Efficient refrigerating system and control method
A refrigeration system, high-efficiency technology, applied in refrigerators, refrigeration components, refrigeration and liquefaction, etc., can solve the problems of small cooling capacity, poor heat transfer capacity of evaporator, delay of control system, etc., to achieve heat transfer capacity improvement, evaporation The effect of increasing temperature and reducing PUE
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
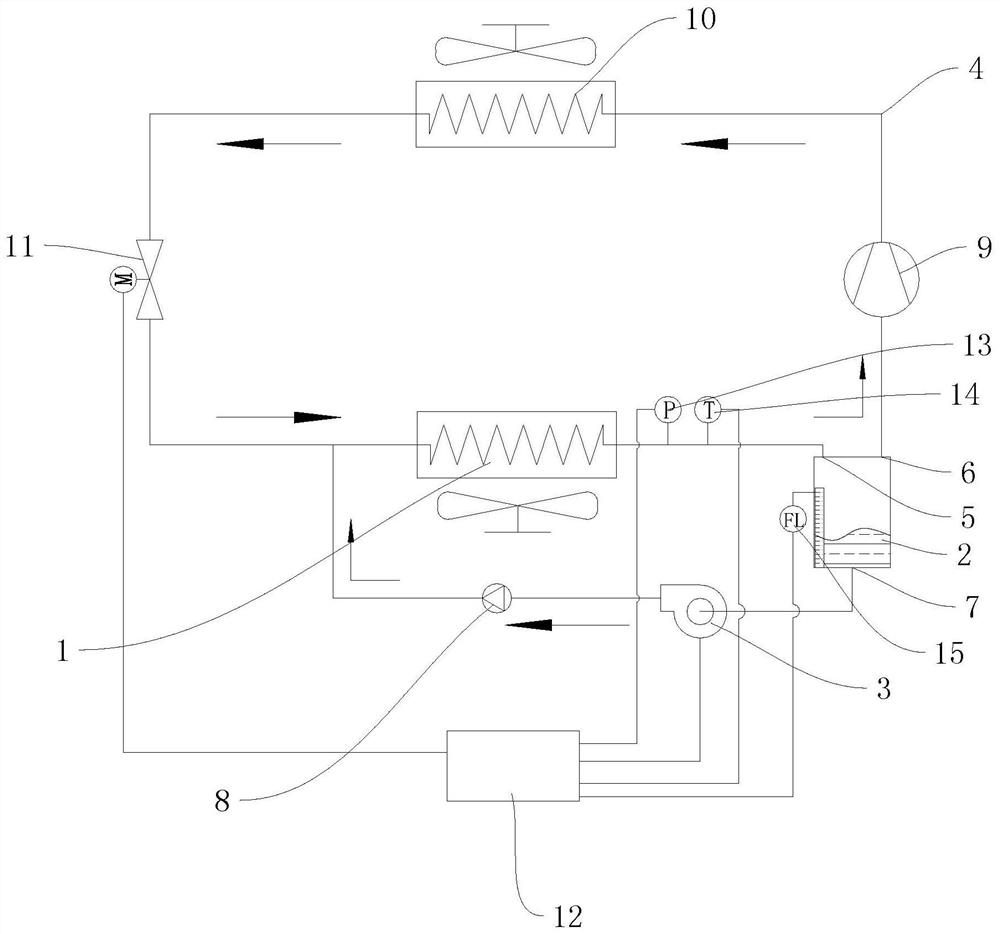
[0048] provide an efficient cooling system such as figure 2 As shown, it includes an evaporator 1 , a liquid separation tank 2 communicated with the evaporator 1 , a fluorine pump 3 communicated with the liquid separation tank 2 and a first pipeline 4 . The outlet end of the evaporator 1 is communicated with the liquid separation tank 2, the inlet of the fluorine pump 3 is communicated with the liquid separation tank 2, the outlet end is communicated with the inlet end of the evaporator 1, and the fluorine pump 3 is used to remove the refrigerant in the liquid separation tank 2. Suck it out and enter the port evaporator 1 through the inlet port. Wherein, the liquid separation tank 2 is provided with an air inlet 5, an air outlet 6 and a liquid outlet 7, the liquid separation tank 2 is cylindrical, and the air inlet 5 and the air outlet 6 are respectively arranged on the top of the liquid separation tank 2. The liquid port 7 is arranged at the bottom of the liquid separation ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Corresponding to the above embodiments, the present application provides a control method based on the above-mentioned high-efficiency refrigeration system, the method comprising:
[0055] Step S1: Receive the pressure and temperature when the gas is output to the evaporator 1, and obtain the real-time superheat SH.
