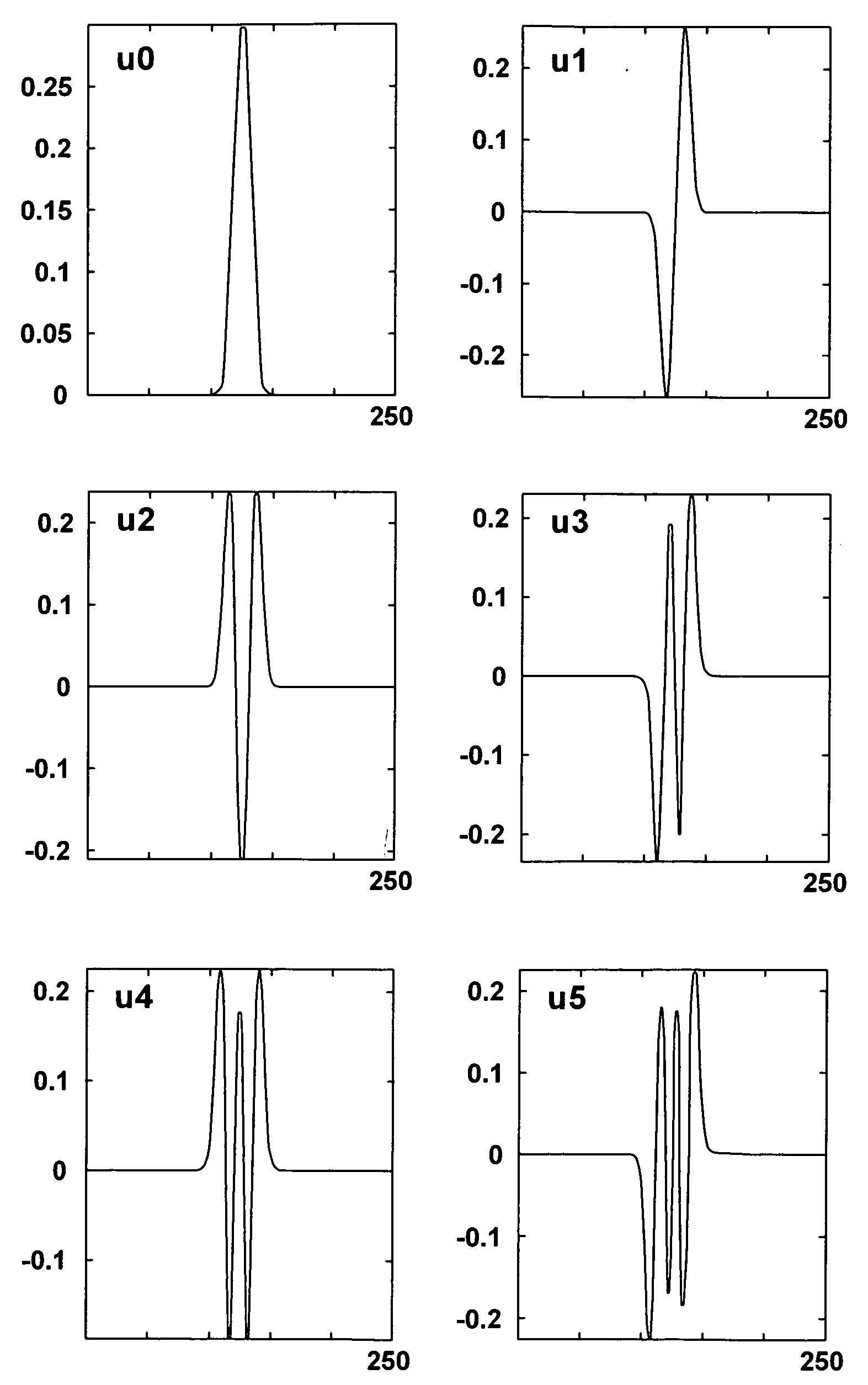
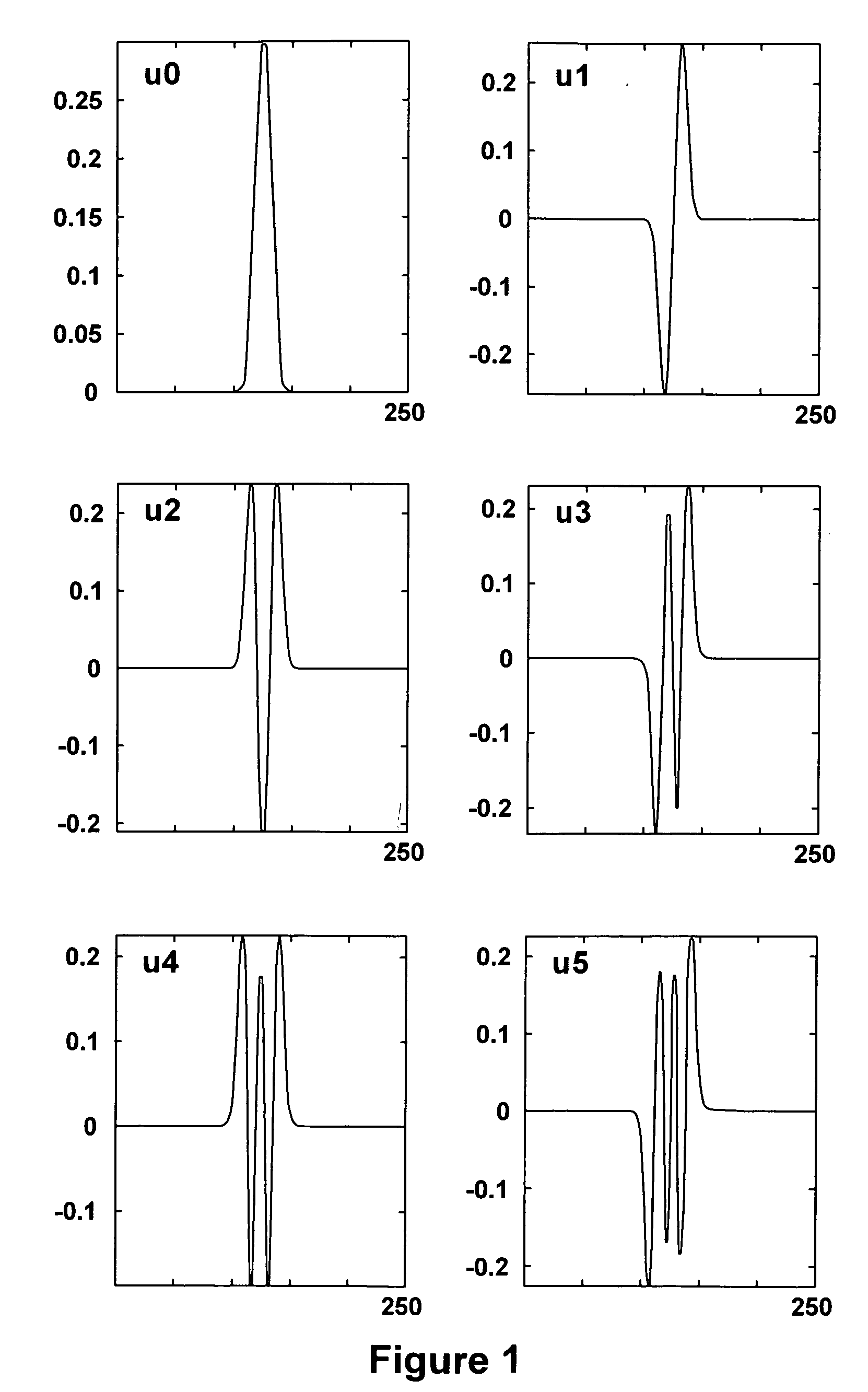
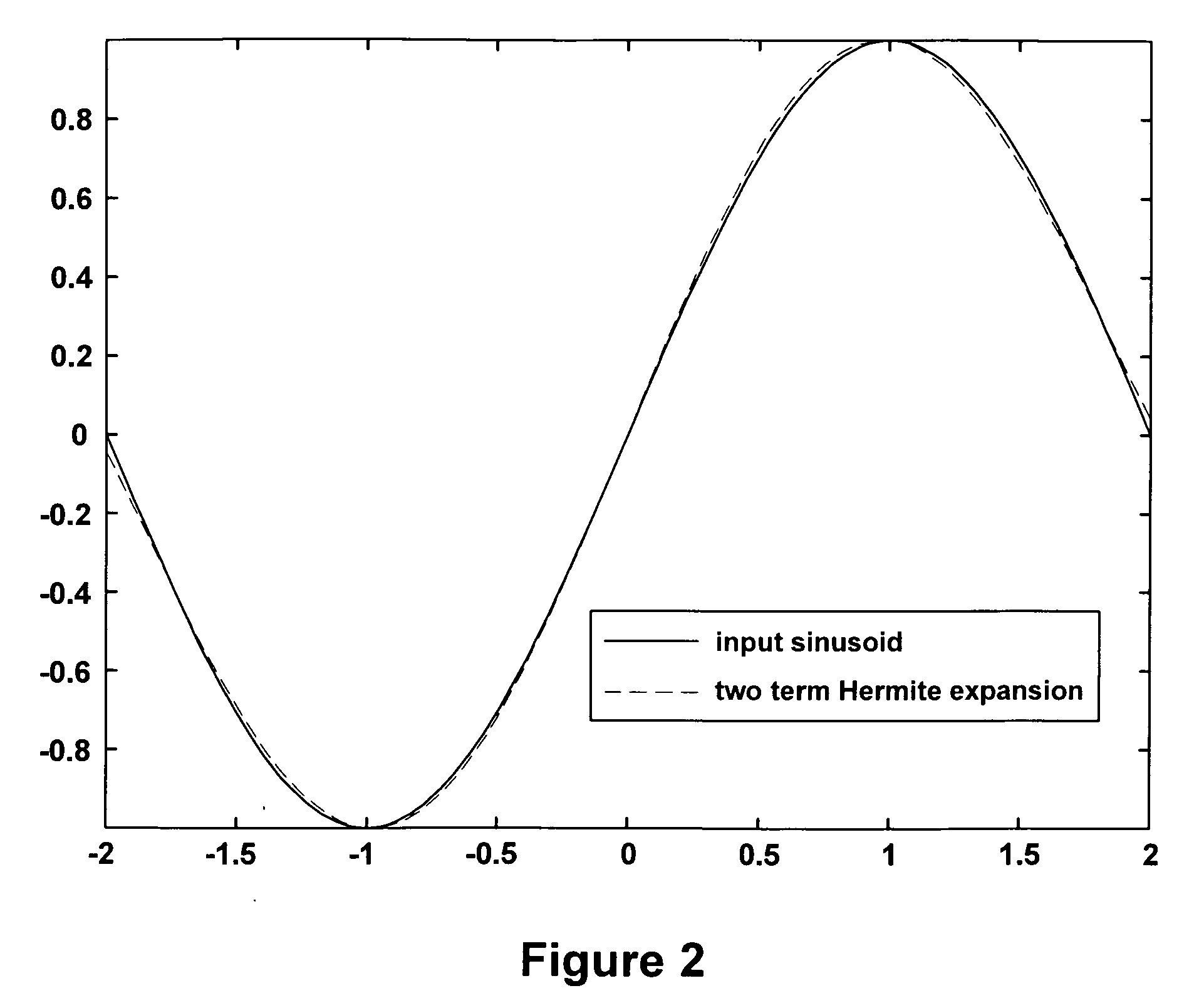
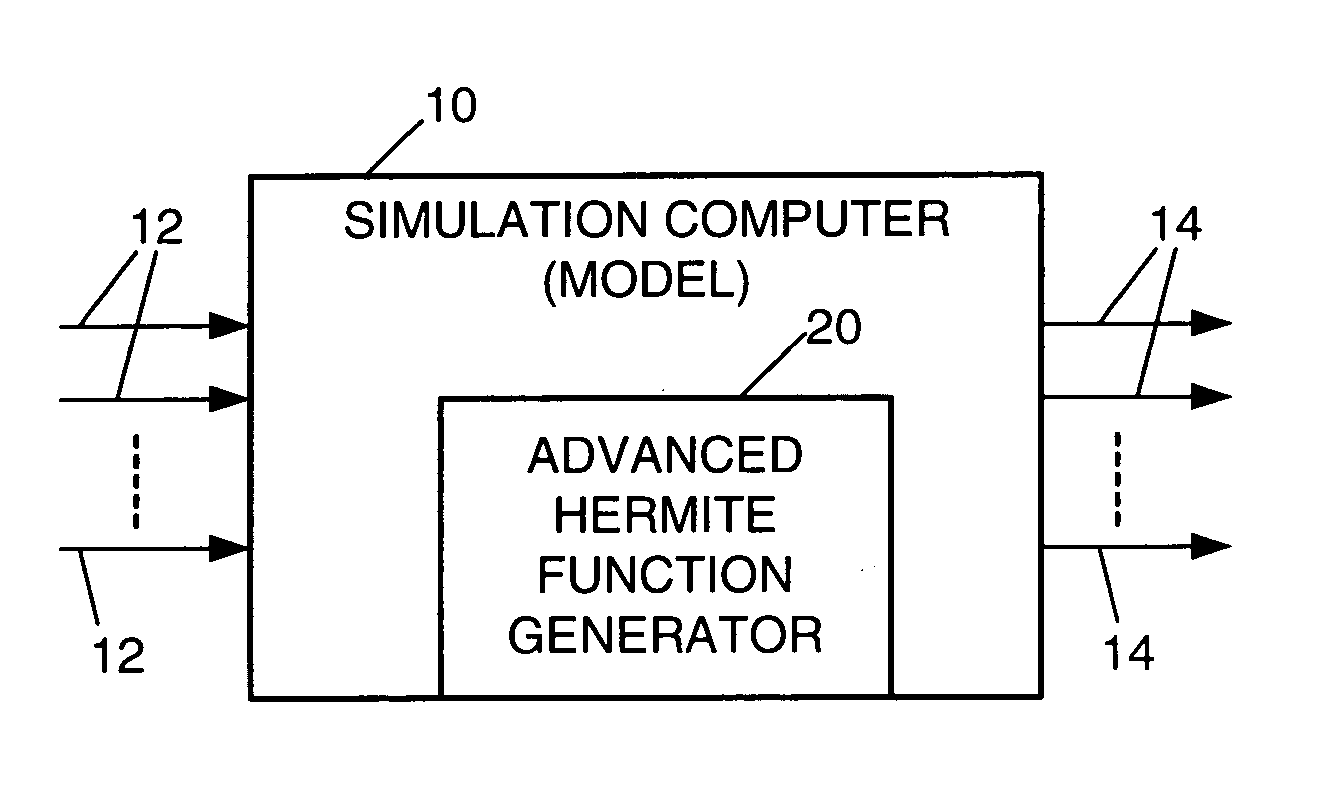
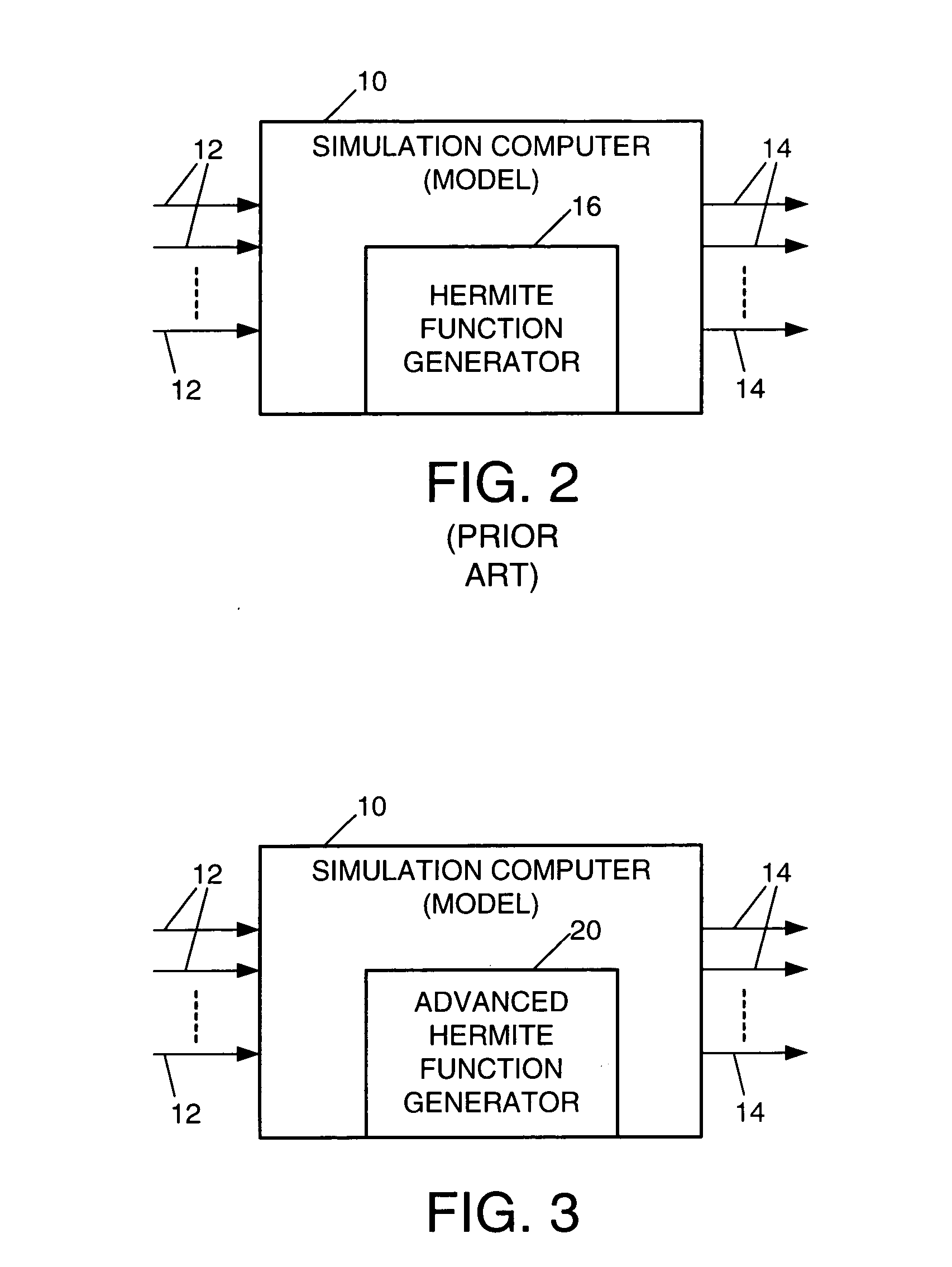
Method and means for generating high-order hermite functions for simulation of electromagnetic wave devices
InactiveUS20060200324A1High precisionComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationHermite functionsComputer science
A technique for generating very-high-order Hermite functions needed for accurately simulating operation of various devices and structures involving propagation of electromagnetic waves. By using modified recursion formulas, the technique generates asymptotic Hermite functions, smooth Hermite functions or optimized smooth Hermite functions, allowing for very high orders of the functions to be generated without the intermediate function values becoming so large as to exceed the capacity of conventional computers. The disclosed method for generating smooth Hermite functions provides for generation of well-behaved functions of order 30,000 or higher.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Electrocardiosignal transmission method in environment of multihop wireless body area network based on adaptive codebook
InactiveCN101841928ATo achieve the effect of joint controlNetwork topologiesDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalT wave
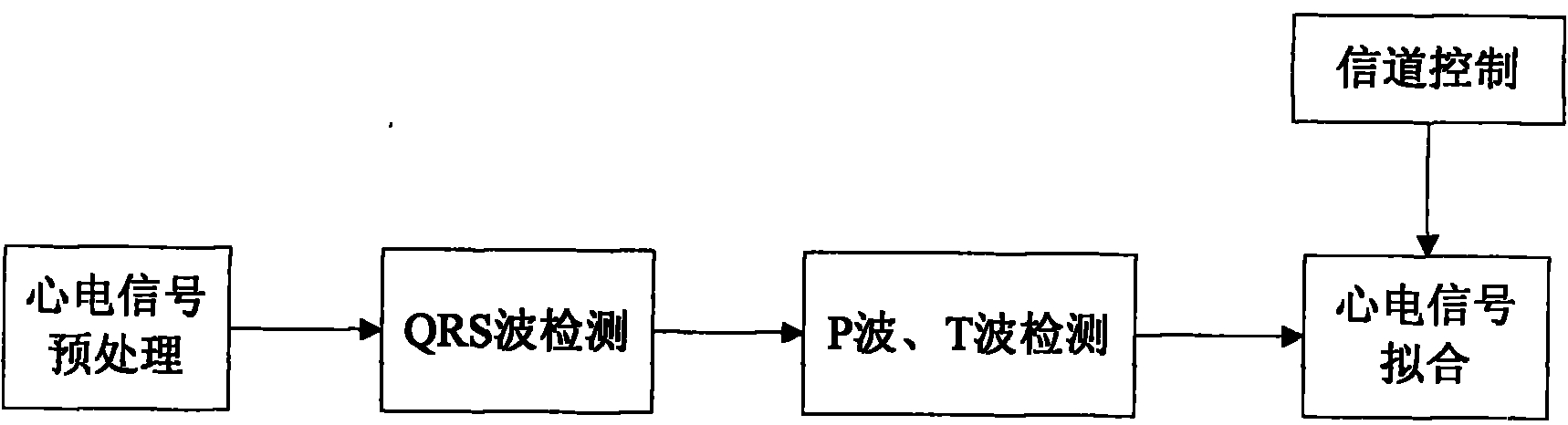
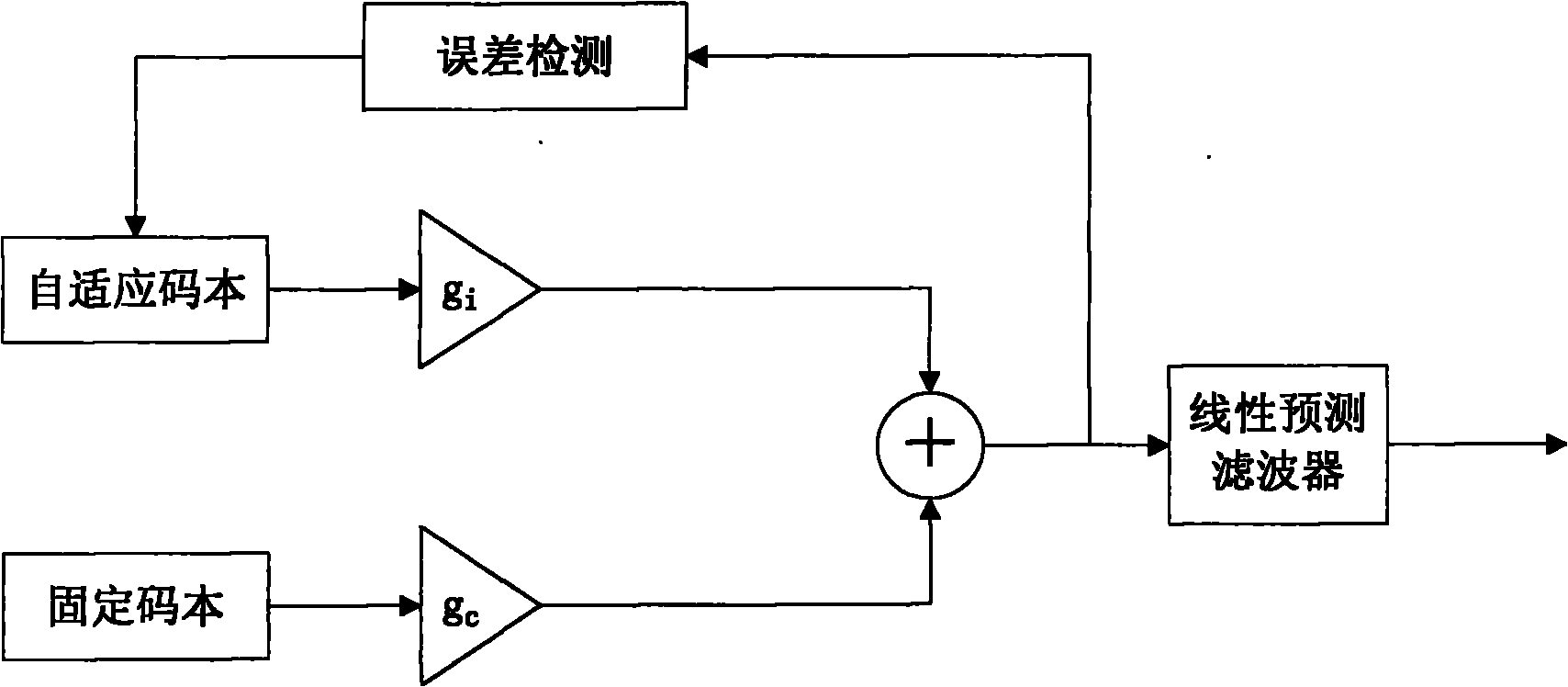
The invention provides an electrocardiosignal transmission method in a wireless body area network, which comprises following steps: (1) carrying out pretreatment on the electrocardiosignal; (2) detecting the electrocardiosignal; (3) extracting characteristic parameters and searching a codebook; and (4) carrying out channel control. The electrocardiosignal transmission method adopts high-pass and low-pass filtering to carry out pretreatment on the electrocardiosignal. A difference thresholding method and a wavelet analysis method are adopted respectively to carry out detection marking on a