Extreme learning machine face dimension reduction method based on discriminant shared neighborhood preservation
An extreme learning machine and neighborhood preservation technology, applied in neural learning methods, computer parts, character and pattern recognition, etc., can solve the problems of reduced dimensionality reduction performance, poor neighborhood information ability, and inability to consider category information, etc. The effect of reducing production costs, avoiding processing, and improving production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
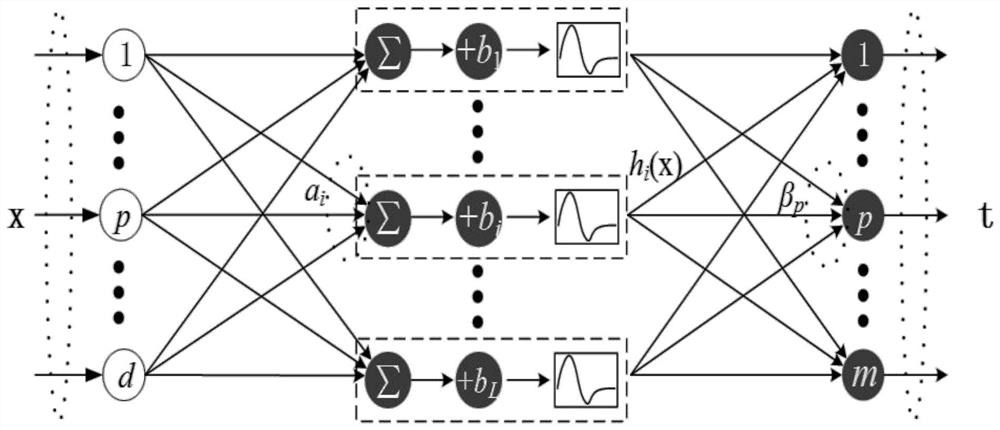
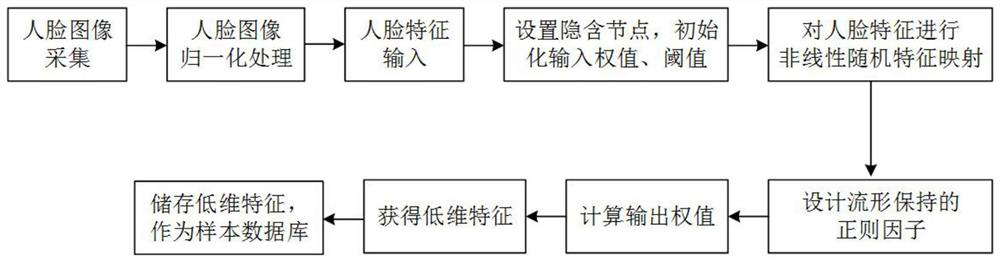
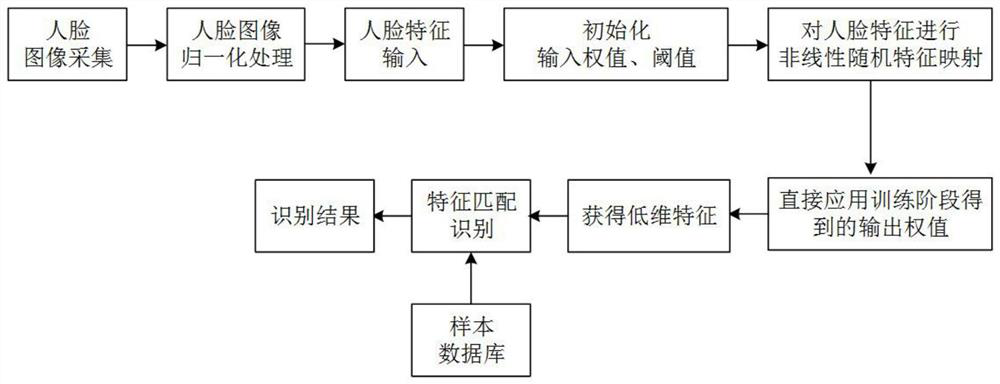
[0066] Example 1: The present invention provides as Figure 1-3 An extreme learning machine face dimensionality reduction method based on discriminative shared neighborhood preservation, the workflow in the training phase is as follows figure 2 As shown, the steps are implemented as follows:
[0067] S1. Image preprocessing: perform scale normalization processing on the face images collected by the face image collection module;
[0068] S2. Input layer: input the face feature X after scale normalization;
[0069] S3. Hidden layer: select a nonlinear excitation function (sigmoid function) to randomly non-linearly map the single-sample face feature X to the N-dimensional feature space, and transform to obtain the feature H(X);
[0070] S4. Output layer: fixed feature H(X). First, the classical Dijkstra algorithm is used to calculate the geodesic distance between sample points, and the weighted category distance is added or subtracted from the geodesic distance to obtain the d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com