Fluoropolymer composition and preparation method thereof
A composition and polymer technology, applied in the field of compositions, can solve the problems of reducing crystallization kinetics, reducing the melting point of PVDF, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
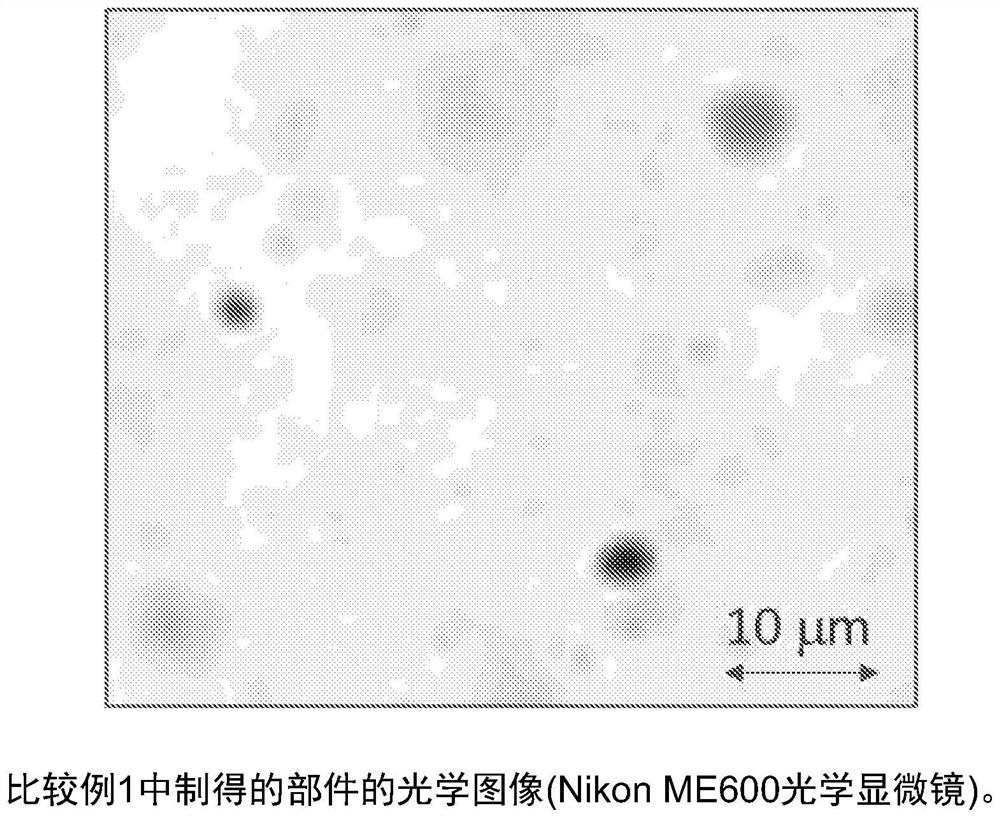
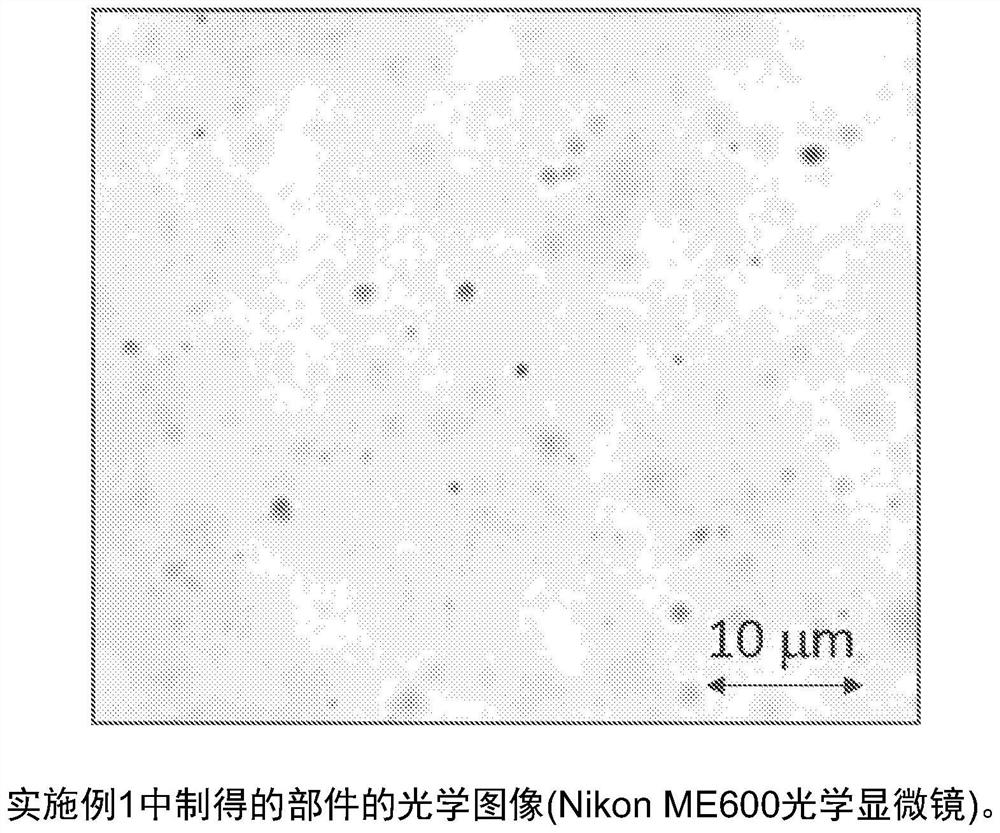
[0073] The acrylic polymer Plexiglas V825-100 from Arkema was first mixed (dry blend) with 0.5% by weight of carbon black having a discrete particle size of 20 nm in a high shear mixer. After that, in a twin screw extruder, the resulting material was blended in an amount of 10% by weight with a copolymer of VDF / HFP (15% by weight HFP) (dry) at 230C to produce pellets. The final material contained VDF / HFP polymer, 9.95 wt% dispersant V825-100 and 0.05 wt% nucleating additive carbon black. The pellets were moulded into 1 mm thick plates at 230C, 5MT pressure and cooled to room temperature within 10 minutes. ASTM D1003 was used to measure the haze of the sample panels. The haze was 35%. The haze is much lower than that of Comparative Example 1, which proves the effect of the dispersant. In fact, light microscopy showed that the size of the carbon black particles was less than 2 microns, and less than 30% of the carbon black was present in the form of agglomerates larger than 2...
Embodiment 2
[0075] The acrylic copolymer Paraloid B-44 from Dow was first mixed (dry blend) with 0.5% by weight of carbon black having a discrete particle size of 20 nm in a high shear mixer. After that, in a twin screw extruder, the resulting material was blended in an amount of 10% by weight with a