QRS wave group, a P wave and a T wave of the electrocardiosignal. Finally a fixed codebook and an adaptive codebook are searched, suitable code vectors are selected to make a minimum mean squared error for compounding the electrocardiosignal and the original electrocardiosignal the minimum, and the parameters such as code vector addresses, gain and the like are transmitted. The electrocardiosignal transmission method determines search of different orders of a Hermite function by channel control so as to fulfill the aim of source and channel combination control. The invention relates to the electrocardiosignal transmission method in the environment of the multihop wireless body area network based on the adaptive codebook.
Owner:付汀
Improved FISTA temperature field reconstruction algorithm based on ultrasonic waves
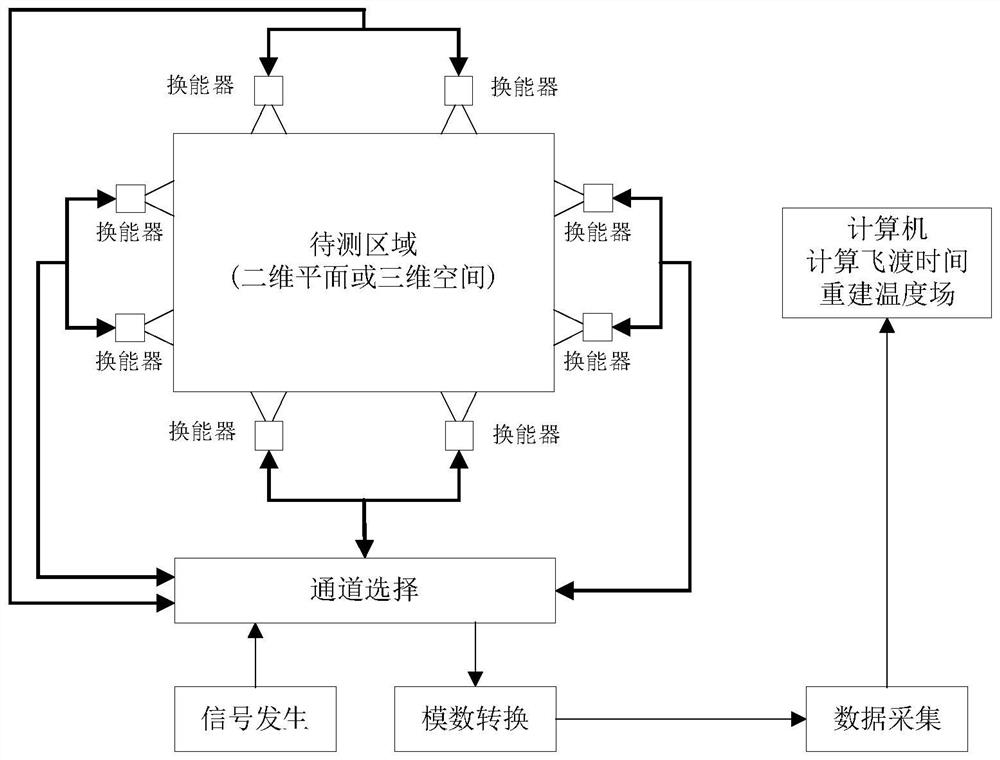
PendingCN114353993ASolve problems such as cumbersome iteration process and slow iteration speedImprove rebuild speedThermometers using physical/chemical changesComputational physicsAcoustic wave
The invention discloses an improved FISTA temperature field reconstruction algorithm based on ultrasonic waves, and the algorithm comprises the following steps: 1, dividing a measurement region into a certain number of discrete grids; step 2, constructing a temperature error objective function based on discrete grid points; step 3, based on the measured sound wave flying time data, solving the objective function by using an improved FISTA algorithm to obtain temperature distribution of the measurement area under the grid; and 4, carrying out cubic Hermite interpolation on the temperature distribution obtained under the measurement area grid to obtain the temperature field distribution of the whole measurement area. According to the improved FISTA algorithm provided by the invention, the physical information and the sound wave flying time of the detected area are utilized, and the rapid reconstruction of the temperature field is realized. By resetting the acceleration parameter, the problem of fluctuation instability in the iterative reconstruction process of the temperature field is solved. Meanwhile, according to the algorithm, a positive definite matrix is introduced into a gradient function, and the reconstruction speed and the reconstruction precision of the temperature field are improved.