[0056] Among them, SH is the suction superheat degree, and its value is the difference between the temperature when the refrigerant is output to the evaporator 1 (that is, the suction temperature T when the gas enters the compressor 9) and the saturation temperature corresponding to the suction pressure P, its physical meaning Indicates the degree to which the gas temperature exceeds the saturated gas temperature under this pressure; its physical meaning determines that the suction superheat degree of the compressor 9 is greater than or equal to 0.
[0057] Specifically, a pressure sensor 13 and a temperature sensor 14 are installed at the outlet of the ev...
Embodiment 3
[0079] In a present embodiment, a computer-readable storage medium is provided, on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the following steps are implemented:
[0080] Receive the pressure and temperature when the gas is output to the evaporator 1, and obtain the real-time superheat SH;
[0081] Receive the liquid level in the liquid separation tank 2 to obtain the real-time liquid level H;
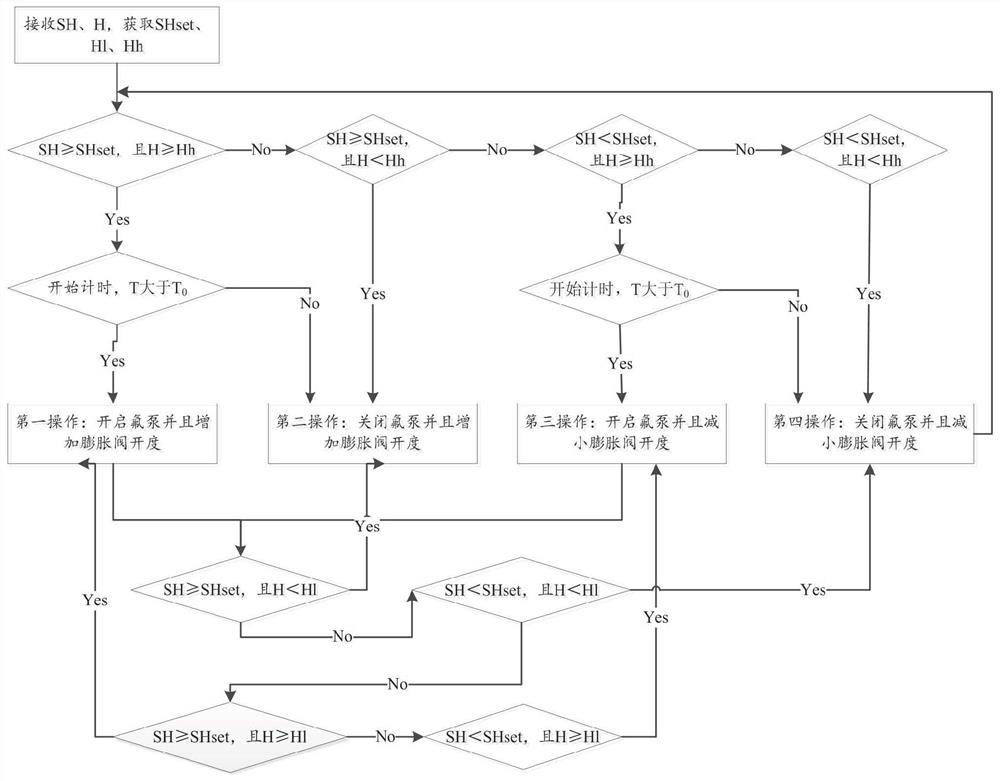
[0082] Comparing the real-time superheat degree with the preset superheat degree SHset, and comparing the real-time liquid level H with the preset high liquid level Hh or the preset low liquid level H1, to obtain a comparison result;
[0083] According to the comparison result, the states of the fluorine pump 3 and the electronic expansion valve 11 are regulated.
[0084] Specifically, when the staff sets the system to start running, it enters the first control mode, and performs the corresponding operation through the comparison bet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com