copolymer of VDF / HFP (15% by weight HFP) (dry) at 230C to produce pellets. The final blend material contained VDF / HFP polymer, 9.95 wt% dispersant B-44 and 0.05 wt% nucleating additive carbon black. The pellets were moulded into 1 mm thick plates at 230C, 5MT pressure and cooled to room temperature within 10 minutes. ASTM D1003 was used to measure the haze of the sample panels. The haze was 38%. The haze is much lower than that of Comparative Example 1, which proves the effect of the dispersant. In fact, light microscopy revealed that the carbon black particles were less than 1 micron in size, and less than 20% of the carbon black was present as agglomerates larger than 1 micron.
Embodiment 3
[0079] The blend consists of a VDF / HFP copolymer (15 wt% HFP), a nucleating additive PTFE with a discrete particle size of 200 nm (0.05 wt% of the blend) and an acrylic polymer Plexiglas V825-100 from Arkema (9.95% of the blend). The latex of VDF / HFP copolymer and PTFE was first mixed in a centrifugal star mixer to produce a latex blend, then dried in an oven at 80C for 12 hours. The obtained dry powder was then blended with acrylic polymer (dry) in a twin screw extruder at 230C to produce pellets. The pellets were moulded into 1 mm thick plates at 230C, 5MT pressure and cooled to room temperature within 10 minutes. ASTM D1003 was used to measure the haze of the sample panels. The haze was 36%. The haze is much lower than that of Comparative Example 3, which proves the effect of the dispersant. We speculate that the dispersant helps break up aggregates of 200 nm discrete PTFE particles.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com