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINE HUZHOU
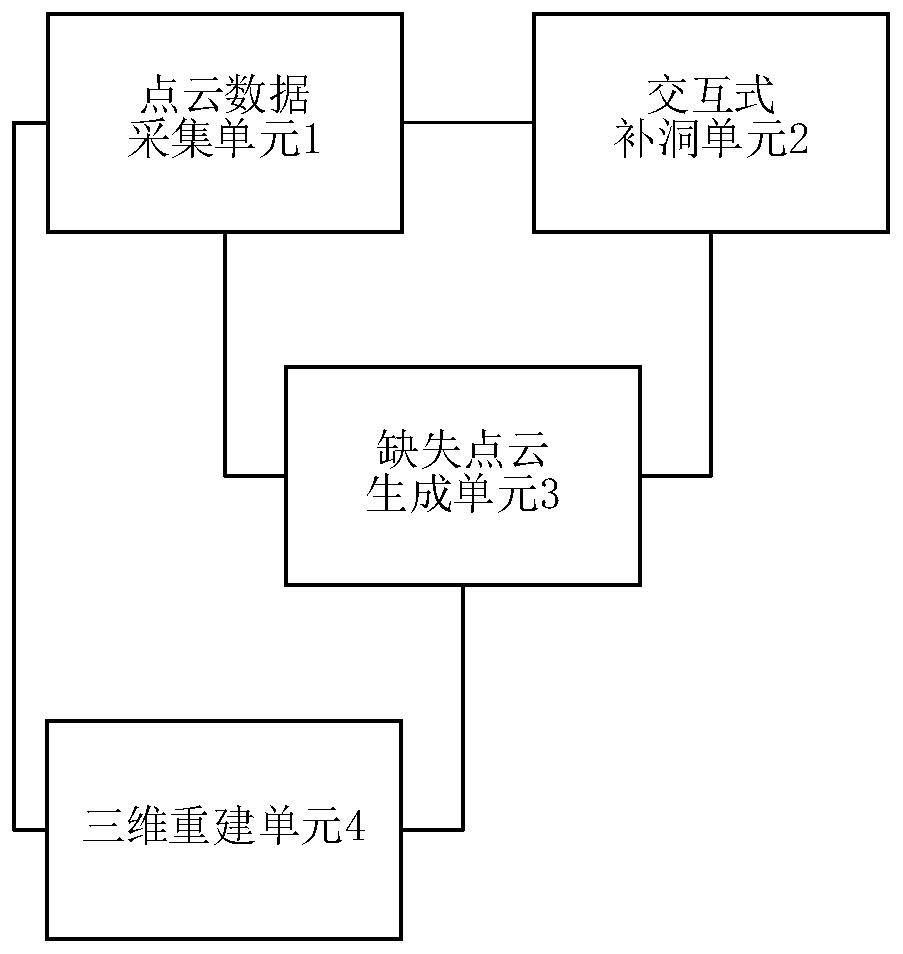
Point cloud data non-uniform three-dimensional reconstruction method, system and device and storage medium
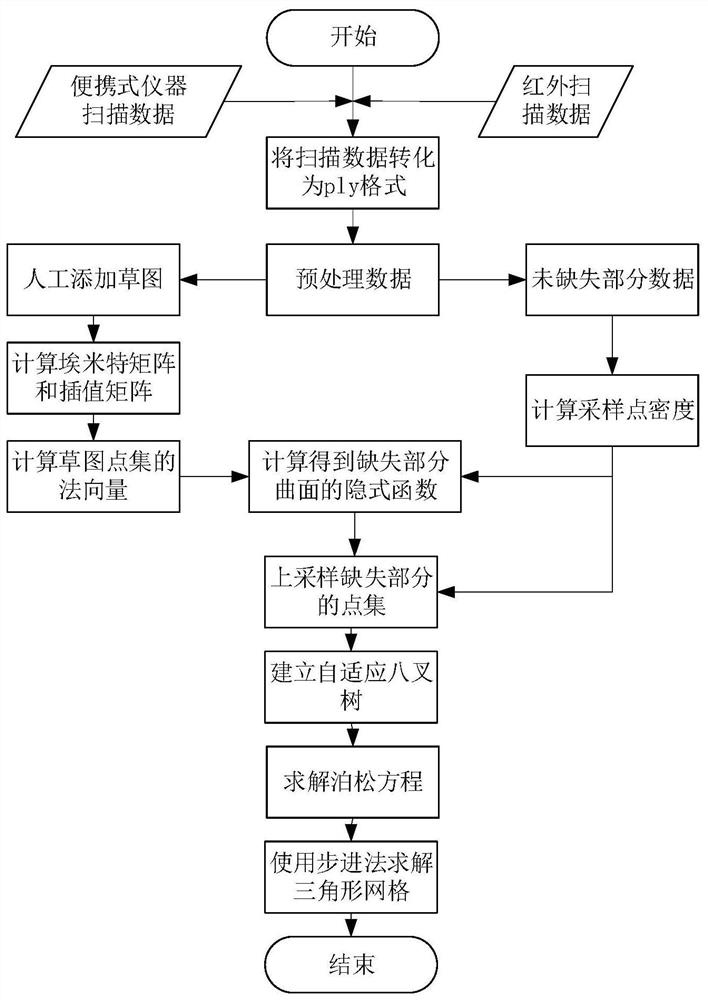
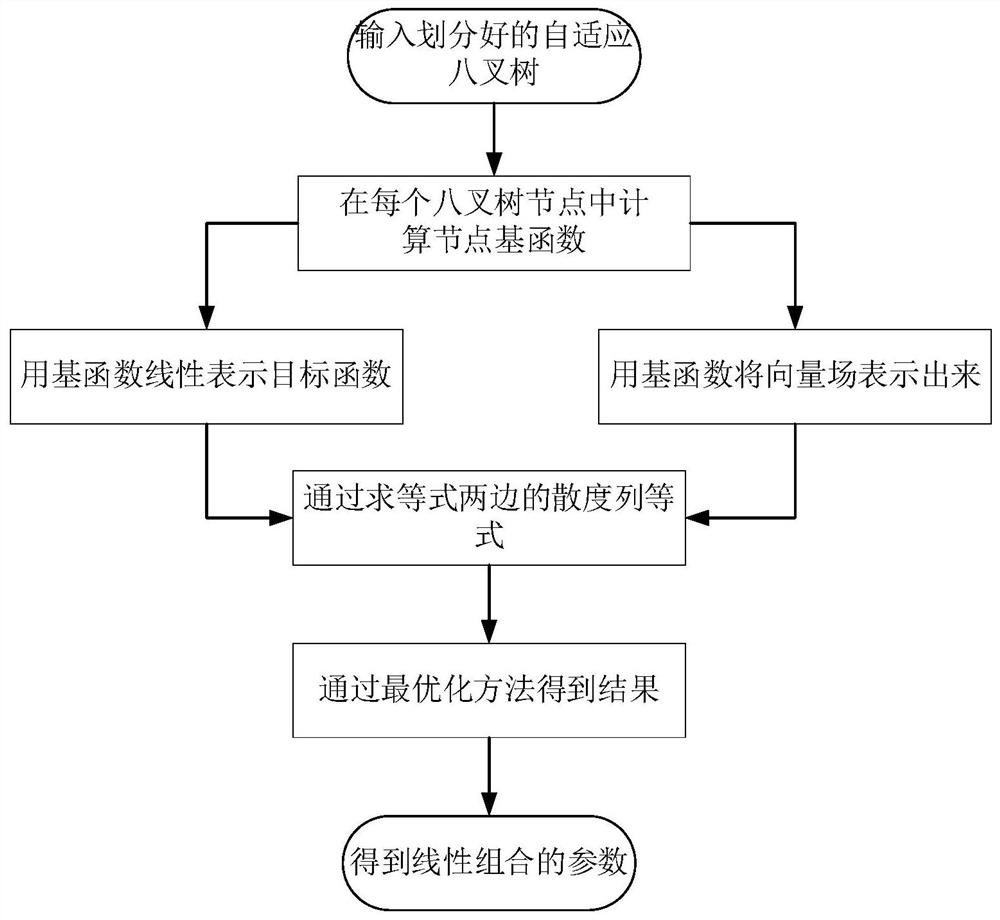
PendingCN113592711ATroubleshoot Surface Reconstruction IssuesGeometric image transformation3D modellingMissing dataPoint cloud
The invention discloses a point cloud data non-uniform three-dimensional reconstruction method. Comprising the steps of scanning an object to obtain complete point set data, and performing preprocessing such as normal vector normalization; adding a brief contour line artificially for missing data, and obtaining a sparse point set; constructing a Hermite matrix by using the sparse point set and obtaining a normal vector; calculating the normal vector and the point set data to obtain an interpolation function, and then performing up-sampling to obtain a final point cloud; and performing triangulation operation to obtain a final three-dimensional reconstruction model. The invention also discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction system for non-uniform point cloud data, computer equipment and a computer readable storage medium. According to the invention, the object surface reconstruction problem of the missing part is solved by using the interpolation method, the missing part of the model can be freely modified by combining the shape information complementation of the artificial sketch, and a relatively complete reconstruction model can be obtained by well combining the geometric features of the sample points of the actual object and the features of the artificially added sketch.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
