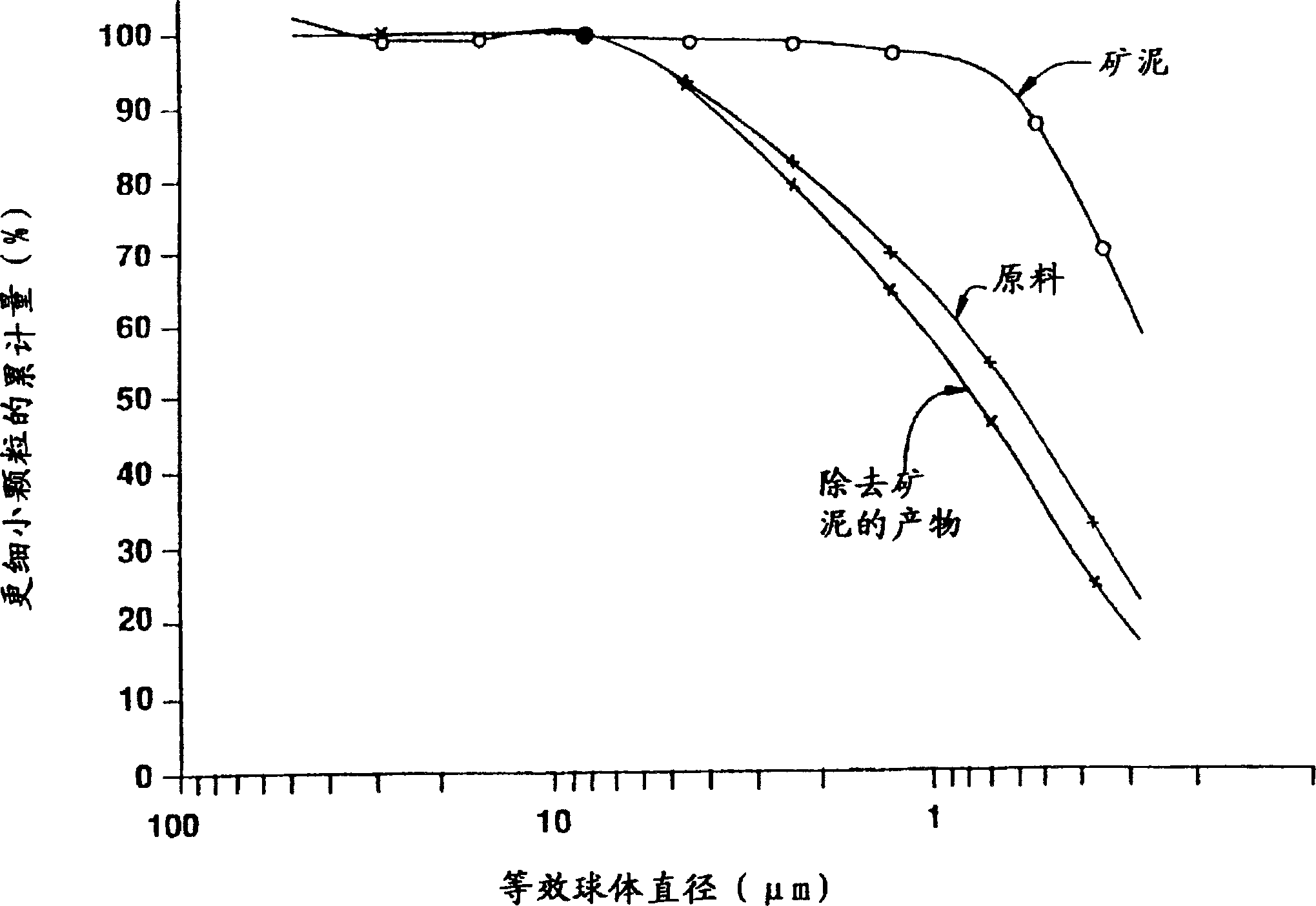
Chemical fractionation of mineral particles based on particle size
A particle size distribution and particle technology, applied in the direction of solid separation, non-fiber pulp addition, other household appliances, etc., can solve the problem of limited commercial value of kaolin products or by-products, and achieve the effect of high recovery rate and low operating cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] The raw clay to be processed is pre-beneficiated in an industrial flotation device. Grade #2 was obtained as spillage by mixing a Georgia kaolin ore with a hydrosol dispersant with water and removing the grit and grading it in a known manner in a Bird centrifuge points (70-80%<2μm), so that the raw material clay needed for flotation in flotation equipment is obtained. The #2 isolate was beneficiated by essentially the same ULTRAFLOTATION technique using a calcite support as described in US Patent 2,990,958 (Greene et al.).
[0054] The pH value of fraction #2 refined by the flotation method was 8.6, and its solid phase content was 21.8wt.%. The product slurry is then subjected to ozone treatment to decolorize remaining flotation reagents. The ozonated slurry at pH 8.1 was used as a control sample for the following tests at this pH. A portion of the ozonated slurry was caustic treated to increase the pH to 10.3 and was used as a control sample for higher pH experiment...
Embodiment 2
[0079] A similar experiment to the above was performed on a non-floatable #1 kaolin slurry nominally having a PSD of 88-92% < 2 [mu]m. The solid phase substance content in the raw material slurry is 22.1%, and its pH value is 8.3. The dispersant used to prepare the slurry is a hydrosol.
[0080] The raw material slurry is a control sample in which no reagent or dispersant is added. The following reagents and dispersants were added to a portion of the slurry with continuous agitation for 3 minutes:
[0081] Calcium chloride at 1.2# / ton of clay and sodium polyacrylate at 0.25# / ton of clay, C-211.
[0082] 2.2# / ton of clay calcium chloride and 0.50# / ton of clay sodium hexametaphosphate.
[0083] After 3 minutes, each sample, including the control, was treated with 0.3 dry # / ton of clay (as a 0.025% solution) of the flocculating polymer, Sharpfloc 9950. Agitation was stopped and the slurry settled at a rate of 60 sec / inch depth. The unflocculated supernatant layer was decante...
Embodiment 3
[0088]This example illustrates the role of dispersants in controlling the removal of colloidal fines from kaolin minerals and the effect of dispersants on the rheology of the product. This example describes the application of the invention to a coarse fraction of raw kaolin clay having a typical listed morphology.
[0089] A coarse white-based raw ore slurry that has been beneficiated by an ultrafine flotation (ULTRAFLOTATION) method is treated with an increasing amount of C-211 sodium polyacrylate. It can be noted that the ultrafine flotation product slurry contains a significant concentration of calcium ions due to the use of calcite support in the flotation process. According to the present invention, 0.3 lb / ton of Sharpfloc TM 9950 polymer was added to the slurry at a concentration of 0.025% (20% solids) under gentle agitation. Flocs started to appear right away. Once agitation ceased, the flocs quickly began to settle. The flocs settled at a rate of 3 inches / minute. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com