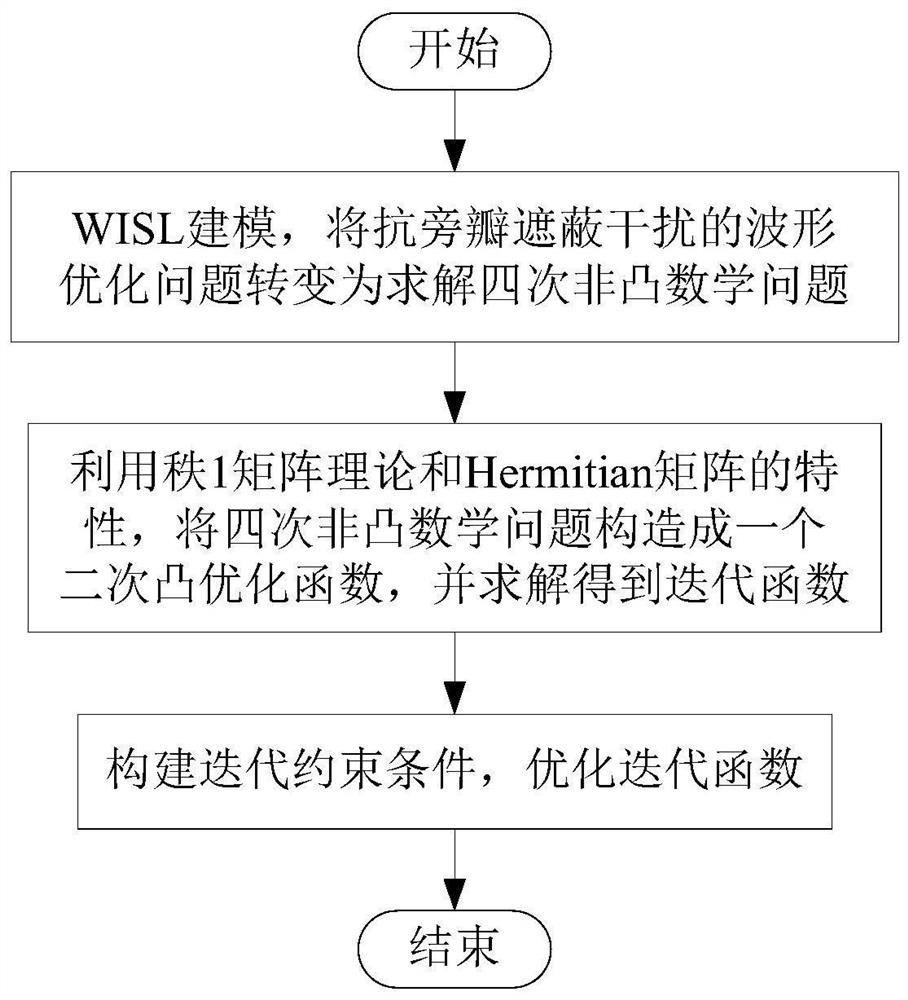
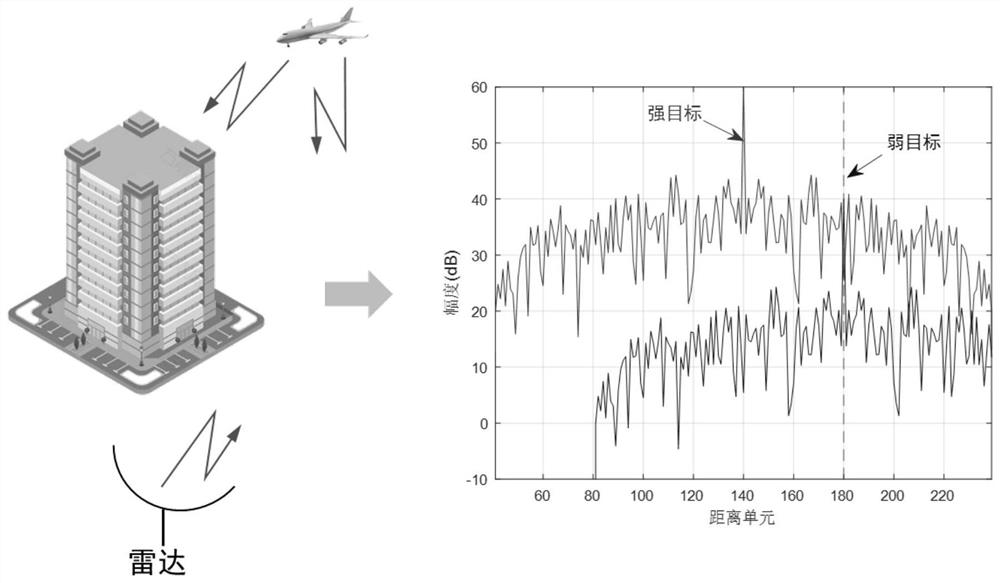
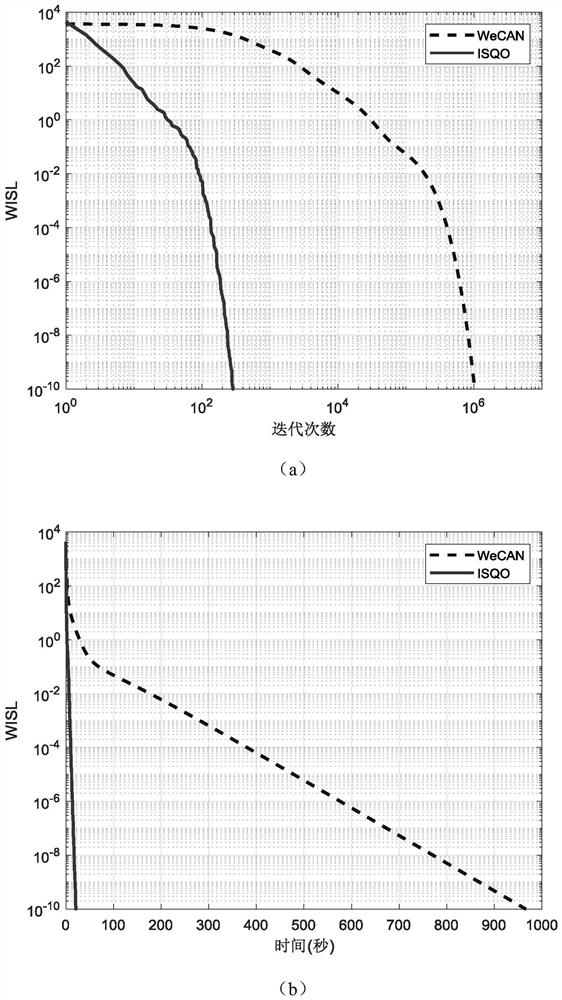
Waveform optimization design method for resisting sidelobe shielding interference
ActiveCN113239554ASuppress interferenceImprove detection rateWave based measurement systemsDesign optimisation/simulationTarget signalWave shape
The invention discloses a waveform optimization design method for resisting sidelobe shielding interference; the method comprises the following steps: s1, carrying out WISL modeling, and converting a waveform optimization problem for resisting sidelobe shielding interference into a four-time non-convex mathematical solving problem; s2, constructing a quadric non-convex mathematical problem into a quadratic convex optimization function by using a rank 1 matrix theory and characteristics of a Hermitian matrix, and solving the quadratic convex optimization function to obtain an iterative function; s3, constructing an iteration constraint condition, and optimizing an iteration function. According to the method, the prior information is utilized, the sidelobe level of the region of interest of the signal is reduced, the interference of a strong target sidelobe on weak target signal detection can be inhibited, the detection probability of the weak target signal is improved, and the signal with the required waveform can be designed in a short time, so that the method has important application prospects in complex detection scenes.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
LMD equipment fault diagnosis method and system
InactiveCN112683393AProtect fractal structureAvoid destructionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmMonitoring system
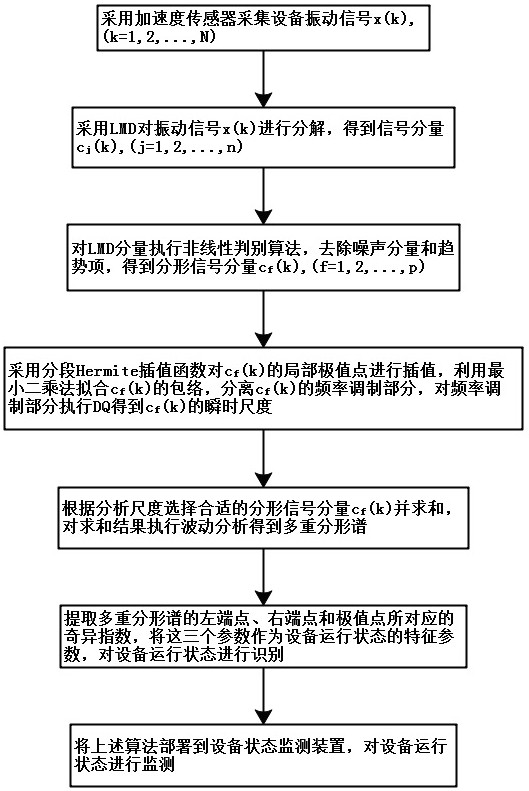
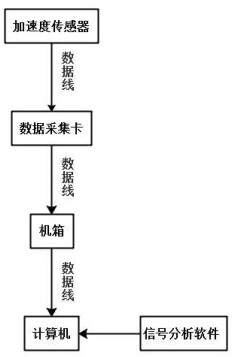
The invention discloses an LMD equipment fault diagnosis method and system. An LMD algorithm is used to decompose equipment vibration signals, a nonlinear discrimination algorithm is used to remove a decomposition noise component and a trend term, a fractal signal component is retained, a piecewise Hermite interpolation function is used to interpolate an extreme point, least square fitting enveloping is utilized to separate a frequency modulation part, a DQ algorithm is used to estimate instantaneous frequency and calculate a corresponding instantaneous scale, a vibration signal detrending result is determined according to the analysis scale, a multi-fractal spectrum of the detrending signal is calculated, and coordinates of a left end point, a right end point and an extreme point of the multi-fractal spectrum are extracted as characteristic parameters of an equipment operation state to identify the equipment operation state. The algorithm is deployed to an equipment state monitoring system, the equipment operation state can be accurately distinguished, and the equipment state monitoring system has good flexibility and portability and is convenient for engineering application.
Owner:山东柯瑞申智能科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for approximation using polynomials
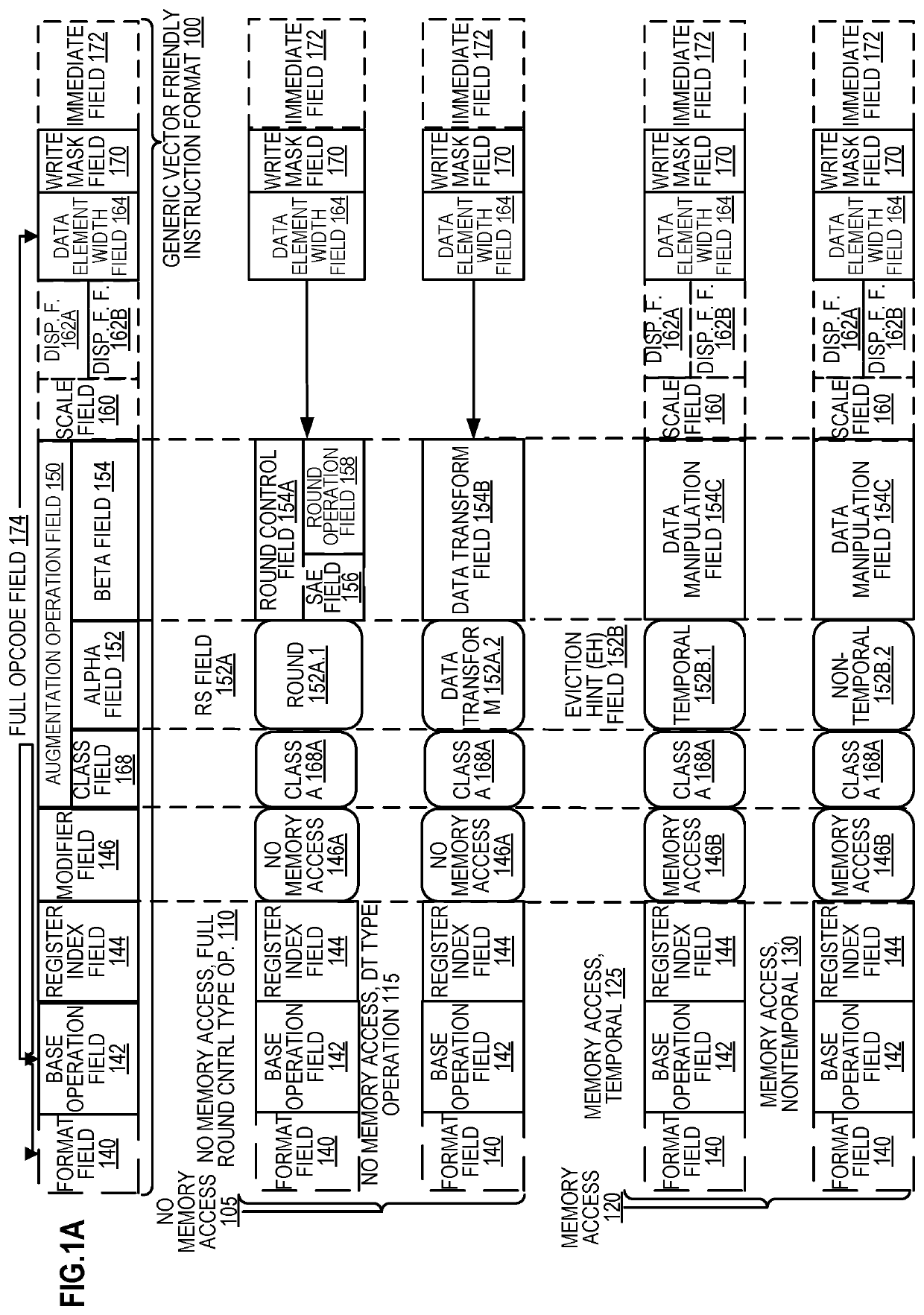
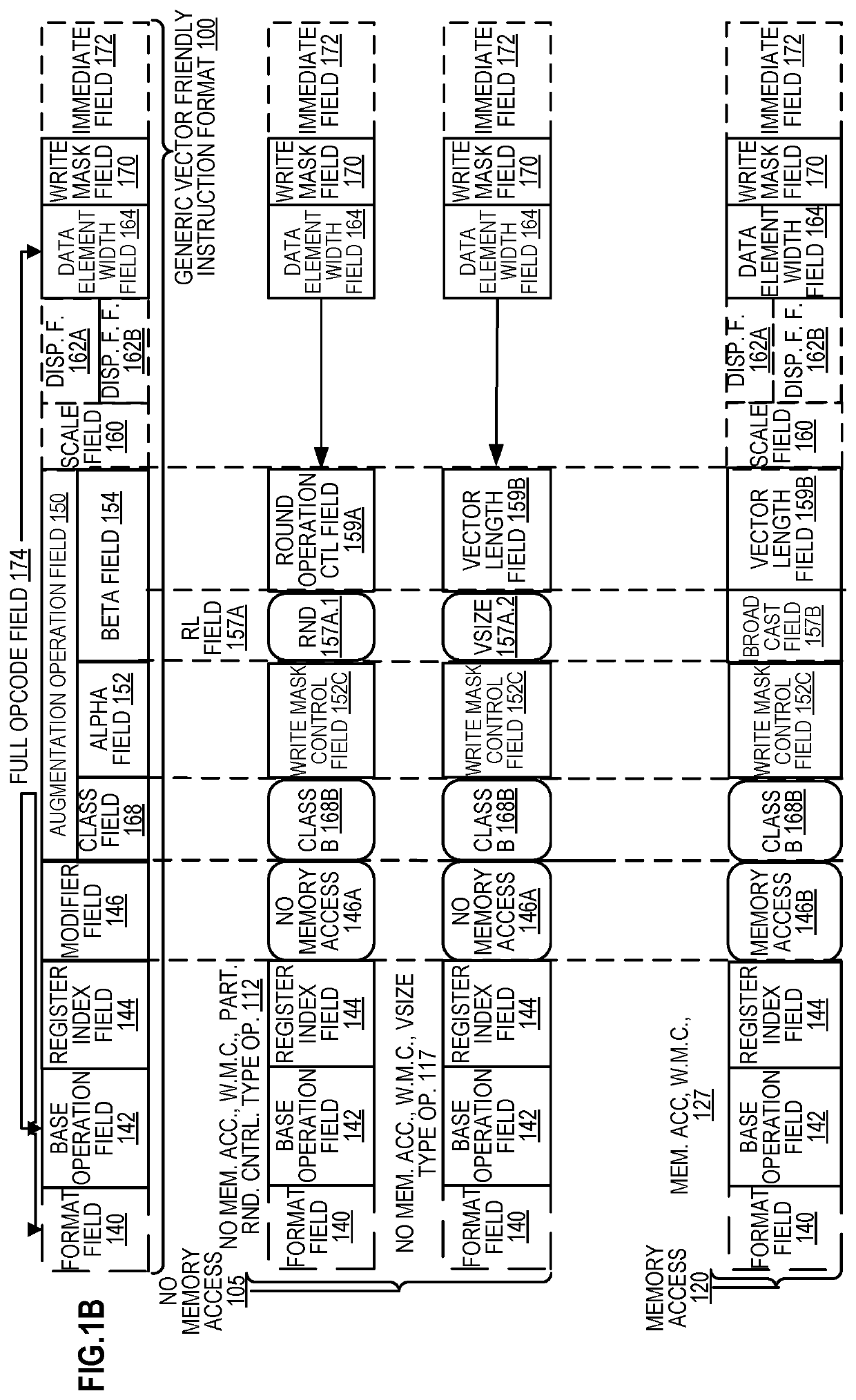
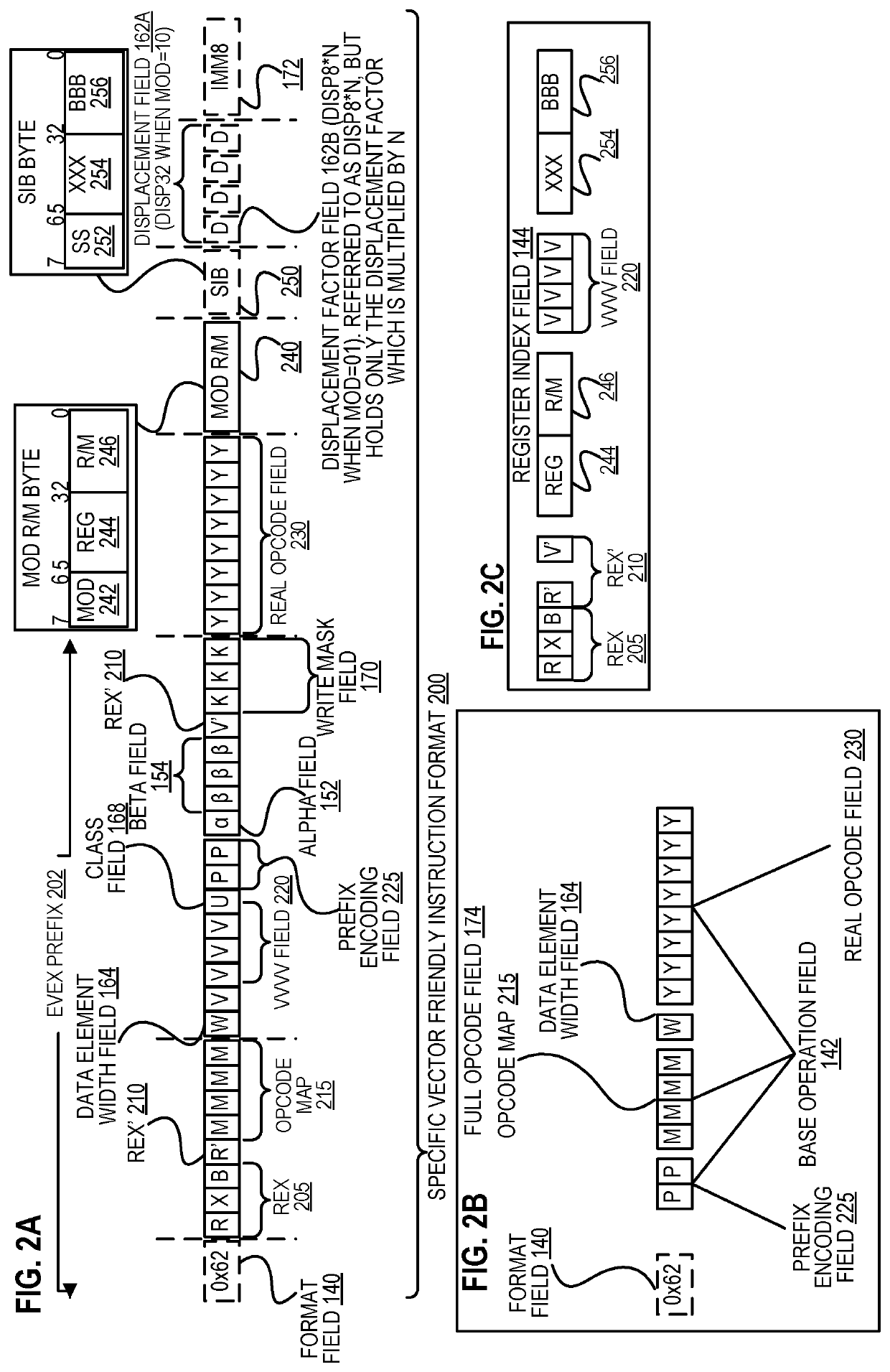
Methods and apparatus for approximation using polynomial functions are disclosed. In one embodiment, a processor comprises decoding and execution circuitry. The decoding circuitry is to decode an instruction, where the instruction comprises a first operand specifying an output location and a second operand specifying a plurality of data element values to be computed. The execution circuitry is to execute the decoded instruction. The execution includes to compute a result for each of the plurality of data element values using a polynomial function to approximate a complex function, where the computation uses coefficients stored in a lookup location for the complex function, and where data element values within different data element value ranges use different sets of coefficients. The execution further includes to store results of the computation in the output location.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Harmonic encoding for FWI
ActiveUS10422899B2Seismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingDeterministic methodFeature vector
A deterministic method for selecting a set of encoding weights for simultaneous encoded-source inversion of seismic data that will cause the iterative inversion to converge faster than randomly chosen weights. The encoded individual source gathers are summed (83), forming a composite gather, and simulated in a single simulation operation. The invention creates multiple realizations of the simulation (84), each with its own encoding vector (82) whose components are the weights for the shots in the composite gather. The encoding vectors of the invention are required to be orthogonal (82), which condition cannot be satisfied by random weights, and in various embodiments of the invention are related to eigenvectors of a Laplacian matrix, sine or cosine functions, or Chebyshev nodes as given by the roots of Chebyshev polynomials. For non-fixed receiver geometry, an encoded mask (61) may be used to approximately account for non-listening receivers.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
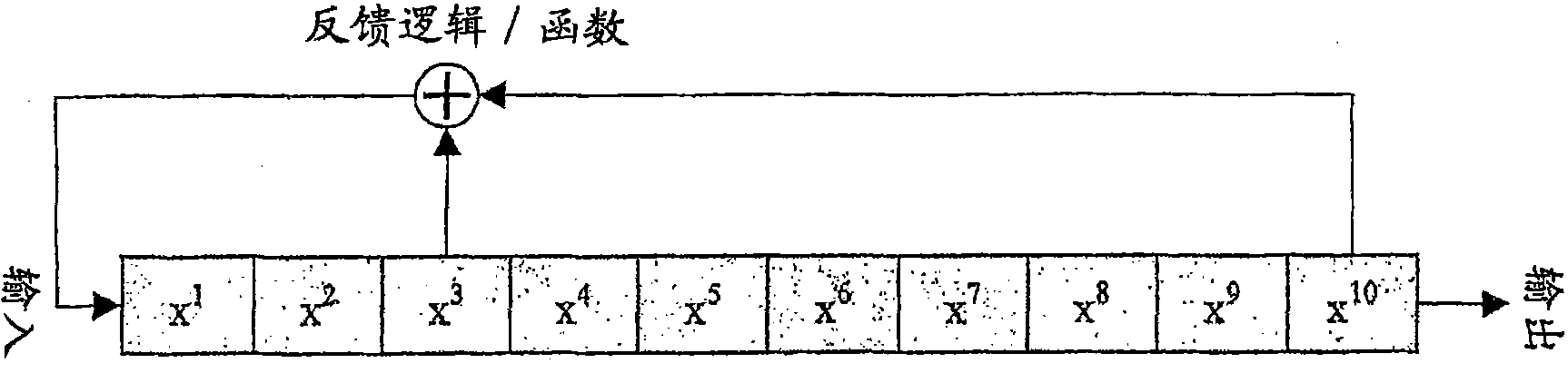
Method and device for generating pseudo random numbers
InactiveCN101019099BRandom number generatorsDigital storageEngineeringLinear feedback shift register
The present invention discloses a methodology implementable in form of a hardware or software module for generating a pseudo random number. The pseudo random number corresponds to a pseudo random sequence of bits, which form the pseudo random number. A plurality of m polynomials is provided. The polynomials are derived from an original polynomial, which defines a feedback function of a linear feedback shift register capable for generating the pseudo random number. The polynomials are functions of n bits, which serve as initial bits and seed bits, respectively. Then, the polynomials are applied on the initial bits for generating the pseudo random number, which comprises at least m bits resulting from the m polynomials. Due to the fact that the polynomials are independent from each other, i.e. the initial bits serve as input values to the polynomials, the polynomials can be applied substantially simultaneously or in any other sequence.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Suspension system early fault detection method based on random matrix theory and cumulative sum
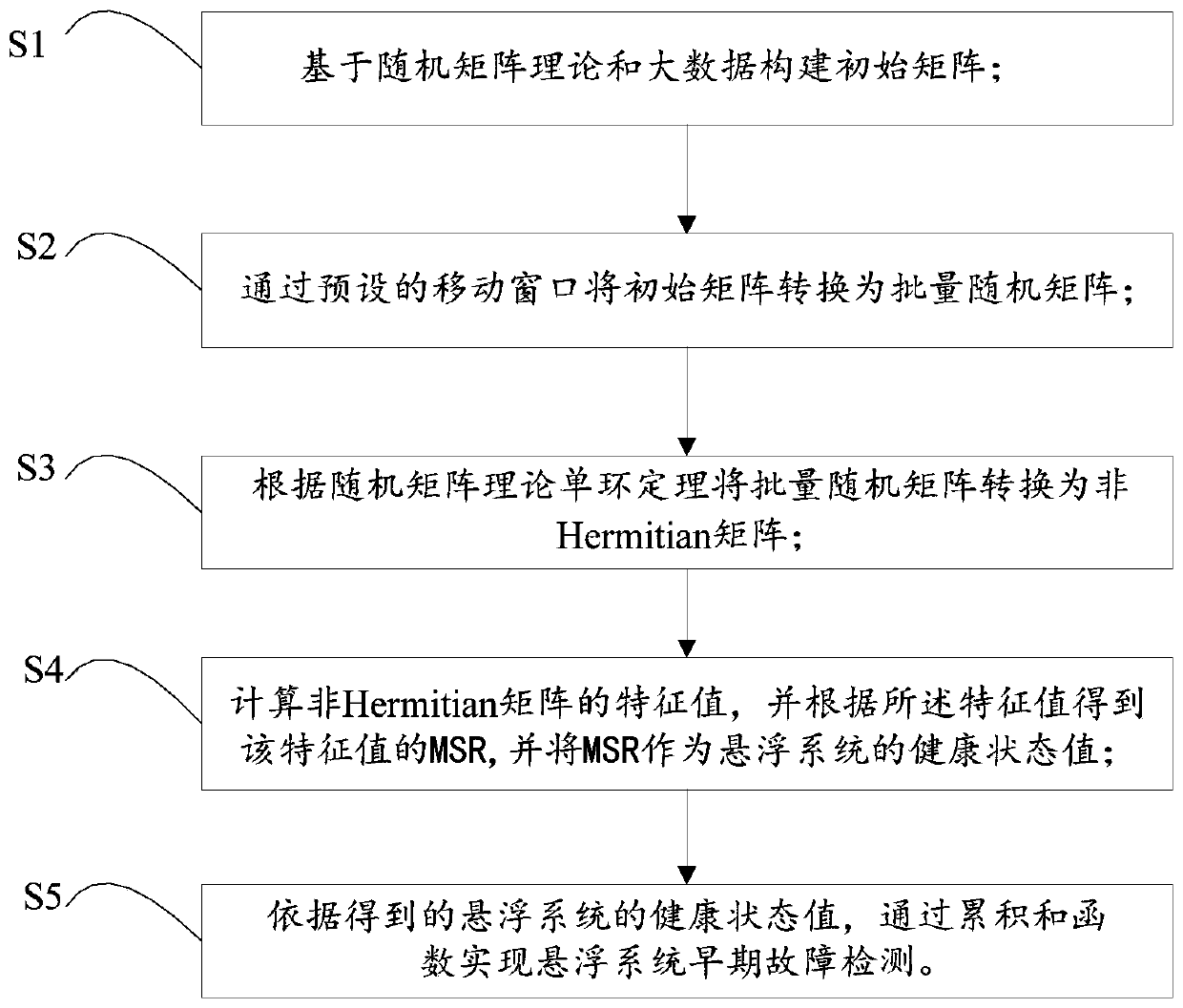
ActiveCN111259490AEnables early fault detectionEasy to detectGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmHermite functions
The invention discloses a suspension system early fault detection method based on a random matrix theory and cumulative sum. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing an initial matrix based on the random matrix theory and big data; S2, converting the initial matrix into a batch random matrix through a preset moving window; S3, converting the batch random matrix into a non-Hermitematrix according to a random matrix theory monocyclic theorem; S4, calculating a characteristic value of the non-Hermite matrix, obtaining an MSR of the characteristic value according to the characteristic value, and taking the MSR as a health state value of the suspension system; and S5, realizing early fault detection of the suspension system through a cumulative sum function according to the obtained health state value of the suspension system. According to the method, the health state value of the suspension system is obtained through the random matrix theory, early fault detection is achieved through the historical value of the health state of the suspension system and the cumulative sum function, and the method has the advantages of being simple in detection and high in reliability.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH +1
Mechanical structure residual life prediction method based on Wiener process and P-EMD
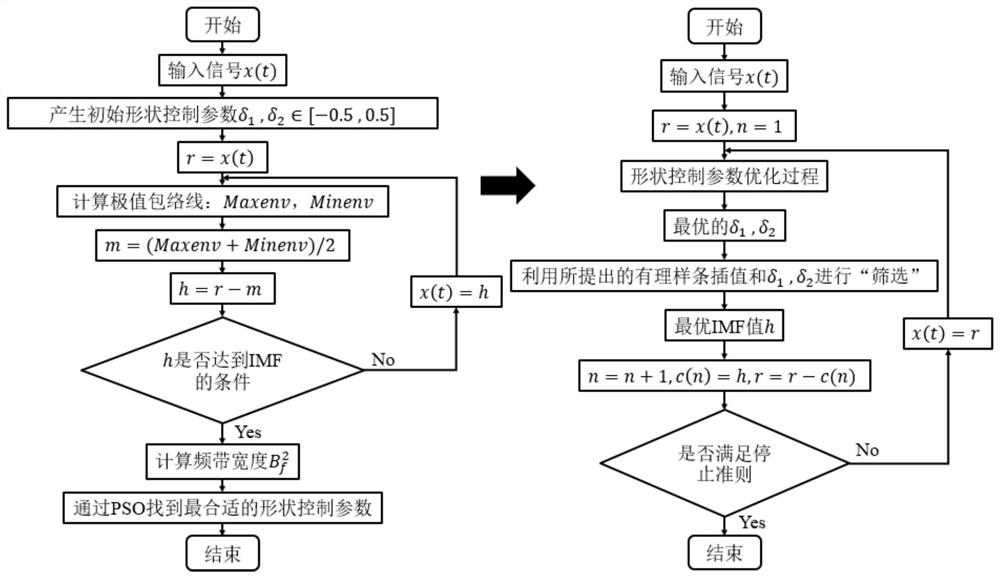
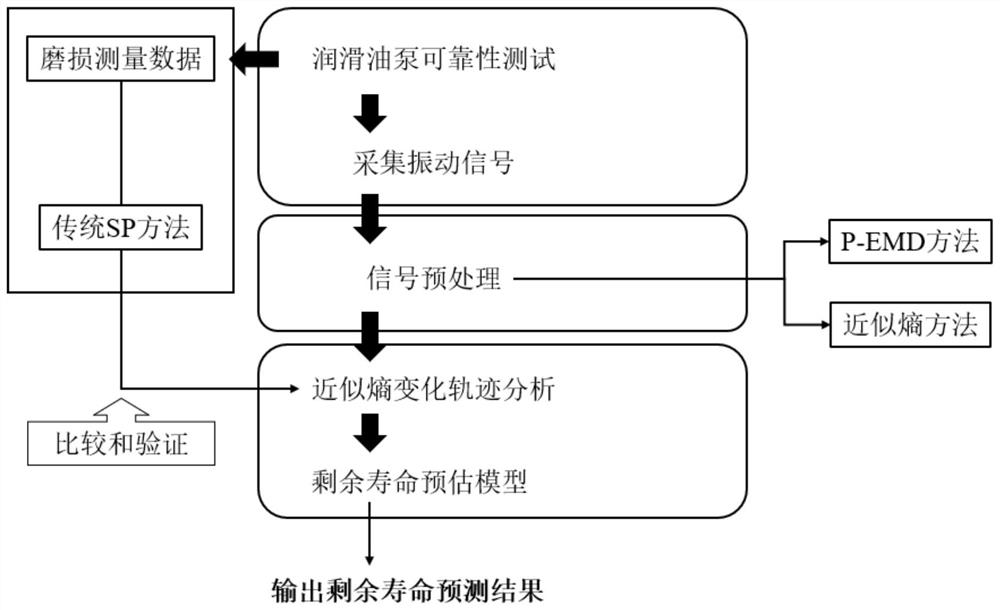
PendingCN114417534ASuppression of overshootAvoid difficultiesGeometric CADMachine part testingMechanical productsHermite functions
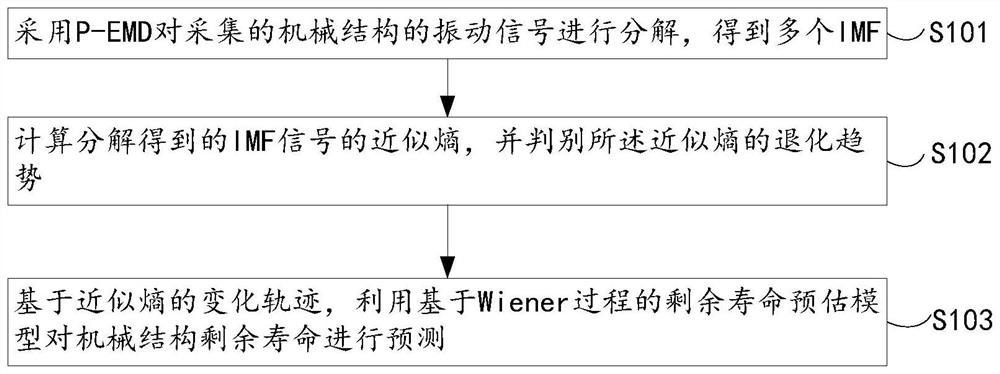
The invention provides a mechanical structure residual life prediction method based on a Wiener process and P-EMD, and belongs to the technical field of mechanical product residual life prediction. The method comprises the steps that a P-EMD is adopted to decompose a collected vibration signal of a mechanical structure to obtain a plurality of IMFs, the P-EMD represents empirical mode decomposition based on particle swarm optimization and Hermite interpolation polynomial, and the IMFs represent eigenmode functions; calculating the approximate entropy of the IMF signal obtained by decomposition, and judging the degradation trend of the approximate entropy; and based on the change trajectory of the approximate entropy, predicting the residual life of the mechanical structure by using a residual life prediction model based on a Wiener process. The method can improve the prediction precision of the residual life of the mechanical structure.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +2
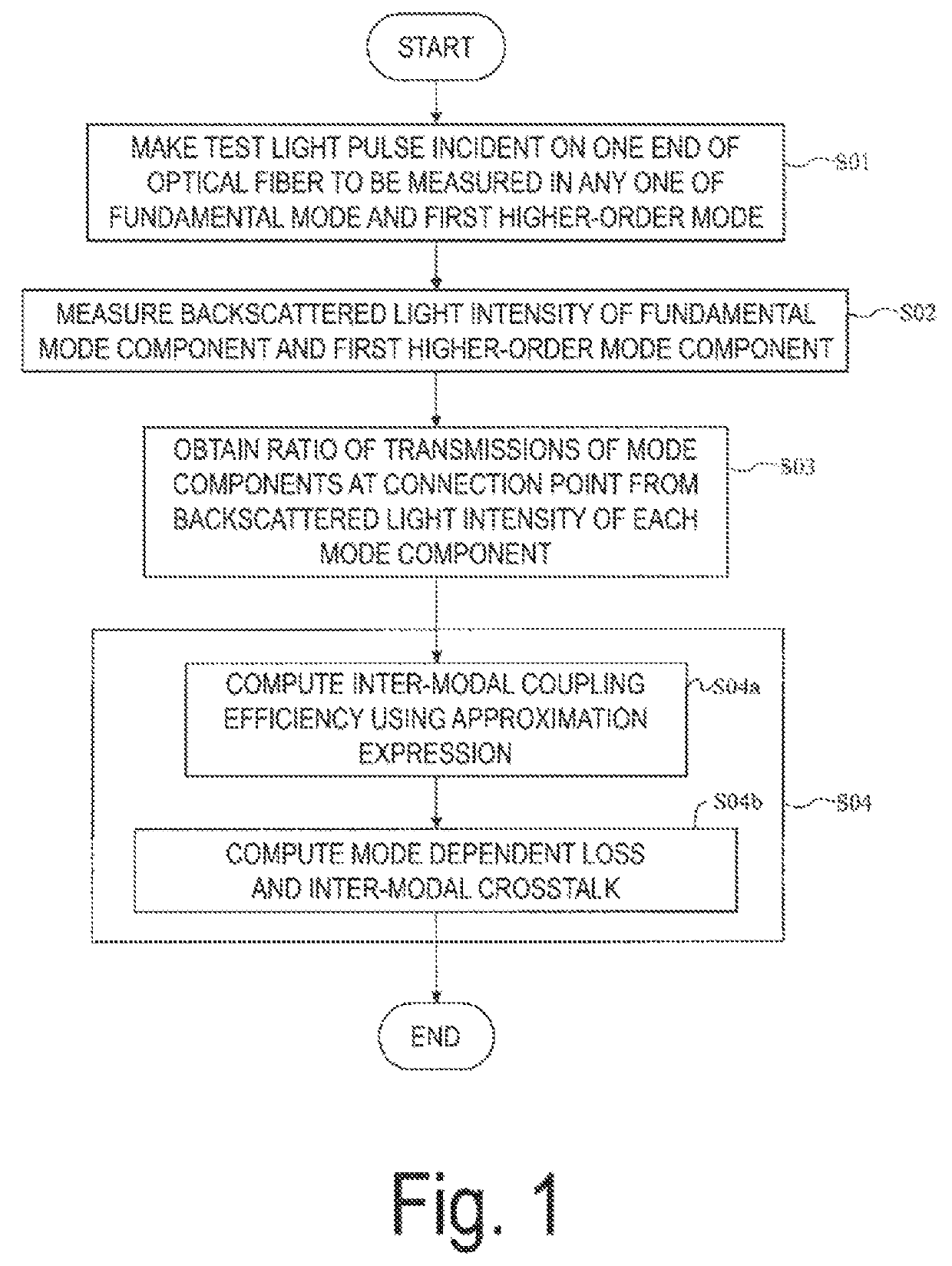
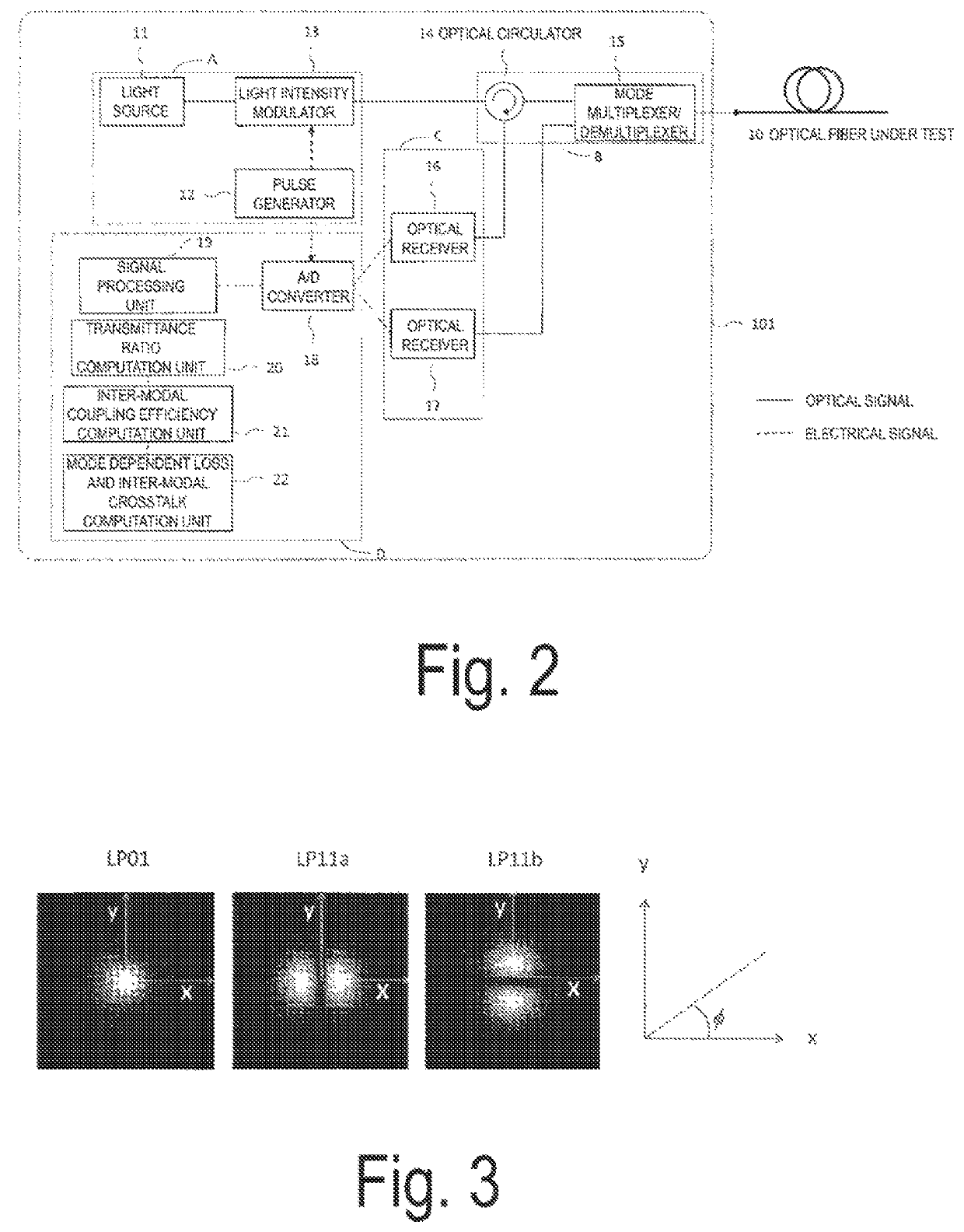
Optical fiber testing method and optical fiber testing device
ActiveUS11391644B2Reflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainFiberGaussian function
The present invention has an object to provide an optical fiber test method and an optical fiber test apparatus for measuring a mode dependent loss and an inter-modal crosstalk in a fundamental mode and a first higher-order mode at a connection point of a few-mode fiber. In the optical fiber test method and test apparatus according to the present invention, the mode dependent loss and the inter-modal crosstalk in the fundamental mode and the first higher-order mode at the connection point are calculated by using an approximation expression of an inter-modal coupling efficiency that is obtained in approximating electric field distributions of the fundamental mode and the first higher-order mode in a few-mode fiber by Gaussian function and Hermite Gaussian function.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com